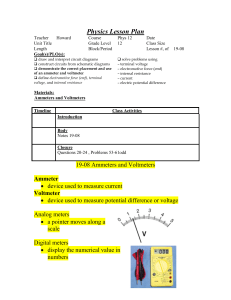
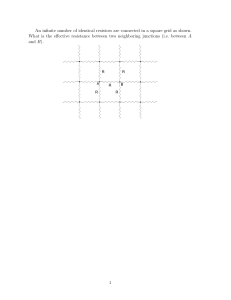
Introduction to Photovoltaics Powerpoint
... Electrical Current – how many electrons Voltage – how hard they’re pushed Power – what they can accomplish Circuit – where they can go Series Circuit – one pathway only Parallel Circuit – so many choices! ...
... Electrical Current – how many electrons Voltage – how hard they’re pushed Power – what they can accomplish Circuit – where they can go Series Circuit – one pathway only Parallel Circuit – so many choices! ...
Lecture 1 - University of Minnesota Duluth
... electricity and forms the foundation of modern electrical theory • 1800’s: Alessandro Volta makes his Voltaic Pile using zinc and copper disks submersed in an electrolytic solution (acid), thus re-inventing the battery, 1800 years after the Persians ...
... electricity and forms the foundation of modern electrical theory • 1800’s: Alessandro Volta makes his Voltaic Pile using zinc and copper disks submersed in an electrolytic solution (acid), thus re-inventing the battery, 1800 years after the Persians ...
kvl_lect
... Electricity is the flow of electrons through metal wires and other devices such as motors, light bulbs, computers, etc. An electron is a very small particle that has a negative charge. Electricity is often described in terms of three basic quantities: voltage, current and power. These quantities hav ...
... Electricity is the flow of electrons through metal wires and other devices such as motors, light bulbs, computers, etc. An electron is a very small particle that has a negative charge. Electricity is often described in terms of three basic quantities: voltage, current and power. These quantities hav ...
What is a series-parallel circuit
... Voltage drops add to equal total voltage. All components share the same (equal) current. Resistances add to equal total resistance. ...
... Voltage drops add to equal total voltage. All components share the same (equal) current. Resistances add to equal total resistance. ...
Test Paper
... 19. Calculate the energy consumed in 20 days, if two bulbs of 30 w work for 6 hrs , three fans of 80 w work for 10 hrs daily and one tube of 60 w works for 3 hrs daily.(3) ...
... 19. Calculate the energy consumed in 20 days, if two bulbs of 30 w work for 6 hrs , three fans of 80 w work for 10 hrs daily and one tube of 60 w works for 3 hrs daily.(3) ...
Lecture 1 - ECE 2006 - University of Minnesota Duluth
... electricity and forms the foundation of modern electrical theory • 1800’s: Alessandro Volta makes his Voltaic Pile using zinc and copper disks submersed in an electrolytic solution (acid), thus re-inventing the battery, 1800 years after the Persians ...
... electricity and forms the foundation of modern electrical theory • 1800’s: Alessandro Volta makes his Voltaic Pile using zinc and copper disks submersed in an electrolytic solution (acid), thus re-inventing the battery, 1800 years after the Persians ...
AC Series and Parallel Circuits
... IV. Lab Procedure. Time Required: 45 minutes. Check-off each step as you complete it. Step One: Construct an AC series parallel circuit ...
... IV. Lab Procedure. Time Required: 45 minutes. Check-off each step as you complete it. Step One: Construct an AC series parallel circuit ...
CS 436 HCI Technology Basic Electricity/Electronics Review 1 Basic Quantities and Units
... Sometimes the human body/ground is used as one plate, and thus proximity of you (or your hand) can be inferred by determining the capacitance between you and a metal plate. Capacitors exhibit a form of complex resistance (1/conductance) called Impedance (1/admittance), equal to 1/sC, where ...
... Sometimes the human body/ground is used as one plate, and thus proximity of you (or your hand) can be inferred by determining the capacitance between you and a metal plate. Capacitors exhibit a form of complex resistance (1/conductance) called Impedance (1/admittance), equal to 1/sC, where ...
Note Guide Ohm`s Law, Power and Electrical Energy
... Note Guide Ohm’s Law, Power and Electrical Energy Slide 1 – Voltage (Potential Difference) 1. Voltage measures __________________________. Measure of ____________ ___________ 2. Unit for voltage is ________ (__) 3. “Potential difference” flows from ____________ energy to ______________ energy. 4. Th ...
... Note Guide Ohm’s Law, Power and Electrical Energy Slide 1 – Voltage (Potential Difference) 1. Voltage measures __________________________. Measure of ____________ ___________ 2. Unit for voltage is ________ (__) 3. “Potential difference” flows from ____________ energy to ______________ energy. 4. Th ...
Electric Currents
... The Electron Drift velocity Electrons in a conductor have large, random speeds just due to their temperature. When a potential difference is applied, the electrons also acquire an average drift velocity, which is generally considerably smaller than the thermal velocity. ...
... The Electron Drift velocity Electrons in a conductor have large, random speeds just due to their temperature. When a potential difference is applied, the electrons also acquire an average drift velocity, which is generally considerably smaller than the thermal velocity. ...
Chapter 17 Electric Current and Resistance
... Electrons do not flow like water in a pipe. In the absence of voltage, they move randomly at high speeds, due to their temperature. When a voltage is applied, a very small drift velocity is added to the thermal motion, typically around 1 mm/s; this is enough to yield the observed current. ...
... Electrons do not flow like water in a pipe. In the absence of voltage, they move randomly at high speeds, due to their temperature. When a voltage is applied, a very small drift velocity is added to the thermal motion, typically around 1 mm/s; this is enough to yield the observed current. ...
Basic Electricity
... The power would be 0.61 × 20 V = 12 watts. Plenty enough to fry a 1 watt resistor. It is important that we ensure that any current limiting resistors can dissipate the power through them. The above situation could be highly dangerous. ...
... The power would be 0.61 × 20 V = 12 watts. Plenty enough to fry a 1 watt resistor. It is important that we ensure that any current limiting resistors can dissipate the power through them. The above situation could be highly dangerous. ...
Electricity (1)
... build up of an electric charge on the surface of an object. The charge builds up but does not flow. Static electricity is potential energy. It does not move. It is stored. ...
... build up of an electric charge on the surface of an object. The charge builds up but does not flow. Static electricity is potential energy. It does not move. It is stored. ...
Unit of Instruction: Electricity
... Unit Map ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Unit of Instruction: Electricity Learning Target ...
... Unit Map ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Unit of Instruction: Electricity Learning Target ...
Define and Explain on Current and Resistance
... immediately to the electric field and is set in motion almost simultaneously, even though individual charges move slowly. The battery provides a voltage (V) between its terminals. The electric field set up in a wire connected to the battery terminals causes the current to flow, which occurs when th ...
... immediately to the electric field and is set in motion almost simultaneously, even though individual charges move slowly. The battery provides a voltage (V) between its terminals. The electric field set up in a wire connected to the battery terminals causes the current to flow, which occurs when th ...