Propositional Discourse Logic
... and f all statements can even be assigned classical truth-values. At f 0 , however, it dissolves again. At this point it exemplifies all phenomena we will address, so there is no need to extend it. Open-endedness means, in particular, that many statements are undetermined at the moment they are made ...
... and f all statements can even be assigned classical truth-values. At f 0 , however, it dissolves again. At this point it exemplifies all phenomena we will address, so there is no need to extend it. Open-endedness means, in particular, that many statements are undetermined at the moment they are made ...
Programming with Classical Proofs
... need to be in the language. Since negation is usually defined as ¬A := A ! ?, we do not necessarily have negation in mFOL. Firstly, we need to specify what language we work with. Definition 2.2.1 (The language of first-order logic). Given a signature S consisting of functional symbols and relational ...
... need to be in the language. Since negation is usually defined as ¬A := A ! ?, we do not necessarily have negation in mFOL. Firstly, we need to specify what language we work with. Definition 2.2.1 (The language of first-order logic). Given a signature S consisting of functional symbols and relational ...
arXiv:1410.5037v2 [cs.LO] 18 Jun 2016
... The satisfiability problem of two-variable logic FO2 was shown to be NEXPTIME-complete in [9]. The extension of two-variable logic with counting quantifiers, FOC2 , was proved decidable in [10,21], and it was subsequently shown to be NEXPTIME-complete in [22]. Research on extensions and variants of ...
... The satisfiability problem of two-variable logic FO2 was shown to be NEXPTIME-complete in [9]. The extension of two-variable logic with counting quantifiers, FOC2 , was proved decidable in [10,21], and it was subsequently shown to be NEXPTIME-complete in [22]. Research on extensions and variants of ...
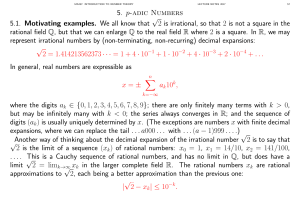
5. p-adic Numbers 5.1. Motivating examples. We all know that √2 is
... As a first example of a p-adic number for p = 7, we consider the quadratic congruences x2 ≡ 2 (mod 7k ) for k = 1, 2, 3 . . . . When k = 1 there are two solutions: x = x1 ≡ ±3 (mod 7). Any solution x2 to the congruence modulo 72 must also be a solution modulo 7, hence of the form x2 = x1 + 7y = ±3 + ...
... As a first example of a p-adic number for p = 7, we consider the quadratic congruences x2 ≡ 2 (mod 7k ) for k = 1, 2, 3 . . . . When k = 1 there are two solutions: x = x1 ≡ ±3 (mod 7). Any solution x2 to the congruence modulo 72 must also be a solution modulo 7, hence of the form x2 = x1 + 7y = ±3 + ...
The lecture notes in PDF (version August 2016)
... (c) The equality relation “ = ” is a relation on every set. This relation is often denoted by I (and also called the “identity” relation). Because, however, every set has its “own” identity relation we sometimes use subscription to distinguish all these different identity relations. That is, for eve ...
... (c) The equality relation “ = ” is a relation on every set. This relation is often denoted by I (and also called the “identity” relation). Because, however, every set has its “own” identity relation we sometimes use subscription to distinguish all these different identity relations. That is, for eve ...
Solutions - CMU Math
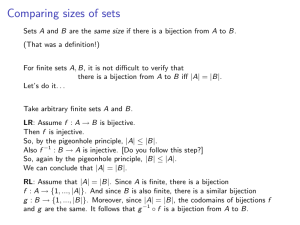
... Y ⊆ [0, 1] and so Y = [0, 1]. It follows that X is uncountable: if X were at most countable, then X + r (which is in bijection with X via the function x 7→ x + r) must be at most countable for every rational r, and there are only countably many rationals so [0, 1] would be a countable union of at mo ...
... Y ⊆ [0, 1] and so Y = [0, 1]. It follows that X is uncountable: if X were at most countable, then X + r (which is in bijection with X via the function x 7→ x + r) must be at most countable for every rational r, and there are only countably many rationals so [0, 1] would be a countable union of at mo ...















![arXiv:1410.5037v2 [cs.LO] 18 Jun 2016](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007883898_2-29c425582568c0e0d15c3d815896c9cf-300x300.png)