1 - Marine Institute
... b) Write them using phasor notation. c) Calculate the RMS resultant of the two voltages. (82.6VRMS) ...
... b) Write them using phasor notation. c) Calculate the RMS resultant of the two voltages. (82.6VRMS) ...
Some hints regarding Thevenin Equivalents and Circuits with
... Normally, one can find RTH by using RTH = (VOC / ISC ). However, what is the value of 0V/0A ??? The answer: we do not know. (RTH is NOT equal to 2R || R. You can only zero out independent sources.) A different approach is needed. RTH is the resistance seen looking back into the circuit when all inde ...
... Normally, one can find RTH by using RTH = (VOC / ISC ). However, what is the value of 0V/0A ??? The answer: we do not know. (RTH is NOT equal to 2R || R. You can only zero out independent sources.) A different approach is needed. RTH is the resistance seen looking back into the circuit when all inde ...
Series and Parallel Circuits - Mrs. Anthony
... will go DOWN (lights will dim) If you remove a light bulb or one burns out—all go out! ...
... will go DOWN (lights will dim) If you remove a light bulb or one burns out—all go out! ...
PHYSICAL SCIENCE
... • Compare series and parallel circuits. Conceptually explore the flow of electricity in series and parallel circuits. (Calculations may be used to develop conceptual understanding or as enrichment.) • Explain how the flow of electricity through series and parallel circuits is affected by voltage and ...
... • Compare series and parallel circuits. Conceptually explore the flow of electricity in series and parallel circuits. (Calculations may be used to develop conceptual understanding or as enrichment.) • Explain how the flow of electricity through series and parallel circuits is affected by voltage and ...
Unit 43: Current, voltage and resistance Dr. Basil Hamed Technical
... B. Voltage and Resistance The amount of current (in amps) flowing through a circuit will partly depend on the electromotive force (EMF) of the electrical supply. Electromotive force is measured in volts (V), and is generally called voltage. The voltage depends on the 'strength' of the electrical su ...
... B. Voltage and Resistance The amount of current (in amps) flowing through a circuit will partly depend on the electromotive force (EMF) of the electrical supply. Electromotive force is measured in volts (V), and is generally called voltage. The voltage depends on the 'strength' of the electrical su ...
Ohm`s Law
... current through it., V = I R, where V is Voltage in Volts and I is the current in Amps • The larger the resistance, the weaker the current that flows through the resistor (assuming same voltage). ...
... current through it., V = I R, where V is Voltage in Volts and I is the current in Amps • The larger the resistance, the weaker the current that flows through the resistor (assuming same voltage). ...
Announcements l Help room hours (1248 BPS) LON-CAPA #6 due Oct. 18
... potential, i.e. to ground ◆ plus a useful safety feature l That way multiple circuits can be used at the same time and their reference potentials will be the same ...
... potential, i.e. to ground ◆ plus a useful safety feature l That way multiple circuits can be used at the same time and their reference potentials will be the same ...
Voltage and Current Conventions
... • Voltage is a relative measure of the Energy of a charged body at point A with respect to its energy at point B. • If it requires Energy of amount U to move a body having charge Q from point B to point A, then we say that there is a “potential difference” between points A and B of U/Q = VAB volts. ...
... • Voltage is a relative measure of the Energy of a charged body at point A with respect to its energy at point B. • If it requires Energy of amount U to move a body having charge Q from point B to point A, then we say that there is a “potential difference” between points A and B of U/Q = VAB volts. ...
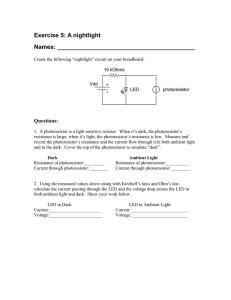
Exercise 1:
... Names: _________________________________________ Create the following “nightlight” circuit on your breadboard: ...
... Names: _________________________________________ Create the following “nightlight” circuit on your breadboard: ...
AS Level Electricity - the basics - revision from GCSE
... • Components resist a current flowing through them. • The bigger their resistance, the smaller the current produced by a particular voltage, or the bigger the voltage needed to produce a particular current. • Resistance (R) is measured in ohms (W) ...
... • Components resist a current flowing through them. • The bigger their resistance, the smaller the current produced by a particular voltage, or the bigger the voltage needed to produce a particular current. • Resistance (R) is measured in ohms (W) ...
COVENANT UNIVERSITY 2014/2015 Academic Session COURSE
... A magnet gives rise to a field that surrounds them and which causes forces on other magnets, iron and steel objects, and current- carrying wires. The part of a magnet where the field emerges is called the N pole, and where the field enters the magnet is called the S pole. Magnets always have both N ...
... A magnet gives rise to a field that surrounds them and which causes forces on other magnets, iron and steel objects, and current- carrying wires. The part of a magnet where the field emerges is called the N pole, and where the field enters the magnet is called the S pole. Magnets always have both N ...
Slide 1
... • Components resist a current flowing through them. • The bigger their resistance, the smaller the current produced by a particular voltage, or the bigger the voltage needed to produce a particular current. • Resistance (R) is measured in ohms (W) ...
... • Components resist a current flowing through them. • The bigger their resistance, the smaller the current produced by a particular voltage, or the bigger the voltage needed to produce a particular current. • Resistance (R) is measured in ohms (W) ...
Resistance and Ohm`s Law
... *The purpose of measuring reversed current is to see if a current value will be changed by flipping the resistor. Just make sure of that for 2 or 3 cases. *You will plot the data as voltage vs. current. According to Ohm’s Law, the slope of the line should be the resistance. If you know how to plot t ...
... *The purpose of measuring reversed current is to see if a current value will be changed by flipping the resistor. Just make sure of that for 2 or 3 cases. *You will plot the data as voltage vs. current. According to Ohm’s Law, the slope of the line should be the resistance. If you know how to plot t ...
Introduction
... • An electric circuit is a “continues” chain of conductors where one end of the chain is connected to the other • Circuit + voltage will generate current • Non perfect conductors resist the current and slow it – those are resistors ...
... • An electric circuit is a “continues” chain of conductors where one end of the chain is connected to the other • Circuit + voltage will generate current • Non perfect conductors resist the current and slow it – those are resistors ...
Physics Sample Paper for Engg Entrance Exam 1
... a) Its electric field b) Its coils c) Its magnetic field d) Both electric and magnetic fields 31.Two different coils have self inductance 8mH and 2mH. The current in both coils are increased at same constant rate. The ratio of the induced emfs in the coil is a) 4:1 b) 1:4 c) 1:2 d) 2:1 32.A coil of ...
... a) Its electric field b) Its coils c) Its magnetic field d) Both electric and magnetic fields 31.Two different coils have self inductance 8mH and 2mH. The current in both coils are increased at same constant rate. The ratio of the induced emfs in the coil is a) 4:1 b) 1:4 c) 1:2 d) 2:1 32.A coil of ...
What causes the electrical faults or voltage dips? These electrical
... on lower voltage networks, by various factors including wildlife and lightning. ...
... on lower voltage networks, by various factors including wildlife and lightning. ...
Circuits, Volts, Amps, Ohms
... List 3 characteristics of a wire that affect its resistance. A light bulb passes a current of 0.83 A when the potential difference is 120V. What is the bulb’s resistance? What is the potential difference across an electric water heater element that has a resistance of 32ohms when a current through i ...
... List 3 characteristics of a wire that affect its resistance. A light bulb passes a current of 0.83 A when the potential difference is 120V. What is the bulb’s resistance? What is the potential difference across an electric water heater element that has a resistance of 32ohms when a current through i ...
Freshman Science Study Guide
... 7. The voltage difference in a circuit is a measure of the ________________ per _____________ of electricity flowing in a circuit. The symbol for voltage difference is: ...
... 7. The voltage difference in a circuit is a measure of the ________________ per _____________ of electricity flowing in a circuit. The symbol for voltage difference is: ...
Special Assignment_1_EEE
... The temperature coefficient of resistance is defined as (A) increase in resistance per ohm per oC. (B) increase in resistance per oC. (C) decrease in resistance per ohm per oC. (D) the ratio of decrease in resistance per oC to the resistance at 0oC. A battery is made by combination of 6 cells in ser ...
... The temperature coefficient of resistance is defined as (A) increase in resistance per ohm per oC. (B) increase in resistance per oC. (C) decrease in resistance per ohm per oC. (D) the ratio of decrease in resistance per oC to the resistance at 0oC. A battery is made by combination of 6 cells in ser ...
Objectives of Physics for Grade Nine
... Know the laws of voltages and currents in an electric circuit. Measure a DC voltage using an oscilloscope. Alternating voltage Distinguish between a DC voltage and an alternating voltage. Relate the effective voltage to the maximum voltage of a sinusoidal alternating current. Know that in ...
... Know the laws of voltages and currents in an electric circuit. Measure a DC voltage using an oscilloscope. Alternating voltage Distinguish between a DC voltage and an alternating voltage. Relate the effective voltage to the maximum voltage of a sinusoidal alternating current. Know that in ...