Electricity Within a Circuit - St. John Paul II Collegiate
... (electrons) flow on a path from the negative terminal of a battery to the positive terminal of the battery. - is similar to a rivers current. A strong river current means that water flows rapidly; a fast flow rate. ...
... (electrons) flow on a path from the negative terminal of a battery to the positive terminal of the battery. - is similar to a rivers current. A strong river current means that water flows rapidly; a fast flow rate. ...
19.2 Current and voltage
... in light bulbs, increases as temperature increases. A graph of current versus voltage for a light bulb shows a curve. A device with constant resistance would show a straight line on this graph. ...
... in light bulbs, increases as temperature increases. A graph of current versus voltage for a light bulb shows a curve. A device with constant resistance would show a straight line on this graph. ...
Name ______ period ____
... 15. Mr. Robinson and his seventh-grade science class are conducting an experiment. The class needs to choose a good insulator. What type of material could be used as an insulator? 16. There is a potential difference of 12 V across a resistor with 0.25 A of current in it. The resistance of the resist ...
... 15. Mr. Robinson and his seventh-grade science class are conducting an experiment. The class needs to choose a good insulator. What type of material could be used as an insulator? 16. There is a potential difference of 12 V across a resistor with 0.25 A of current in it. The resistance of the resist ...
KIRCHOFF`S CURRENT LAW AND KIRCHOFF`S VOLTAGE LAW
... Figure 2. Close path in a circuit. 2. Kirchoff’s voltage law for DC circuits The Kirchoff’s voltage law is stated as: the algebraic sum of all the voltages around any closed path in a circuit equals zero. This applies to DC stationary circuits, with magnetic field density constant with respect to ti ...
... Figure 2. Close path in a circuit. 2. Kirchoff’s voltage law for DC circuits The Kirchoff’s voltage law is stated as: the algebraic sum of all the voltages around any closed path in a circuit equals zero. This applies to DC stationary circuits, with magnetic field density constant with respect to ti ...
Types of Electric Circuits Series Circuit Mini-Lab
... A schematic diagram is a special diagram that describes an electric circuit, using certain symbols to represent different devices in the circuit. ...
... A schematic diagram is a special diagram that describes an electric circuit, using certain symbols to represent different devices in the circuit. ...
Resistance - Leaving Cert Physics
... Now let's go back and try again to understand the Wheatstone bridge: The galvanometer in the middle is used to detect current. If it reads zero then no current flows between the two points. We say that the bridge is balanced. Now the key to this is to realise that not only can the bridge be balance ...
... Now let's go back and try again to understand the Wheatstone bridge: The galvanometer in the middle is used to detect current. If it reads zero then no current flows between the two points. We say that the bridge is balanced. Now the key to this is to realise that not only can the bridge be balance ...
Voltage, Current, Resistance, and Ohm`s Law
... more charge than another. This difference in charge between the two points is called voltage. It is measured in volts, which, technically, is the potential energy difference between two points that will impart one joule of energy per coulomb of charge that passes through it (don’t panic if this make ...
... more charge than another. This difference in charge between the two points is called voltage. It is measured in volts, which, technically, is the potential energy difference between two points that will impart one joule of energy per coulomb of charge that passes through it (don’t panic if this make ...
Resistance of a wire - The Thomas Cowley High School
... The total current into and out of the supply is always the same. What are the missing currents? A1 = 0.6A A2 = 0.4A (A1-A3 = 0.6A-0.2A) A3 = 0.2A A4 = 0.6A (A1 = A4) ...
... The total current into and out of the supply is always the same. What are the missing currents? A1 = 0.6A A2 = 0.4A (A1-A3 = 0.6A-0.2A) A3 = 0.2A A4 = 0.6A (A1 = A4) ...
Electricity - The Bored of Studies Community
... - a conducting path which allows electrons to flow around the circuit. Current: An electric current is a flow of electric charge. It is measured in amps (A), using an ammeter. For current to flow, there must be a complete pathway from the negative terminal to the positive terminal. Charge has the sy ...
... - a conducting path which allows electrons to flow around the circuit. Current: An electric current is a flow of electric charge. It is measured in amps (A), using an ammeter. For current to flow, there must be a complete pathway from the negative terminal to the positive terminal. Charge has the sy ...
INTERMEDIATE/SECONDARY ARTICLE: Measuring Electricity
... don’t really think about what those measurements mean. We are confident that when we plug them in, they will work. It is important to understand electricity, because we rely on it for so many things. Electricity is the flow of electrons. Using the flow of water as an analogy can make concepts of ele ...
... don’t really think about what those measurements mean. We are confident that when we plug them in, they will work. It is important to understand electricity, because we rely on it for so many things. Electricity is the flow of electrons. Using the flow of water as an analogy can make concepts of ele ...
Electric Current and Circuits
... fact that a bird can sit on a high-voltage wire without harm, since both of its feet are at the same voltage. You can also see that the bird is not "grounded" -- you will not be shocked by touching a high voltage if there is no path for the current to reach the Earth or a different voltage point. Ty ...
... fact that a bird can sit on a high-voltage wire without harm, since both of its feet are at the same voltage. You can also see that the bird is not "grounded" -- you will not be shocked by touching a high voltage if there is no path for the current to reach the Earth or a different voltage point. Ty ...
ECE 211 Workshop: Thevenin`s and Norton`s Theorems
... 1.Calculate the output voltage, V, when in open circuit condition (no load resistor—meaning infinite resistance). This is VTh. 2.Calculate the output current, IAB, when the output terminals are short circuited (load resistance is 0). RTh equals VTh divided by this IAB. Step 2 could also be thought o ...
... 1.Calculate the output voltage, V, when in open circuit condition (no load resistor—meaning infinite resistance). This is VTh. 2.Calculate the output current, IAB, when the output terminals are short circuited (load resistance is 0). RTh equals VTh divided by this IAB. Step 2 could also be thought o ...
Electricity
... to move through • Advantages – when one branch is opened (turn off a light) the current flows through the other branches ...
... to move through • Advantages – when one branch is opened (turn off a light) the current flows through the other branches ...
Safety Example Using Low
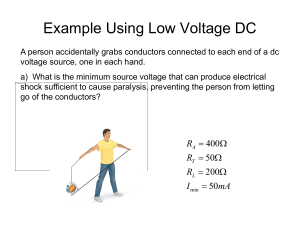
... Example Using Low Voltage DC A person accidentally grabs conductors connected to each end of a dc voltage source, one in each hand. a) What is the minimum source voltage that can produce electrical shock sufficient to cause paralysis, preventing the person from letting go of the conductors? ...
... Example Using Low Voltage DC A person accidentally grabs conductors connected to each end of a dc voltage source, one in each hand. a) What is the minimum source voltage that can produce electrical shock sufficient to cause paralysis, preventing the person from letting go of the conductors? ...
QUESTIONS ON OHM`S LAW AND KIRCHHOFF`S LAW A
... 1. Define ‘strength of the electric current’. Derive a relation between electric current and drift velocity. 2. Assuming the expression for electric current in terms of drift velocity, deduce Ohm’s law. Define SI unit of resistance. 3. What is effective resistance? Derive the expression for effectiv ...
... 1. Define ‘strength of the electric current’. Derive a relation between electric current and drift velocity. 2. Assuming the expression for electric current in terms of drift velocity, deduce Ohm’s law. Define SI unit of resistance. 3. What is effective resistance? Derive the expression for effectiv ...
current
... Q2 : current of 15A passes through a radio for 4 minutes. A- how much charge passes through the radio B- how many electrons pass through the radio. Q3 :If there is a current of 10 amperes in a circuit for 10 minutes, what quantity of electric charge flows in through the circuit? Q4:. How much curren ...
... Q2 : current of 15A passes through a radio for 4 minutes. A- how much charge passes through the radio B- how many electrons pass through the radio. Q3 :If there is a current of 10 amperes in a circuit for 10 minutes, what quantity of electric charge flows in through the circuit? Q4:. How much curren ...
Series and Parallel Circuits
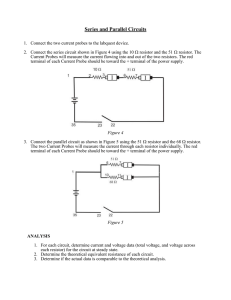
... 1. Connect the two current probes to the labquest device. 2. Connect the series circuit shown in Figure 4 using the 10 resistor and the 51 resistor. The Current Probes will measure the current flowing into and out of the two resistors. The red terminal of each Current Probe should be toward the ...
... 1. Connect the two current probes to the labquest device. 2. Connect the series circuit shown in Figure 4 using the 10 resistor and the 51 resistor. The Current Probes will measure the current flowing into and out of the two resistors. The red terminal of each Current Probe should be toward the ...
The experiments with the electrical circuits address multiple
... The experiments with the electrical circuits address multiple difficulties that students often have. The experiment exercises the students' abilities to represent a circuit in multiple ways. It emphasizes that current is a measure of the rate of charge flow while voltage is a comparison of potential ...
... The experiments with the electrical circuits address multiple difficulties that students often have. The experiment exercises the students' abilities to represent a circuit in multiple ways. It emphasizes that current is a measure of the rate of charge flow while voltage is a comparison of potential ...