Chapter 14 - United States in WWII
... learned this firsthand in October 1941. At the time, the United States had not yet entered the war. Its ships, however, were serving as escorts to convoys carrying goods from American ports to Great Britain. It was while on such a mission that the Reuben James was attacked by a German U-boat. Follow ...
... learned this firsthand in October 1941. At the time, the United States had not yet entered the war. Its ships, however, were serving as escorts to convoys carrying goods from American ports to Great Britain. It was while on such a mission that the Reuben James was attacked by a German U-boat. Follow ...
The Bombing of Dresden
... The Allied bombing of Dresden during WWII was an extremely controversial piece of World War II, as the loss of life and tremendous damage caused an excessive amount of unnecessary destruction. The reason for targeting Dresden was mainly to attack any form of Nazi Germany, and to stop the production ...
... The Allied bombing of Dresden during WWII was an extremely controversial piece of World War II, as the loss of life and tremendous damage caused an excessive amount of unnecessary destruction. The reason for targeting Dresden was mainly to attack any form of Nazi Germany, and to stop the production ...
Chapter 12: America and World War II, 1941-1945 - Bend
... the tide in favor of the Allies. In less than four years, the United States achieved what no other nation had ever done—it fought and won a two-front war against two powerful military empires, forcing each to surrender unconditionally. The United States was able to expand its war production so rapid ...
... the tide in favor of the Allies. In less than four years, the United States achieved what no other nation had ever done—it fought and won a two-front war against two powerful military empires, forcing each to surrender unconditionally. The United States was able to expand its war production so rapid ...
World War II Part One
... Invasion of China 1937 • In July 1937, Hideki Tojo, Chief of Staff of Japan’s Army, launched the invasion into China. • As French, Dutch, and British colonies lay unprotected in Asia, Japanese leaders leaped at the opportunity to unite East Asia under Japanese control by seizing the colonial lands. ...
... Invasion of China 1937 • In July 1937, Hideki Tojo, Chief of Staff of Japan’s Army, launched the invasion into China. • As French, Dutch, and British colonies lay unprotected in Asia, Japanese leaders leaped at the opportunity to unite East Asia under Japanese control by seizing the colonial lands. ...
Chapter 25-America & World War II 1941-1945
... wanted a new international political organization. • In 1944 delegates from 39 countries met to discuss the new organization that was to be called the United Nations (UN). ...
... wanted a new international political organization. • In 1944 delegates from 39 countries met to discuss the new organization that was to be called the United Nations (UN). ...
17.1 from appeasement to war
... Britain and France protested, but they were unwilling to go to war. ...
... Britain and France protested, but they were unwilling to go to war. ...
From Appeasement to War - Trimble County Schools
... Britain and France protested, but they were unwilling to go to war. ...
... Britain and France protested, but they were unwilling to go to war. ...
World War II European Front
... • was the instrument that allowed military commanders to designate areas "from which any or all persons may be excluded." Under this order all Japanese and Americans of Japanese ancestry were removed from Western coastal regions to guarded camps in the interior. : ...
... • was the instrument that allowed military commanders to designate areas "from which any or all persons may be excluded." Under this order all Japanese and Americans of Japanese ancestry were removed from Western coastal regions to guarded camps in the interior. : ...
Jeopardy - Solon City Schools
... were fascist and believed in placing the state above the individual, shared a dislike of communism, and saw an advantage in working with each other ...
... were fascist and believed in placing the state above the individual, shared a dislike of communism, and saw an advantage in working with each other ...
Chapter 5
... During WWI, what did the women who were left at home do (did they go on with their normal life or what did they do differently)? Explain the term “total war.” What is an armistice? When was the armistice signed in WWI? U.S. president Woodrow Wilson wanted a fair and lasting peace for the world after ...
... During WWI, what did the women who were left at home do (did they go on with their normal life or what did they do differently)? Explain the term “total war.” What is an armistice? When was the armistice signed in WWI? U.S. president Woodrow Wilson wanted a fair and lasting peace for the world after ...
Canada and the Second World War
... Union would likely regard Germany’s actions as a threat to its own security. In August 1939, Hitler stunned the world by signing a non-aggression pact with Joseph Stalin, leader of the Soviet Union, even though the Nazis hated communists and vice versa. Both countries pledged not to fight each other ...
... Union would likely regard Germany’s actions as a threat to its own security. In August 1939, Hitler stunned the world by signing a non-aggression pact with Joseph Stalin, leader of the Soviet Union, even though the Nazis hated communists and vice versa. Both countries pledged not to fight each other ...
A Nation on the Move (cont.)
... Striking Germany and Italy (cont.) • Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin reached the following agreements at the Tehran Conference: – Stalin would launch a full-scale offensive against the Germans when the Allies invaded in 1944. – Germany would be divided after the war to decrease its power. ...
... Striking Germany and Italy (cont.) • Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin reached the following agreements at the Tehran Conference: – Stalin would launch a full-scale offensive against the Germans when the Allies invaded in 1944. – Germany would be divided after the war to decrease its power. ...
Japan - Nicholas Senn High School
... • World War II (Length) • Sept 1st, 1939 - Officially starts when Germany invades Poland • December 8th, 1941 - US declares War on Japan (day after Pearl Harbor) – 2300 servicemen,18 ships and 150 planes lost – Congress voted; Senate 82-0 and House 388-1 to declare war on Japan ...
... • World War II (Length) • Sept 1st, 1939 - Officially starts when Germany invades Poland • December 8th, 1941 - US declares War on Japan (day after Pearl Harbor) – 2300 servicemen,18 ships and 150 planes lost – Congress voted; Senate 82-0 and House 388-1 to declare war on Japan ...
Chapter 29
... 1944 (June 6) D-day: U.S., British, and Canadian troops land in Normandy 1945 (May 7) Germany surrenders ...
... 1944 (June 6) D-day: U.S., British, and Canadian troops land in Normandy 1945 (May 7) Germany surrenders ...
Final Exam Review File
... b) What were the two British secrets weapons 184. How did Germany get pulled into North Africa? 185. Explain how the US became involved in an undeclared naval war with the Germans. 186. The Japanese invasion of China placed an economic strain on Japan, what did Japan do to solve this problem? 187. W ...
... b) What were the two British secrets weapons 184. How did Germany get pulled into North Africa? 185. Explain how the US became involved in an undeclared naval war with the Germans. 186. The Japanese invasion of China placed an economic strain on Japan, what did Japan do to solve this problem? 187. W ...
USH Ch. 14 Text
... In November 1918, World War I ended when Germany surrendered to the Allies. In 1919, delegates from 27 nations met in Versailles to hammer out a peace agreement, but only Britain, France, and the United States had a real say in most of the important decisions. Germany and Russia were not even presen ...
... In November 1918, World War I ended when Germany surrendered to the Allies. In 1919, delegates from 27 nations met in Versailles to hammer out a peace agreement, but only Britain, France, and the United States had a real say in most of the important decisions. Germany and Russia were not even presen ...
AS-100 Chapter 4 Lesson 2.2
... Before the United States joined Britain in its campaign to free Europe, leaders of the two countries met many times The United States was already supplying Britain with ships, planes, and parts The United States and England came to some important conclusions They decided that even if Japan s ...
... Before the United States joined Britain in its campaign to free Europe, leaders of the two countries met many times The United States was already supplying Britain with ships, planes, and parts The United States and England came to some important conclusions They decided that even if Japan s ...
VE Day - The Marches School
... • For large parts of the war the countries and people that were most affected were in Europe. Many countries were invaded or bombed. British towns and cities were bombed from the summer of 1940 until 1945. That is five years of killing and injuring thousands and making many more homeless. Most food ...
... • For large parts of the war the countries and people that were most affected were in Europe. Many countries were invaded or bombed. British towns and cities were bombed from the summer of 1940 until 1945. That is five years of killing and injuring thousands and making many more homeless. Most food ...
Korematsu v. US - Calhoun City Schools
... June 1941; $11b lend-lease sent; army and winter stopped Hitler. Atlantic Charter – Churchill and FDR – self-determination, selfgovernment, collective security; supported by Stalin but not isolationists ...
... June 1941; $11b lend-lease sent; army and winter stopped Hitler. Atlantic Charter – Churchill and FDR – self-determination, selfgovernment, collective security; supported by Stalin but not isolationists ...
Introducing World War II
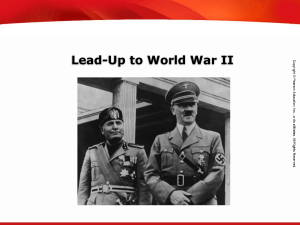
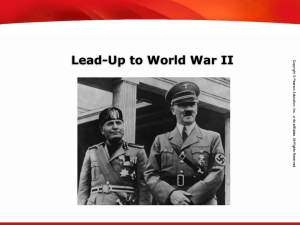
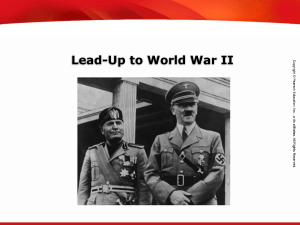
... Germany and Italy became allies in Europe. This alliance became known as the Axis Powers. Germany also signed a treaty with the Soviet Union’s new dictator, Joseph Stalin, that kept them from fighting each other. Japan began to increase its territory by attacking its neighbor, China. Of course, the ...
... Germany and Italy became allies in Europe. This alliance became known as the Axis Powers. Germany also signed a treaty with the Soviet Union’s new dictator, Joseph Stalin, that kept them from fighting each other. Japan began to increase its territory by attacking its neighbor, China. Of course, the ...
The 1920`s and the Great Depression
... nations for cash only and they have to ship it back on non-US ships. D. Neutrality Act of 1939 – E. SEPT 1940 – Tripartite Pact – F. Axis Powers – GER, Japan, Italy agreed to attack the US if any of them were attacked. G. Two-Front War – H. FDR sent 80,000 machine guns, 500,000 rifles and 50 destroy ...
... nations for cash only and they have to ship it back on non-US ships. D. Neutrality Act of 1939 – E. SEPT 1940 – Tripartite Pact – F. Axis Powers – GER, Japan, Italy agreed to attack the US if any of them were attacked. G. Two-Front War – H. FDR sent 80,000 machine guns, 500,000 rifles and 50 destroy ...
Ch 35 World War II - Brookville Local Schools
... who had declared war on Germany October 1943 • Italy appeared to be a dead end • Rome was finally taken on June 4, 1944 • The Allies continued to fight into northern Italy • May 2, 1945, only five days before Germany’s official surrender, several hundred thousand Axis troops in Italy laid down their ...
... who had declared war on Germany October 1943 • Italy appeared to be a dead end • Rome was finally taken on June 4, 1944 • The Allies continued to fight into northern Italy • May 2, 1945, only five days before Germany’s official surrender, several hundred thousand Axis troops in Italy laid down their ...
Diplomatic history of World War II

The Diplomatic history of World War II includes the major foreign policies and interactions inside the opposing coalitions, the Allies and the Axis powers. The military history of the war is covered at World War II.