Reading Quizzes III
... a) Higher if the number of secondary turns is lower b) Higher if the number of secondary turns is higher c) Only the currents are transformed ...
... a) Higher if the number of secondary turns is lower b) Higher if the number of secondary turns is higher c) Only the currents are transformed ...
Electric Current
... in salt solution Electric Cell – two plates or rods (electrodes) of dissimilar metal placed a solution (like dilute acid) Battery – several cells connected together ...
... in salt solution Electric Cell – two plates or rods (electrodes) of dissimilar metal placed a solution (like dilute acid) Battery – several cells connected together ...
test3
... D. (2 points) Draw the electric field due to i) a positive charge and ii) a dipole. (Remember electric ...
... D. (2 points) Draw the electric field due to i) a positive charge and ii) a dipole. (Remember electric ...
Video Transcript - Rose
... From the given equation, we know that v4 = 2*v3 because their ratio is 2:1. Set our equation equal to 6 V. So v3 should be 6/3 = 2 V. This means that v4 = vs – v3 = 6-2 = 4V. We can use Ohm’s law again to find the resistances for R3 and R4. R3 will be its voltage divided by its current. This gives 2 ...
... From the given equation, we know that v4 = 2*v3 because their ratio is 2:1. Set our equation equal to 6 V. So v3 should be 6/3 = 2 V. This means that v4 = vs – v3 = 6-2 = 4V. We can use Ohm’s law again to find the resistances for R3 and R4. R3 will be its voltage divided by its current. This gives 2 ...
Document
... ► Wood, plastic, glass, rubber, and minerals— because of tightly bound atoms or molecules ...
... ► Wood, plastic, glass, rubber, and minerals— because of tightly bound atoms or molecules ...
Electric Current - Warren County Public Schools
... Any flow of charge is called an electric current. ...
... Any flow of charge is called an electric current. ...
montgomery college - Prince Mohammad Bin Fahd University
... Q2. If you connect a diode being used in the Reverse biased mode to an ohm-meter, what reading will you observe on the meter? ...
... Q2. If you connect a diode being used in the Reverse biased mode to an ohm-meter, what reading will you observe on the meter? ...
Electric Current
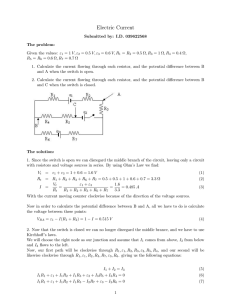
... With the current moving counter clockwise because of the direction of the voltage sources. Now in order to calculate the potential difference between B and A, all we have to do is calculate the voltage between these points: VBA = ε1 − I(R1 + R2 ) = 1 − I = 0.515 V ...
... With the current moving counter clockwise because of the direction of the voltage sources. Now in order to calculate the potential difference between B and A, all we have to do is calculate the voltage between these points: VBA = ε1 − I(R1 + R2 ) = 1 − I = 0.515 V ...
electric current
... • However, electrons are another matter: in direct current they drift through the circuit very slowly (3 hours for a meter of wire) in alternating current there is no net movement at all – back and forth only ...
... • However, electrons are another matter: in direct current they drift through the circuit very slowly (3 hours for a meter of wire) in alternating current there is no net movement at all – back and forth only ...
Circuit Analysis Handout
... Node– Any point you measure on a circuit. Every node has a voltage associated with it. Wires – Connecting nodes and elements, there is no voltage decrease across a wire o Elements/Nodes must be connected with wire for current to flow through them Current flows from high voltage to low voltage, the r ...
... Node– Any point you measure on a circuit. Every node has a voltage associated with it. Wires – Connecting nodes and elements, there is no voltage decrease across a wire o Elements/Nodes must be connected with wire for current to flow through them Current flows from high voltage to low voltage, the r ...
Ohm`s Law Lab
... recording the readings. Record your readings in the table on the back. 5. Disconnect everything in the circuit, use the voltmeter to set the voltage source to 6 volts and repeat #2-4. You will have to change the meter sensitivity settings. 6. Repeat this procedure for three more different resistors ...
... recording the readings. Record your readings in the table on the back. 5. Disconnect everything in the circuit, use the voltmeter to set the voltage source to 6 volts and repeat #2-4. You will have to change the meter sensitivity settings. 6. Repeat this procedure for three more different resistors ...
Basic Electronics
... • One volt is equal to one joule of work of coulomb of charge. (1V= J/C). Just a heat flows through a heat conductor until there is no longer a temperature difference, charge wants to flow through an electric conductor until there is no more potential difference(voltage) • When measuring voltage, o ...
... • One volt is equal to one joule of work of coulomb of charge. (1V= J/C). Just a heat flows through a heat conductor until there is no longer a temperature difference, charge wants to flow through an electric conductor until there is no more potential difference(voltage) • When measuring voltage, o ...
circuits and current review
... 1. What two things are needed for charge to flow between two points? 2. What is actually flowing in a current carrying wire? 3. What is an ampere? 4. The resistance of a wire depends on what three factors? 5. Which has more resistance, a thick wire or a thin wire? 6. What is the unit of resistance? ...
... 1. What two things are needed for charge to flow between two points? 2. What is actually flowing in a current carrying wire? 3. What is an ampere? 4. The resistance of a wire depends on what three factors? 5. Which has more resistance, a thick wire or a thin wire? 6. What is the unit of resistance? ...