Power 3
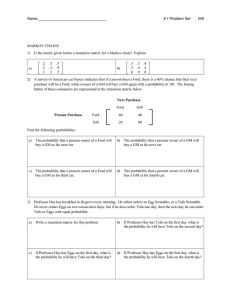
... • Example: in rolling two dice, what is the probability of getting a red one given that you rolled a white one? – P(R1/W1) ? ...
... • Example: in rolling two dice, what is the probability of getting a red one given that you rolled a white one? – P(R1/W1) ? ...
SOLUTIONS ACTIVITY 5 - Penn State Department of Statistics
... c. Determine E(X), the mean rating given by females. {HINT: Find (rating*probability) for each rating, and then add up those values.} E(X) = (1)(.04) + 2(.05) + 3(.09) + 4(.24) + 5(.32) + 6(.26) = .04+.10+.27+.96+1.60+1.56 = 4.53 d. Find the probability that the rating given is 3 or less. Note: When ...
... c. Determine E(X), the mean rating given by females. {HINT: Find (rating*probability) for each rating, and then add up those values.} E(X) = (1)(.04) + 2(.05) + 3(.09) + 4(.24) + 5(.32) + 6(.26) = .04+.10+.27+.96+1.60+1.56 = 4.53 d. Find the probability that the rating given is 3 or less. Note: When ...
Solution 1 - JEJAK 1000 PENA
... Arrange the digits 1 through 9 in increasing order, and exclude 0 because a positive integer cannot begin with 0. To get a monotonous number, we can either include or exclude each of the remaining 9 digits, and there are ways to do this. However, we cannot exclude every digit at once, so we subtract ...
... Arrange the digits 1 through 9 in increasing order, and exclude 0 because a positive integer cannot begin with 0. To get a monotonous number, we can either include or exclude each of the remaining 9 digits, and there are ways to do this. However, we cannot exclude every digit at once, so we subtract ...
Computing q-Horn Strong Backdoor Sets: a preliminary
... is to focus on the clauses for which the sum of the value of the literals (provided by the certifying function) is greater than 1. This means that there is at least 3 literals per clause having the value 1/2. The Strong Backdoor corresponds to the smallest set of variables of Q such that, when withd ...
... is to focus on the clauses for which the sum of the value of the literals (provided by the certifying function) is greater than 1. This means that there is at least 3 literals per clause having the value 1/2. The Strong Backdoor corresponds to the smallest set of variables of Q such that, when withd ...
Example - WordPress.com
... problem can be judged infeasible before a significant amount of time or money is spent. ...
... problem can be judged infeasible before a significant amount of time or money is spent. ...
Lecture 11: Algorithms - United International College
... successive terms of the sequence are examined. max is updated to the value of a term if the term exceeds the maximum of the terms previously examined. • Finiteness: it terminates after all the integers in the sequence have been examined. • Effectiveness: the algorithm can be carried out in a finite ...
... successive terms of the sequence are examined. max is updated to the value of a term if the term exceeds the maximum of the terms previously examined. • Finiteness: it terminates after all the integers in the sequence have been examined. • Effectiveness: the algorithm can be carried out in a finite ...
Introduction to Randomized Algorithms.
... uniformly at random. We only consider deterministic algorithms that does not probe the same box twice. By symmetry we can assume that the probe order for the deterministic algorithm is 1 through n. B Yao’s in-equality, we have Min A έ A E[C(A; Ip)] =∑i/n = (n+1)/2 <= max I έ I E[C(I;Aq)] Therefore a ...
... uniformly at random. We only consider deterministic algorithms that does not probe the same box twice. By symmetry we can assume that the probe order for the deterministic algorithm is 1 through n. B Yao’s in-equality, we have Min A έ A E[C(A; Ip)] =∑i/n = (n+1)/2 <= max I έ I E[C(I;Aq)] Therefore a ...
Simulated annealing

Simulated annealing (SA) is a generic probabilistic metaheuristic for the global optimization problem of locating a good approximation to the global optimum of a given function in a large search space. It is often used when the search space is discrete (e.g., all tours that visit a given set of cities). For certain problems, simulated annealing may be more efficient than exhaustive enumeration — provided that the goal is merely to find an acceptably good solution in a fixed amount of time, rather than the best possible solution.The name and inspiration come from annealing in metallurgy, a technique involving heating and controlled cooling of a material to increase the size of its crystals and reduce their defects. Both are attributes of the material that depend on its thermodynamic free energy. Heating and cooling the material affects both the temperature and the thermodynamic free energy. While the same amount of cooling brings the same amount of decrease in temperature it will bring a bigger or smaller decrease in the thermodynamic free energy depending on the rate that it occurs, with a slower rate producing a bigger decrease.This notion of slow cooling is implemented in the Simulated Annealing algorithm as a slow decrease in the probability of accepting worse solutions as it explores the solution space. Accepting worse solutions is a fundamental property of metaheuristics because it allows for a more extensive search for the optimal solution.The method was independently described by Scott Kirkpatrick, C. Daniel Gelatt and Mario P. Vecchi in 1983, and by Vlado Černý in 1985. The method is an adaptation of the Metropolis–Hastings algorithm, a Monte Carlo method to generate sample states of a thermodynamic system, invented by M.N. Rosenbluth and published in a paper by N. Metropolis et al. in 1953.