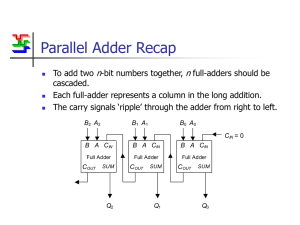
Justification logic with approximate conditional probabilities
... grammar for justification terms is the following: t ::= c | x | (t · t) | (t + t) | !t, where c ∈ C, x ∈ V . The set of all terms will be denoted by Term. For any non-negative integer n, we define !0 t := t and !n+1 t :=!(!n t). As usual, ! has greater precedence than · and +, and · has greater prec ...
... grammar for justification terms is the following: t ::= c | x | (t · t) | (t + t) | !t, where c ∈ C, x ∈ V . The set of all terms will be denoted by Term. For any non-negative integer n, we define !0 t := t and !n+1 t :=!(!n t). As usual, ! has greater precedence than · and +, and · has greater prec ...
Logic Programming, Functional Programming, and Inductive
... Essentially, they develop the theory of inductive definitions so as to distinguish divergent computations from finite failures. Negation goes beyond monotone inductive definitions: with negated subgoals, the function φ above may not be monotone. However, perhaps the database can be partitioned into ...
... Essentially, they develop the theory of inductive definitions so as to distinguish divergent computations from finite failures. Negation goes beyond monotone inductive definitions: with negated subgoals, the function φ above may not be monotone. However, perhaps the database can be partitioned into ...
Formal systems of fuzzy logic and their fragments∗
... This paper can be read in two different ways by two different groups of readers. First, the readers familiar with and/or interested in fuzzy logics can read this paper in a top-to-bottom ∗ The work of the first and the second author was supported by project 1M0021620808 of the Ministry of Education, ...
... This paper can be read in two different ways by two different groups of readers. First, the readers familiar with and/or interested in fuzzy logics can read this paper in a top-to-bottom ∗ The work of the first and the second author was supported by project 1M0021620808 of the Ministry of Education, ...
abdullah_thesis_slides.pdf
... Given d,t ∈ N, we can define the concept of type signatures of radius d with threshold t such that the values (#Type1 ,...,#Typen ) are counted only upto a threshold t and anything ≥ t is considered ∞. Two structures A and B, are said to be d-equivalent with threshold t if their type signatures with ...
... Given d,t ∈ N, we can define the concept of type signatures of radius d with threshold t such that the values (#Type1 ,...,#Typen ) are counted only upto a threshold t and anything ≥ t is considered ∞. Two structures A and B, are said to be d-equivalent with threshold t if their type signatures with ...
pdf
... e.g. for the rewrite system for the Hydra battle [Mos09, Fle07], since the terms one obtains are simpler in some specifiable sense. It turns out that in the present situation the crux is, as becomes clear from Kripke’s further remarks, that he considers the case where one chooses at each elimination ...
... e.g. for the rewrite system for the Hydra battle [Mos09, Fle07], since the terms one obtains are simpler in some specifiable sense. It turns out that in the present situation the crux is, as becomes clear from Kripke’s further remarks, that he considers the case where one chooses at each elimination ...
Nonmonotonic Reasoning - Computer Science Department
... knowledge and is never withdrawn so long as the premises are maintained. This gives rise to a unique deductive closure of the set of premises, consisting of all deductive consequences of the premises. Thus it was that we have accumulated over thousands of years a larger and larger body of theorems ...
... knowledge and is never withdrawn so long as the premises are maintained. This gives rise to a unique deductive closure of the set of premises, consisting of all deductive consequences of the premises. Thus it was that we have accumulated over thousands of years a larger and larger body of theorems ...














![pdf [local copy]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008792181_1-47413cdb5e764f6349d9f6a68b906d36-300x300.png)