AP Quiz #24 Circuits
... 3. A battery with an emf of 24 volts and an internal resistance of 1 ohm is connected to an external circuit as shown above. Determine each of the following (a) the equivalent resistance of the combination of the 4-ohm, 8-ohm, and 12-ohm resistors ...
... 3. A battery with an emf of 24 volts and an internal resistance of 1 ohm is connected to an external circuit as shown above. Determine each of the following (a) the equivalent resistance of the combination of the 4-ohm, 8-ohm, and 12-ohm resistors ...
PHYS111_26 - MrLaFazia.com
... • “Why do most people hire electricians”? – what does “electricity” actually do to you... • …on the small scale? • …on the large scale? ...
... • “Why do most people hire electricians”? – what does “electricity” actually do to you... • …on the small scale? • …on the large scale? ...
Electricity powerpoint
... The simplest type of circuit involves electricity going around with no “choices” (electrons don’t really choose). This is called a Series circuit. Draw the path the electrons travel. The other main type of circuit has two or more branches. This is called a Parallel circuit. Draw on the electron flow ...
... The simplest type of circuit involves electricity going around with no “choices” (electrons don’t really choose). This is called a Series circuit. Draw the path the electrons travel. The other main type of circuit has two or more branches. This is called a Parallel circuit. Draw on the electron flow ...
current - Irion County ISD
... The simplest type of circuit involves electricity going around with no “choices” (electrons don’t really choose). This is called a Series circuit. Draw the path the electrons travel. The other main type of circuit has two or more branches. This is called a Parallel circuit. Draw on the electron flow ...
... The simplest type of circuit involves electricity going around with no “choices” (electrons don’t really choose). This is called a Series circuit. Draw the path the electrons travel. The other main type of circuit has two or more branches. This is called a Parallel circuit. Draw on the electron flow ...
• Kirchhoff`s Laws and Basic Circuit • Energy and Power • Resistors
... In resistor: work done on charges qEd kinetic (accelerate) between collisions thermal energy of lattice after collisions After many collisions over length L of resistor: ∆Eth = qEL = q∆VR ...
... In resistor: work done on charges qEd kinetic (accelerate) between collisions thermal energy of lattice after collisions After many collisions over length L of resistor: ∆Eth = qEL = q∆VR ...
Lecture 4: Methods of Analysis
... • Other current and voltage sources must be factored in to either the KCL equations or the unknown voltages. They sometimes actually make the equations easier. • Solve for the unknown voltages. ...
... • Other current and voltage sources must be factored in to either the KCL equations or the unknown voltages. They sometimes actually make the equations easier. • Solve for the unknown voltages. ...
Figure 12–4 - WordPress.com
... • Electron flow changes direction • More economical to produce than direct current ...
... • Electron flow changes direction • More economical to produce than direct current ...
D-3 Notes
... resistance. Fixed Resistors are usually made of a heat conducting material to control the current and voltage levels. Resistors that do not change as other variables change are also called Ohmic Resistors Variable Resistors change their resistance in response to a changing variable such as temperatu ...
... resistance. Fixed Resistors are usually made of a heat conducting material to control the current and voltage levels. Resistors that do not change as other variables change are also called Ohmic Resistors Variable Resistors change their resistance in response to a changing variable such as temperatu ...
06AP_Physics_C_-_Internal_Resistance
... INTERNAL RESISTANCE All components in a circuit off some type of resistance regardless of how large or small it is. Batteries especially have what is called an internal resistance, r. Within the schematic it will be represented as a resistor symbol next to a battery symbol and between 2 points that ...
... INTERNAL RESISTANCE All components in a circuit off some type of resistance regardless of how large or small it is. Batteries especially have what is called an internal resistance, r. Within the schematic it will be represented as a resistor symbol next to a battery symbol and between 2 points that ...
Notes25
... A transistor is a sandwich of p, n & p (or n, p & n) semiconductors. Normally, this construction is insulating—a voltage placed across the two end plates will not flow. A small metal electrode placed above the center material injects extra electrons in the center semiconductor which dramatically cha ...
... A transistor is a sandwich of p, n & p (or n, p & n) semiconductors. Normally, this construction is insulating—a voltage placed across the two end plates will not flow. A small metal electrode placed above the center material injects extra electrons in the center semiconductor which dramatically cha ...
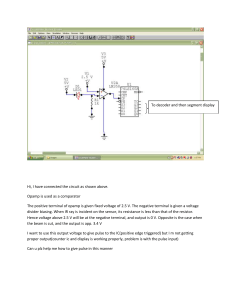
Hi, I have connected the circuit as shown above. Opamp is used as
... Hi, I have connected the circuit as shown above. Opamp is used as a comparator The positive terminal of opamp is given fixed voltage of 2.5 V. The negative terminal is given a voltage divider biasing. When IR ray is incident on the sensor, its resistance is less than that of the resistor. Hence volt ...
... Hi, I have connected the circuit as shown above. Opamp is used as a comparator The positive terminal of opamp is given fixed voltage of 2.5 V. The negative terminal is given a voltage divider biasing. When IR ray is incident on the sensor, its resistance is less than that of the resistor. Hence volt ...
conductivity and resistance
... current is flowing through it? What is the voltage across the resistor? What current would produce heat at half the present rate? 4. At (2.0 × 101 ) ◦C, copper has a resistivity of 1.7 × 10−6 ohm-cm. What is the resistance of a 1.0 meter length of copper wire that has a diameter of 1.0 mm? 5. If a p ...
... current is flowing through it? What is the voltage across the resistor? What current would produce heat at half the present rate? 4. At (2.0 × 101 ) ◦C, copper has a resistivity of 1.7 × 10−6 ohm-cm. What is the resistance of a 1.0 meter length of copper wire that has a diameter of 1.0 mm? 5. If a p ...
Unit 4 - Section 13.9 2011 Solving Problems with Ohms Law
... The generator produced 7 200 J of energy. 4. If a generator in Question #3 burned enough gasoline to produce 28.8 kJ, what would be the charge be at the negative terminal? ...
... The generator produced 7 200 J of energy. 4. If a generator in Question #3 burned enough gasoline to produce 28.8 kJ, what would be the charge be at the negative terminal? ...
Ohms Law Ohmic Resistors versus Lightbulbs
... Current and Voltage Defined Conventional Current: (the current in electrical circuits) Flow of current from positive terminal to the negative ...
... Current and Voltage Defined Conventional Current: (the current in electrical circuits) Flow of current from positive terminal to the negative ...
Video Transcript - Rose
... If we set I2 at zero, we can find z11. [math equation] The voltage that crosses the first port is V1. Let’s look at the top node. We can label the current flow through the two resistors as I3 and I4. Based on the Kirchoff Current Law, we know that I1 should be equal to the sum of I3 and I4. [math eq ...
... If we set I2 at zero, we can find z11. [math equation] The voltage that crosses the first port is V1. Let’s look at the top node. We can label the current flow through the two resistors as I3 and I4. Based on the Kirchoff Current Law, we know that I1 should be equal to the sum of I3 and I4. [math eq ...
Chapter 5 Electrostatics
... • Conductors – Matter that conducts the current • Insulators – Matter that INHIBITS current flow • SUPERCONDUCTOR – Like an MRI unit – low resistance (niobium/titanium) • Semi-conductor = depending on the conditions, can be either a conductor/insulator ...
... • Conductors – Matter that conducts the current • Insulators – Matter that INHIBITS current flow • SUPERCONDUCTOR – Like an MRI unit – low resistance (niobium/titanium) • Semi-conductor = depending on the conditions, can be either a conductor/insulator ...