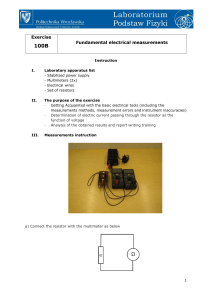
Exercise Fundamental electrical measurements
... measurements methods, measurement errors and instrument inaccuracies) Determination of electric current passing through the resistor as the function of voltage Analysis of the obtained results and report writing training ...
... measurements methods, measurement errors and instrument inaccuracies) Determination of electric current passing through the resistor as the function of voltage Analysis of the obtained results and report writing training ...
living with the lab - Louisiana Tech University
... We frequently draw diagrams that represent various types of electric circuits. The most simple diagram is that of a direct current (DC) power source and a resistive element such as a light bulb or resistor. ...
... We frequently draw diagrams that represent various types of electric circuits. The most simple diagram is that of a direct current (DC) power source and a resistive element such as a light bulb or resistor. ...
Ohm`s Law and Basic Circuit Theory – Answer Sheet
... for voltage and current into the spreadsheet. Plot the voltage on the y-axis and the current on the x-axis. Make sure you use a scatter plot. Add a trend line to the graph that is plotted and make sure that you display the equation of the line on the graph. Q6) What is the equation of this line and ...
... for voltage and current into the spreadsheet. Plot the voltage on the y-axis and the current on the x-axis. Make sure you use a scatter plot. Add a trend line to the graph that is plotted and make sure that you display the equation of the line on the graph. Q6) What is the equation of this line and ...
Worksheet on Ohms Law
... A certain electric stove has a 16 Ω heating element. (The resistance is 16 Ω. ) The current going through the element is 15 A. Calculate the voltage across the element. ...
... A certain electric stove has a 16 Ω heating element. (The resistance is 16 Ω. ) The current going through the element is 15 A. Calculate the voltage across the element. ...
ECE1250F14_PracticeEx1p2soln
... We look first for components in series carrying the same current. This happens in the second branch with R1 and the dependent voltage source, but we are unconcerned about the current in the voltage source, so we move on. We get equivalent equations from both essential nodes. If we sum the currents ...
... We look first for components in series carrying the same current. This happens in the second branch with R1 and the dependent voltage source, but we are unconcerned about the current in the voltage source, so we move on. We get equivalent equations from both essential nodes. If we sum the currents ...
Name: Practice – 20.2 Ohm`s Law: Resistance and Simple Circuits 1
... Practice – 20.2 Ohm’s Law: Resistance and Simple Circuits 1. The IR drop across a resistor means that there is a change in potential or voltage across the resistor. Is there any change in current as it passes through a resistor? ...
... Practice – 20.2 Ohm’s Law: Resistance and Simple Circuits 1. The IR drop across a resistor means that there is a change in potential or voltage across the resistor. Is there any change in current as it passes through a resistor? ...
Current
... Ohm’s Law: Ohm's Law …says that, for many materials under a wide range of conditions, the voltage, V, and current, I, are linearly related, which implies resistance, R, is independent of V and I. When does it not apply? •Circuit elements that change temperature •Examples? •Circuit elements with lar ...
... Ohm’s Law: Ohm's Law …says that, for many materials under a wide range of conditions, the voltage, V, and current, I, are linearly related, which implies resistance, R, is independent of V and I. When does it not apply? •Circuit elements that change temperature •Examples? •Circuit elements with lar ...
Electrical Circuits - WHSFreshmanScience
... • All matter is made up of positive charges and negative charges. – The positives have mass and are not usually free to move. – The negatives have no mass and are free to move through some materials (conductors). ...
... • All matter is made up of positive charges and negative charges. – The positives have mass and are not usually free to move. – The negatives have no mass and are free to move through some materials (conductors). ...
Notes18
... through which electric current flows (p374). There must of source of electrical potential difference (voltage)—such as a battery—in order to produce a current flow. Other components in the circuit dissipate this change in potential energy (caused by the battery), by doing work or dissipating the ene ...
... through which electric current flows (p374). There must of source of electrical potential difference (voltage)—such as a battery—in order to produce a current flow. Other components in the circuit dissipate this change in potential energy (caused by the battery), by doing work or dissipating the ene ...
Voltage, Current, and Resistance Ohm`s Law
... – If current increases, resistance decreases • Inversely proportional ...
... – If current increases, resistance decreases • Inversely proportional ...
Chapter 13 Electricity!
... You have a large flashlight that takes 6 Dcell batteries. If the current in the flashlight is 2 amps, what is the resistance of the light bulb? (Hint: A D-cell battery ...
... You have a large flashlight that takes 6 Dcell batteries. If the current in the flashlight is 2 amps, what is the resistance of the light bulb? (Hint: A D-cell battery ...
6 - 10.5 CYU Suggested Answers - Tse
... (b) Since the resistors are in series, they each get 2.25 V (or one quarter of the 9 V). Using this and Ohm’s law gives 0.10 A in each resistor. (c) The total resistance is 22 Ω x 4 = 88 Ω. 3. (a) The voltage of each resistor is 120 V. (b) The current in each resistor is 0.6 A. (c) The resistance of ...
... (b) Since the resistors are in series, they each get 2.25 V (or one quarter of the 9 V). Using this and Ohm’s law gives 0.10 A in each resistor. (c) The total resistance is 22 Ω x 4 = 88 Ω. 3. (a) The voltage of each resistor is 120 V. (b) The current in each resistor is 0.6 A. (c) The resistance of ...
Ohm`s Laws and Lines Project file
... Essential Questions (What does this project attempt to answer?) This project attempts to relate linear equations in slope-intercept form to Ohm’s Law. Slope-intercept form of an equation of a line: y = mx + b Ohm’s Law: I = V/R ...
... Essential Questions (What does this project attempt to answer?) This project attempts to relate linear equations in slope-intercept form to Ohm’s Law. Slope-intercept form of an equation of a line: y = mx + b Ohm’s Law: I = V/R ...
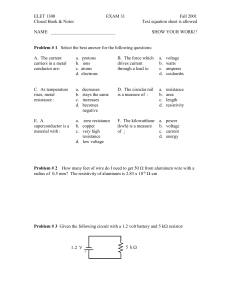
EX: a) Find a symbolic expression for v3 in the circuit below using
... used, we might use any of the tools studied thus far: Ohm's law, KVL, KCL, voltage-divider, current-divider, Thevenin source transformation, or Norton source transformation. The latter four methods require special configurations, which are lacking in this circuit. Although is and R2 are a Norton for ...
... used, we might use any of the tools studied thus far: Ohm's law, KVL, KCL, voltage-divider, current-divider, Thevenin source transformation, or Norton source transformation. The latter four methods require special configurations, which are lacking in this circuit. Although is and R2 are a Norton for ...
Приложение 1 Cardinal Numerals 2. Choose the right answer and
... 2. Choose the right answer and match it. 1. Seventeen ... thirteen equals two hundred and twenty-one. a) times (multiplied by) b) divided by c) minus d) plus 2. Eighty-one ... thirty-three equals forty-eight a) times (multiplied by) b) divided by c) minus d) plus 3. One thousand and six ... twenty-f ...
... 2. Choose the right answer and match it. 1. Seventeen ... thirteen equals two hundred and twenty-one. a) times (multiplied by) b) divided by c) minus d) plus 2. Eighty-one ... thirty-three equals forty-eight a) times (multiplied by) b) divided by c) minus d) plus 3. One thousand and six ... twenty-f ...
QUESTIONS lesson 4 - JUANA
... 4. What happens if a circuit has no resistance? And what if it has infinite resistance? If the circuit has no resistance it can produce a short circuit. In other words , the amount of electrons flowing is so high that the circuit can be burned out. ( in the case where the generator is a battery it w ...
... 4. What happens if a circuit has no resistance? And what if it has infinite resistance? If the circuit has no resistance it can produce a short circuit. In other words , the amount of electrons flowing is so high that the circuit can be burned out. ( in the case where the generator is a battery it w ...