Slide 1 - AccessCardiology
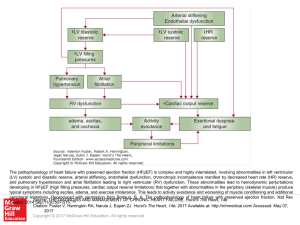
... The pathophysiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is complex and highly interrelated, involving abnormalities in left ventricular (LV) systolic and diastolic reserve, arterial stiffening, endothelial dysfunction, chronotropic incompetence manifest by decreased heart rate ...
... The pathophysiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is complex and highly interrelated, involving abnormalities in left ventricular (LV) systolic and diastolic reserve, arterial stiffening, endothelial dysfunction, chronotropic incompetence manifest by decreased heart rate ...
Fast Facts About Amorcyte Using the Body`s Natural Repair
... Unique Value Proposition: Preventing Subsequent Adverse Cardiac Events ...
... Unique Value Proposition: Preventing Subsequent Adverse Cardiac Events ...
The Management Of Atrial Fibrillation At The Front Door
... •General measures- O2, IV access, bloods (FBC, U+E, LFTs, Bone, Clotting, Glucose, Mg, TFT’s) •Treat pain, hypoxia, hypovolaemia, myocardial ischaemia •Is patient haemodynamically unstable- if so is this due to AF? ...
... •General measures- O2, IV access, bloods (FBC, U+E, LFTs, Bone, Clotting, Glucose, Mg, TFT’s) •Treat pain, hypoxia, hypovolaemia, myocardial ischaemia •Is patient haemodynamically unstable- if so is this due to AF? ...
Chapter 12 A and B questions
... How can pacemaker cells be identified electrically? What would the heart rate be if all neural and hormonal inputs were eliminated? What is an ectopic pacemaker? Which cells usually take over pacemaker functions if the AV node is defective? What events in the heart generate the P, QRS, and T waves o ...
... How can pacemaker cells be identified electrically? What would the heart rate be if all neural and hormonal inputs were eliminated? What is an ectopic pacemaker? Which cells usually take over pacemaker functions if the AV node is defective? What events in the heart generate the P, QRS, and T waves o ...
Topic 1.3a Age, Gender and Blood Pressure File
... • Loss of elasticity with age so lower volume/space in arteries increasing the b.p. • High salt diet- increases the volume of blood due to more water kept by the kidney so higher b.p. • Adrenaline- arteries and arterioles constrict raising b.p. • What is another way in which adrenaline increases the ...
... • Loss of elasticity with age so lower volume/space in arteries increasing the b.p. • High salt diet- increases the volume of blood due to more water kept by the kidney so higher b.p. • Adrenaline- arteries and arterioles constrict raising b.p. • What is another way in which adrenaline increases the ...
[7] Al-Ebrahim Kh, El-Shafei H. Thefirst 100 cases of open heart
... cardiac arrest. Pulmonary artery catheters were inserted in patients with poor left ventricular function. All patients received at least one mammary artery except one 82 years old female presented with myocardial infarction complicated with frequent ventricular fibrillation. Patients were monitored ...
... cardiac arrest. Pulmonary artery catheters were inserted in patients with poor left ventricular function. All patients received at least one mammary artery except one 82 years old female presented with myocardial infarction complicated with frequent ventricular fibrillation. Patients were monitored ...
Lorem Ipsum - NAU jan.ucc.nau.edu web server
... Severe hypertension (>200/110) Tachycardias/bradycardias Uncontrolled metabolic disease High-degree AV blocks ...
... Severe hypertension (>200/110) Tachycardias/bradycardias Uncontrolled metabolic disease High-degree AV blocks ...
Chapter 19: The Heart
... -3- ventricular ejection: when pressure in ventricles exceeds that in arteries. Semilunar valves open. Remaining blood = ESV. SV (stroke volume) = amount ejected. EDV – SV = ESV. Both ventricles with same output – necessary for fluid balance. -4- Isovolumetric relaxation – corresponds to T wave. Ve ...
... -3- ventricular ejection: when pressure in ventricles exceeds that in arteries. Semilunar valves open. Remaining blood = ESV. SV (stroke volume) = amount ejected. EDV – SV = ESV. Both ventricles with same output – necessary for fluid balance. -4- Isovolumetric relaxation – corresponds to T wave. Ve ...
Chapter XII Mechanical assistance
... reduces postload, rhythmic work, to restore the depressed contractile capacity. By means of counterpulsation balloon, cardiac output increases about 20%. ...
... reduces postload, rhythmic work, to restore the depressed contractile capacity. By means of counterpulsation balloon, cardiac output increases about 20%. ...
Costanzo Transcript
... patients that have exceeded the tolerability of oral medications and yet are not sick enough to have devices that provide greater support. What remains true though is that whereas coronary deaths are continuing to decrease, deaths related to heart failure continue to increase. Both end-stage heart d ...
... patients that have exceeded the tolerability of oral medications and yet are not sick enough to have devices that provide greater support. What remains true though is that whereas coronary deaths are continuing to decrease, deaths related to heart failure continue to increase. Both end-stage heart d ...
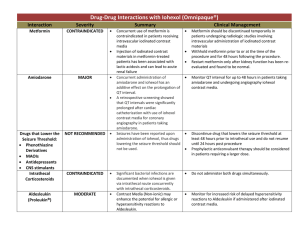
Drug-Drug Interactions with Iohexol (Omnipaque®)
... Concurrent use of metformin is contraindicated in patients receiving intravascular iodinated contrast media Injection of iodinated contrast materials in metformin-treated patients has been associated with lactic acidosis and can lead to acute renal failure Concurrent administration of amiodarone and ...
... Concurrent use of metformin is contraindicated in patients receiving intravascular iodinated contrast media Injection of iodinated contrast materials in metformin-treated patients has been associated with lactic acidosis and can lead to acute renal failure Concurrent administration of amiodarone and ...
Frank-Starling “Law of the Heart”
... Right heart: 160 ml/l Left heart: 200 ml/l Thus, one liter of blood has to pass for 40 ml O2 to be absorbed 200 ml of O2 is absorbed every min (spirometry) FICK’S PRINCIPLE ...
... Right heart: 160 ml/l Left heart: 200 ml/l Thus, one liter of blood has to pass for 40 ml O2 to be absorbed 200 ml of O2 is absorbed every min (spirometry) FICK’S PRINCIPLE ...
Heart SLIDES - Penguin Prof Pages
... Tight stenosis of RCA. This can cause an inferior wall myocardial infarction. Since this is a short lesion, usually percutaneous coronary intervention will be used - balloon dilatation & stinting. ...
... Tight stenosis of RCA. This can cause an inferior wall myocardial infarction. Since this is a short lesion, usually percutaneous coronary intervention will be used - balloon dilatation & stinting. ...
Congestive heart failure in pediatrics age groups Congestive
... to the milk or formula in phases. If the patient is not able to accept feeds, then nasogastric feeding may have to be resorted to. Because of its long half life, serum pre-albumin is a more reliable parameter of nutritional status compared to albumin. The children should be advised to avoid the use ...
... to the milk or formula in phases. If the patient is not able to accept feeds, then nasogastric feeding may have to be resorted to. Because of its long half life, serum pre-albumin is a more reliable parameter of nutritional status compared to albumin. The children should be advised to avoid the use ...
CARDIMAX
... Berberine Sulfate Berberine is a bright yellow alkaloid found in numerous medicinal plants. It has been shown to have numerous effects which benefit the heart such as enhanced coronary heart flow and oxygenation, decreased vasoconstriction, lowered blood pressure and strengthened heart contractility ...
... Berberine Sulfate Berberine is a bright yellow alkaloid found in numerous medicinal plants. It has been shown to have numerous effects which benefit the heart such as enhanced coronary heart flow and oxygenation, decreased vasoconstriction, lowered blood pressure and strengthened heart contractility ...
Introduction to Electrophysiology
... Patients with clinically significant cardiac palpitations thought ...
... Patients with clinically significant cardiac palpitations thought ...
VITAL SIGNS
... accompanied by pain or noises such as wheezing, rattling or stridor. Many of these changes are characteristic of particular illnesses or problems. The respiratory rate should be counted for a full minute. One respiration consists of one inhalation and one exhalation. You should try to assess the res ...
... accompanied by pain or noises such as wheezing, rattling or stridor. Many of these changes are characteristic of particular illnesses or problems. The respiratory rate should be counted for a full minute. One respiration consists of one inhalation and one exhalation. You should try to assess the res ...
AP2 Lab 2 - Cardiac Conduction, ECGs, Pacemakers, Defibrillators
... Distinguish between a “dual chamber” and “biventricular” pacing systems. ...
... Distinguish between a “dual chamber” and “biventricular” pacing systems. ...
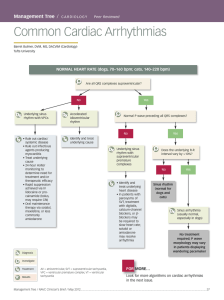
Common Cardiac Arrhythmias
... FOR MORE… Look for more algorithms on cardiac arrhythmias in the next issue. ...
... FOR MORE… Look for more algorithms on cardiac arrhythmias in the next issue. ...
Atrioventricular Septal Defect
... • If the common AVV opens predominantly into the morphologic left ventricle = LV-dominant AV canal • If the common AVV opens predominantly into the morphologic right ventricle = RV-dominant AV canal • Varies from mildly unbalanced with 2 nearly normal-sized ventricles to severely unbalanced with a s ...
... • If the common AVV opens predominantly into the morphologic left ventricle = LV-dominant AV canal • If the common AVV opens predominantly into the morphologic right ventricle = RV-dominant AV canal • Varies from mildly unbalanced with 2 nearly normal-sized ventricles to severely unbalanced with a s ...






![[7] Al-Ebrahim Kh, El-Shafei H. Thefirst 100 cases of open heart](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002089962_1-dbff11424202cceb3878e55875a62abf-300x300.png)