Teacher Notes PDF - TI Education
... Q15. Both smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum are responsible for transport. Where do their contents get transported to? Answer: A. other organelles, B. cell wall, C. outside the cell Q16. Which organelle contains grana? Answer: C. chloroplast Q17. Plants inherit characteristics from their parent ...
... Q15. Both smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum are responsible for transport. Where do their contents get transported to? Answer: A. other organelles, B. cell wall, C. outside the cell Q16. Which organelle contains grana? Answer: C. chloroplast Q17. Plants inherit characteristics from their parent ...
Cells are diverse! Cytoplasm HINT +
... Ways in which all cells are alike. Every cell has a boundary that separates the inside from the outside. That boundary is the cell membrane, a protective covering that encloses the entire cell. Any material coming into or out of the cell must pass through the cell membrane. Contained inside the cell ...
... Ways in which all cells are alike. Every cell has a boundary that separates the inside from the outside. That boundary is the cell membrane, a protective covering that encloses the entire cell. Any material coming into or out of the cell must pass through the cell membrane. Contained inside the cell ...
Reproduction in cells - Allen County Schools
... b. Cell wall c. Chloroplast d. Nucleus 2. Which cell part is found in ALL cells and controls what enters or exits the cell? a. Cell membrane b. Cell wall c. Chloroplast d. Nucleus 3. Which cell part controls what the cell does, when it does it, and how it does it? a. Cell membrane b. Cell wall c. Ch ...
... b. Cell wall c. Chloroplast d. Nucleus 2. Which cell part is found in ALL cells and controls what enters or exits the cell? a. Cell membrane b. Cell wall c. Chloroplast d. Nucleus 3. Which cell part controls what the cell does, when it does it, and how it does it? a. Cell membrane b. Cell wall c. Ch ...
Vacuoles
... Many proteins are bound to inner membrane Cristae are folds of inner membrane Matrix is the fluid surrounding cristae ...
... Many proteins are bound to inner membrane Cristae are folds of inner membrane Matrix is the fluid surrounding cristae ...
Document
... and withdraw patches of the plasma membrane New membrane proteins and lipids are made in the ER, modified in Golgi bodies, and form vesicles that fuse with plasma membrane ...
... and withdraw patches of the plasma membrane New membrane proteins and lipids are made in the ER, modified in Golgi bodies, and form vesicles that fuse with plasma membrane ...
Diffusion, Osmosis, and Active Transport
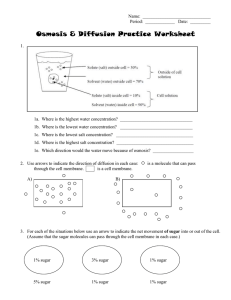
... 1a. Where is the highest water concentration? ________________________________ 1b. Where is the lowest water concentration? ________________________________ 1c. Where is the lowest salt concentration? __________________________________ 1d. Where is the highest salt concentration? ___________________ ...
... 1a. Where is the highest water concentration? ________________________________ 1b. Where is the lowest water concentration? ________________________________ 1c. Where is the lowest salt concentration? __________________________________ 1d. Where is the highest salt concentration? ___________________ ...
Cell WEBQUEST: An interactive journey into the cell!
... 16) Pick one of the diseases and briefly describe what organelle or cell structure is being affect and what symptoms might be associated with that disease. __________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ ...
... 16) Pick one of the diseases and briefly describe what organelle or cell structure is being affect and what symptoms might be associated with that disease. __________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ ...
A novel checkpoint mechanism regulating the G1/S transition
... occurs in G1 and not in S phase, which is further supported by the following: The Cdc2 inhibitor Rum1, which is only expressed in G1 (Benito et al. 1998), was strongly expressed during the delay period (Fig. 1D). Moreover, the activity of the S-phase-specific checkpoint kinase Cds1 was not activated ...
... occurs in G1 and not in S phase, which is further supported by the following: The Cdc2 inhibitor Rum1, which is only expressed in G1 (Benito et al. 1998), was strongly expressed during the delay period (Fig. 1D). Moreover, the activity of the S-phase-specific checkpoint kinase Cds1 was not activated ...
Turgor Pressure and Capillary action
... The NCE-MSTL does not claim ownership rights to the images on this activity sheet. They are used exclusively for educational purposes. ...
... The NCE-MSTL does not claim ownership rights to the images on this activity sheet. They are used exclusively for educational purposes. ...
Chapter 4
... • Cells are small because they are limited by their surface-area-to-volume-ratio. • The surface area of a cell is critical because it must be large enough to allow adequate nutrients to enter the cell. • Cells can increase their surface area with specialized projections such as microvilli. ...
... • Cells are small because they are limited by their surface-area-to-volume-ratio. • The surface area of a cell is critical because it must be large enough to allow adequate nutrients to enter the cell. • Cells can increase their surface area with specialized projections such as microvilli. ...
Two Basic Cell Types: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
... organelles to: • carry out metabolism • provides energy • transport chemicals throughout the cell ...
... organelles to: • carry out metabolism • provides energy • transport chemicals throughout the cell ...
Two Basic Cell Types: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
... organelles to: • carry out metabolism • provides energy • transport chemicals throughout the cell ...
... organelles to: • carry out metabolism • provides energy • transport chemicals throughout the cell ...
Cell Organelle Powerpoint
... Some living things are composed of only one cell and are called UNICELLULAR organsims. Organisms that have many different cells are called MULTICELLULAR organisms. ...
... Some living things are composed of only one cell and are called UNICELLULAR organsims. Organisms that have many different cells are called MULTICELLULAR organisms. ...
The Science of Biology
... • As a group, organisms change over time – As an individual, traits it inherited usually will not change – Over many generations, changes become ...
... • As a group, organisms change over time – As an individual, traits it inherited usually will not change – Over many generations, changes become ...
Types of Programmed Cell Death The mechanisms by which cells
... p53 function appears to be a requirement for most cancers. p53 functions to suppress cancer through at least two mechanisms: in response to cellular damage and/or abnormal signaling, p53 causes cells to enter either apoptosis or senescence, depending upon the signal and the cellular context). Either ...
... p53 function appears to be a requirement for most cancers. p53 functions to suppress cancer through at least two mechanisms: in response to cellular damage and/or abnormal signaling, p53 causes cells to enter either apoptosis or senescence, depending upon the signal and the cellular context). Either ...
3.1 Cell Theory Early studies led to the development of the cell theory.
... Early studies led to the development of the cell theory. • The Cell theory has three principles. – All organisms are made of cells. – All existing cells are produced by other living cells. – The cell is the most basic unit of life. ...
... Early studies led to the development of the cell theory. • The Cell theory has three principles. – All organisms are made of cells. – All existing cells are produced by other living cells. – The cell is the most basic unit of life. ...
Science8__Unit1_Notes
... continue to swell and eventually may burst; plant cell swells beyond its normal size -more water moving out of cells than is moving in: -cell shrinks; red blood cells shrivel up as they lose water; plant cell membrane shrinks away from the cell wall –- carrot is limp, lack of water ...
... continue to swell and eventually may burst; plant cell swells beyond its normal size -more water moving out of cells than is moving in: -cell shrinks; red blood cells shrivel up as they lose water; plant cell membrane shrinks away from the cell wall –- carrot is limp, lack of water ...
Introduction to Physiology and Homeostasis
... • Strive to maintain an internal balance – Homeostasis ...
... • Strive to maintain an internal balance – Homeostasis ...
Stem cells - edizioni scripta manent planet
... that feed them - including the pancreas and liver. After being born, we still maintain areas of stem cells; these somatic stem cells play a very important role in growth, maintenance, and repair. Figure 2 indicates the areas where these stem cells are found in the body. ...
... that feed them - including the pancreas and liver. After being born, we still maintain areas of stem cells; these somatic stem cells play a very important role in growth, maintenance, and repair. Figure 2 indicates the areas where these stem cells are found in the body. ...
Cell Membranes and Transport
... a.Selectively permeable: Allows some molecules in and keeps other molecules out b.Structure is related to its function! Outside of cell Proteins ...
... a.Selectively permeable: Allows some molecules in and keeps other molecules out b.Structure is related to its function! Outside of cell Proteins ...
Protists
... plastids were formerly small prokaryotes that began living within larger cells. (See page 485) ...
... plastids were formerly small prokaryotes that began living within larger cells. (See page 485) ...
Immunity
... • B-cells producing the desired antibody are extracted. • Tumor cells are obtained from another source (tumor cells grow and divide endlessly). • B-cells are fused with tumor cells, producing hybridoma cells that divide endlessly, providing the desired antibodies. • The hybridoma cells are cultured ...
... • B-cells producing the desired antibody are extracted. • Tumor cells are obtained from another source (tumor cells grow and divide endlessly). • B-cells are fused with tumor cells, producing hybridoma cells that divide endlessly, providing the desired antibodies. • The hybridoma cells are cultured ...
CHAPTER 1: CELL STRUCTURES AND TYPES
... organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and are often called the "building blocks of life". 2. Cells consist of a protoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. 3. Organisms can be classified as uni ...
... organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and are often called the "building blocks of life". 2. Cells consist of a protoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. 3. Organisms can be classified as uni ...
File
... • Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane • The direction of osmosis is determined only by a difference in total solute concentration ...
... • Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane • The direction of osmosis is determined only by a difference in total solute concentration ...