Cellular Activities
... Cell membrane surrounds and pinches off to bring large molecules/materials into the cell. Brings in food, proteins, chemical messages into the cell. NEEDS lots of energy from the cell ...
... Cell membrane surrounds and pinches off to bring large molecules/materials into the cell. Brings in food, proteins, chemical messages into the cell. NEEDS lots of energy from the cell ...
Chapter 3 Jeopardy Review
... Forms delicate, thin membranes through out the body that bind body parts together such as skin and underlying organs ...
... Forms delicate, thin membranes through out the body that bind body parts together such as skin and underlying organs ...
Cell Review
... Cells are designed to do specific jobs in the body, and keep us living and breathing. ...
... Cells are designed to do specific jobs in the body, and keep us living and breathing. ...
cell parts.pages
... All the cells are enclosed in a protective membrane called the cell membrane however plant cells have an extra addition the cell wall. The cells have certain organelles that are membrane bound within them, these structures are called cellular organelles. These organelles are specified to perform cer ...
... All the cells are enclosed in a protective membrane called the cell membrane however plant cells have an extra addition the cell wall. The cells have certain organelles that are membrane bound within them, these structures are called cellular organelles. These organelles are specified to perform cer ...
Biology Unit 5: Cellular Structure and Function
... Biology Unit 5: Cellular Structure and Function c. the age of the blood sample used by the biologist d. the chemical make-up of the cell membrane of the blood cells 3.2.F.b 29. *How would a drop in temperature most likely affect the processes of cellular respiration and photosynthesis? a. The rates ...
... Biology Unit 5: Cellular Structure and Function c. the age of the blood sample used by the biologist d. the chemical make-up of the cell membrane of the blood cells 3.2.F.b 29. *How would a drop in temperature most likely affect the processes of cellular respiration and photosynthesis? a. The rates ...
Biological Sciences
... Types of cell division in animals i.e. cell division for growth, repair and replacement of body (somatic) cells, and cell division for the production of sex cells (gametes) DNA Replication - is a precursor for cell division as well as protein synthesis. Students are able to explain the process ...
... Types of cell division in animals i.e. cell division for growth, repair and replacement of body (somatic) cells, and cell division for the production of sex cells (gametes) DNA Replication - is a precursor for cell division as well as protein synthesis. Students are able to explain the process ...
Chapter 3 The Basic Structure of a Cell
... Making a Slide: • Place a clean slide on the table. • For liquid samples, place one or two drops in the center of the slide. For solid samples, place the sample in the center of the slide and add one drop of water or staining solution. • Hold the plastic cover slip by the edges. Do not get fingerpr ...
... Making a Slide: • Place a clean slide on the table. • For liquid samples, place one or two drops in the center of the slide. For solid samples, place the sample in the center of the slide and add one drop of water or staining solution. • Hold the plastic cover slip by the edges. Do not get fingerpr ...
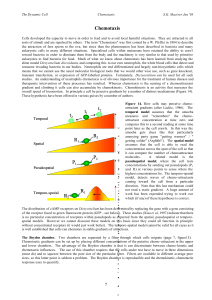
34 Chemotaxis
... Cells developed the capacity to move in order to feed and to avoid local harmful situations. They are attracted to all sorts of stimuli and are repulsed by others. The term "Chemotaxis" was first coined by a W. Pfeffer in 1884 to describe the attraction of fern sperm to the ova, but since then the p ...
... Cells developed the capacity to move in order to feed and to avoid local harmful situations. They are attracted to all sorts of stimuli and are repulsed by others. The term "Chemotaxis" was first coined by a W. Pfeffer in 1884 to describe the attraction of fern sperm to the ova, but since then the p ...
The Cell - Eric Hamber Secondary
... Give a probable tissue or organ that was the source of these cells. Include the function of each organelle in the tissue/organ you named. (8 marks: 1 mark per source, 1 mark per explanation) Explain how structure is related to function for each of the following organelles: a) mitochondrion (3 marks) ...
... Give a probable tissue or organ that was the source of these cells. Include the function of each organelle in the tissue/organ you named. (8 marks: 1 mark per source, 1 mark per explanation) Explain how structure is related to function for each of the following organelles: a) mitochondrion (3 marks) ...
Cell Structure 4A
... sometimes called "the control center of the cell" the cellular region that contains the chromosomes usually the largest organelle in a cell The nucleus has a double unit membrane around it called the nuclear membrane or nuclear envelope. The nuclear envelope has large pores - permitting the passage ...
... sometimes called "the control center of the cell" the cellular region that contains the chromosomes usually the largest organelle in a cell The nucleus has a double unit membrane around it called the nuclear membrane or nuclear envelope. The nuclear envelope has large pores - permitting the passage ...
Biology 12: Chapter 4 Biology 12: Chapter 4
... 5)a) Phospholipids = abundant lipids, amphipathic, main fabric of PM, fluid bilayer Membrane Proteins = also amphipathic, determine most of PM’s specific functions b) Cholesterol = stiffens and strengthens PM, helps regulate its fluidity. 6) Peripheral = partially embedded in bilayer, held in place ...
... 5)a) Phospholipids = abundant lipids, amphipathic, main fabric of PM, fluid bilayer Membrane Proteins = also amphipathic, determine most of PM’s specific functions b) Cholesterol = stiffens and strengthens PM, helps regulate its fluidity. 6) Peripheral = partially embedded in bilayer, held in place ...
Cells Alive - White Plains Public Schools
... Part C; Animal Cell Model - (you will need to return to the "Cell Biology" link to access this page, or hit your back button) - For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there ...
... Part C; Animal Cell Model - (you will need to return to the "Cell Biology" link to access this page, or hit your back button) - For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there ...
Science - B1 Cell Structure and Transport in and out of Cells
... 3. Plug the numbers into the equation 4. Calculate ...
... 3. Plug the numbers into the equation 4. Calculate ...
File
... many years result in producing the large size of trees. 9. The three main types of plant tissue are • dermal tissue: the outer layer of cells that covers all non-woody plants and is responsible for the exchange of matter and gases • cuticle: the thin waxy coating on the leaves of plants that protect ...
... many years result in producing the large size of trees. 9. The three main types of plant tissue are • dermal tissue: the outer layer of cells that covers all non-woody plants and is responsible for the exchange of matter and gases • cuticle: the thin waxy coating on the leaves of plants that protect ...
Cell division - MrMcKennaBiologyPage
... the nucleus called m_______. • Before the nucleus divides each opied so there is a copy chromosome is c_____ ...
... the nucleus called m_______. • Before the nucleus divides each opied so there is a copy chromosome is c_____ ...
I. Introduction
... 2. Fertilization is the union of an egg and a sperm. B. Transport of Sex Cells 1. Before fertilization can occur, a secondary oocyte must be ovulated and enter a uterine tube. 2. To reach the secondary oocyte, sperm cells must move upward through the uterus and uterine tube. 3. Prostaglandins in the ...
... 2. Fertilization is the union of an egg and a sperm. B. Transport of Sex Cells 1. Before fertilization can occur, a secondary oocyte must be ovulated and enter a uterine tube. 2. To reach the secondary oocyte, sperm cells must move upward through the uterus and uterine tube. 3. Prostaglandins in the ...
ch_8 - WordPress.com
... Centromere: The primary constriction in a chromosome that holds two chromatids together. Metacentric chromosome: Centromere at the centre. Sub-metacentric chromosome: Centromere near the centre. Acro centric chromosome: Centromere sub terminal. Telocentric chromosom : Centromere terminal. Satellite: ...
... Centromere: The primary constriction in a chromosome that holds two chromatids together. Metacentric chromosome: Centromere at the centre. Sub-metacentric chromosome: Centromere near the centre. Acro centric chromosome: Centromere sub terminal. Telocentric chromosom : Centromere terminal. Satellite: ...
Doellman, Cell Structure and Function Unit Exam
... 32. You have just discovered a mutant plant that no one else has ever seen before. This plant is very unusual because its cells do not contain a cell wall. Predict how the lack of cell wall will impact the plant’s survival on Earth. (Hint: What will it look like? What accommodations will it have to ...
... 32. You have just discovered a mutant plant that no one else has ever seen before. This plant is very unusual because its cells do not contain a cell wall. Predict how the lack of cell wall will impact the plant’s survival on Earth. (Hint: What will it look like? What accommodations will it have to ...
Spermatogenesis overview
... types of spermatocytes that range in size from cells smaller than a red blood cell (preleptotene) to very large cells (pachytene) that occupy portions of every cross section of seminiferous tubules. Reduction-division is a biological mechanism by which a single germ cell can increase its DNA content ...
... types of spermatocytes that range in size from cells smaller than a red blood cell (preleptotene) to very large cells (pachytene) that occupy portions of every cross section of seminiferous tubules. Reduction-division is a biological mechanism by which a single germ cell can increase its DNA content ...
The blood cell wall has three layers: intima, media and adventitia
... Hemostatis is a balance of the physiological processes which on one hand prevent excessive bleeding after vessel injury, and which on the other hand maintain a viable circulation by keeping the blood in an uncoagulated state. These processes are part of a complex system with many feedback loops and ...
... Hemostatis is a balance of the physiological processes which on one hand prevent excessive bleeding after vessel injury, and which on the other hand maintain a viable circulation by keeping the blood in an uncoagulated state. These processes are part of a complex system with many feedback loops and ...
Cell Membrane Reading Guide
... The phospholipids bilayer serves as a medium for embedding proteins which have many diverse functions. Describe in sentences what you see occurring in each picture below: ...
... The phospholipids bilayer serves as a medium for embedding proteins which have many diverse functions. Describe in sentences what you see occurring in each picture below: ...
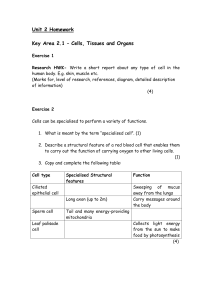
Unit 2 Homework
... today to describe patterns of inheritance in living organisms. Use a variety of sources (eg. books/internet) to research the life and work of Mendel. Present your information as a report that is at least 100 words long. List all of the references that you used and make sure you include details of hi ...
... today to describe patterns of inheritance in living organisms. Use a variety of sources (eg. books/internet) to research the life and work of Mendel. Present your information as a report that is at least 100 words long. List all of the references that you used and make sure you include details of hi ...
Comparing a Cell to a School
... Head custodian In charge of the Maintenance Crew Support beams (walls, ceilings and floors) Boiler Room of the school ...
... Head custodian In charge of the Maintenance Crew Support beams (walls, ceilings and floors) Boiler Room of the school ...
Make your own newton disc
... If you put all four acetates between the light source and the solar cell, is the solar cell still producing a reading? What is going on? The solar cell is absorbing mainly visible light but will also be absorbing a small part of the infra-red and ultra-violet regions too. When the clear acetate is p ...
... If you put all four acetates between the light source and the solar cell, is the solar cell still producing a reading? What is going on? The solar cell is absorbing mainly visible light but will also be absorbing a small part of the infra-red and ultra-violet regions too. When the clear acetate is p ...