Data Analysis of Fuel Cells
... transfer. Transfer of water occurs because of gas humidification and product formation. At high current, the amount of water at the cathode significantly rises until the continued transfer of oxygen from the gas stream to the membrane halts due to blockage of the pores. When this occurs, the voltage ...
... transfer. Transfer of water occurs because of gas humidification and product formation. At high current, the amount of water at the cathode significantly rises until the continued transfer of oxygen from the gas stream to the membrane halts due to blockage of the pores. When this occurs, the voltage ...
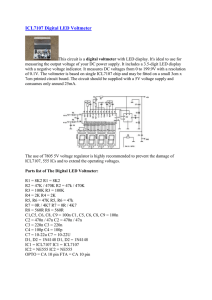
ICL7107 Digital LED Voltmeter
... of 0.1V. The voltmeter is based on single ICL7107 chip and may be fitted on a small 3cm x 7cm printed circuit board. The circuit should be supplied with a 5V voltage supply and consumes only around 25mA. ...
... of 0.1V. The voltmeter is based on single ICL7107 chip and may be fitted on a small 3cm x 7cm printed circuit board. The circuit should be supplied with a 5V voltage supply and consumes only around 25mA. ...
wel come to coe rac sector - ITI College
... It is now necessary to consider the reason for the motion of electrons in an electrical circuit. In order to move free electrons in one direction & so produce a current, a source of electrical energy is required. The torch battery is a source of electrical energy. The battery is said to have an E.M. ...
... It is now necessary to consider the reason for the motion of electrons in an electrical circuit. In order to move free electrons in one direction & so produce a current, a source of electrical energy is required. The torch battery is a source of electrical energy. The battery is said to have an E.M. ...
pre-AP Electricity
... P.d. potential difference- not exactly, but like voltage. In this course, we will use them interchangeably ...
... P.d. potential difference- not exactly, but like voltage. In this course, we will use them interchangeably ...
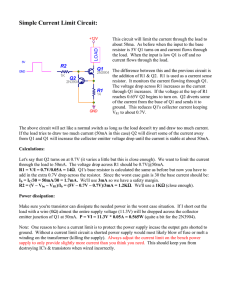
Simple Current Limit Circuit using Transistors
... The above circuit will act like a normal switch as long as the load doesn't try and draw too much current. If the load tries to draw too much current (50mA in this case) Q2 will divert some of the current away from Q1 and Q1 will increase the collector emitter voltage drop until the current is stabl ...
... The above circuit will act like a normal switch as long as the load doesn't try and draw too much current. If the load tries to draw too much current (50mA in this case) Q2 will divert some of the current away from Q1 and Q1 will increase the collector emitter voltage drop until the current is stabl ...
MS Word
... In this problem you are to construct a graphical drawing of the iC – vCE characteristic of the BJT, with base current values of iB = 10 A, 20 A, 30 A, 40 A and 50 A, to estimate amplifier parameters . To simplify the problem we ignore the Early effect ; meaning the output resistance is infinite ...
... In this problem you are to construct a graphical drawing of the iC – vCE characteristic of the BJT, with base current values of iB = 10 A, 20 A, 30 A, 40 A and 50 A, to estimate amplifier parameters . To simplify the problem we ignore the Early effect ; meaning the output resistance is infinite ...
Electricity and Circuits
... Atoms sometimes gain or lose electrons to other atoms. When electrons move from atom to atom a current is produced. Electricity is the movement of electrons from one atom to another. Some atoms hold onto their electrons very tightly. Materials composed of such atoms tend not to let electricity move ...
... Atoms sometimes gain or lose electrons to other atoms. When electrons move from atom to atom a current is produced. Electricity is the movement of electrons from one atom to another. Some atoms hold onto their electrons very tightly. Materials composed of such atoms tend not to let electricity move ...
Kirchhoff`s Laws and Circuit Analysis (EC 2) • Circuit analysis
... Kirchhoff's Laws and Circuit Analysis (EC 2) • Circuit analysis: solving for I and V at each element • Linear circuits: involve resistors, capacitors, inductors • Initial analysis uses only resistors • Power sources, constant voltage and current • Solved using Kirchhoff's Laws (Current and Voltage) ...
... Kirchhoff's Laws and Circuit Analysis (EC 2) • Circuit analysis: solving for I and V at each element • Linear circuits: involve resistors, capacitors, inductors • Initial analysis uses only resistors • Power sources, constant voltage and current • Solved using Kirchhoff's Laws (Current and Voltage) ...
BS7671 Formula and Tips
... Resistance of copper and aluminium conduct Similarly, in order to design circuits for compliance with BS7671 limiting values of earth fault loop impedance given in Tables 41.2 to 41.4, it is necessary to establish the relevant impedance of the circuit conductors concerned at their operating tempera ...
... Resistance of copper and aluminium conduct Similarly, in order to design circuits for compliance with BS7671 limiting values of earth fault loop impedance given in Tables 41.2 to 41.4, it is necessary to establish the relevant impedance of the circuit conductors concerned at their operating tempera ...
Multi-functional Packaged Antennas for Next
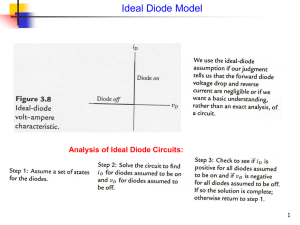
... Only then the voltage appears across the load. In reverse bias, the diode blocks the voltage, i.e. acts as an open circuit. Thus the voltage across the load becomes zero. For ideal diodes, the voltage drop in forward bias is zero. For real diodes the voltage drop is usually few tenths of a volt. The ...
... Only then the voltage appears across the load. In reverse bias, the diode blocks the voltage, i.e. acts as an open circuit. Thus the voltage across the load becomes zero. For ideal diodes, the voltage drop in forward bias is zero. For real diodes the voltage drop is usually few tenths of a volt. The ...
Physics II. :: 2. Electric current
... An ammeter is always placed in series with the resistance or other circuit components through which the current is to be measured. Ammeters should therefore have a low resistance compared with that of the rest of the circuit. An ammeter can be adapted to measure currents larger than its full-scale r ...
... An ammeter is always placed in series with the resistance or other circuit components through which the current is to be measured. Ammeters should therefore have a low resistance compared with that of the rest of the circuit. An ammeter can be adapted to measure currents larger than its full-scale r ...
5.1 Electric potential difference, current and resistance
... • What needs to be done to move a negative charge from the red to ...
... • What needs to be done to move a negative charge from the red to ...
5 - EE@IITM
... radius a carries a charge Q(t), while the outer of radius b carries charge −Q(t). Prove that in this special case, a changing electric field does not lead to a time-varying magnetic field. Hint: Use Ohm’s law, and consider the displacement current. 4) A metal bar of mass m slides frictionlessly on t ...
... radius a carries a charge Q(t), while the outer of radius b carries charge −Q(t). Prove that in this special case, a changing electric field does not lead to a time-varying magnetic field. Hint: Use Ohm’s law, and consider the displacement current. 4) A metal bar of mass m slides frictionlessly on t ...
Series and Parallel Circuits: Comparing Various Parameters J0901
... Method:Using the Multimeter device, I measured the voltage of each individual resistor and the total voltage of both, series & parallel circuit. The values obtained from this measurement, were used to calculate the voltage, current, total resistance using Ohm#s Law and the individual & total power o ...
... Method:Using the Multimeter device, I measured the voltage of each individual resistor and the total voltage of both, series & parallel circuit. The values obtained from this measurement, were used to calculate the voltage, current, total resistance using Ohm#s Law and the individual & total power o ...
Aim: To determine whether the object allocated to you is an Ohmic
... your resistance object. As the value on the power supply is only an estimate you need to be recording the value of the voltmeter in your chart. 4. Increase the voltage to 0.5V and record the current. Use your voltmeter to tell you when you have altered your power supply sufficiently to give you 0.5V ...
... your resistance object. As the value on the power supply is only an estimate you need to be recording the value of the voltmeter in your chart. 4. Increase the voltage to 0.5V and record the current. Use your voltmeter to tell you when you have altered your power supply sufficiently to give you 0.5V ...
Conditions necessary for an electric current
... Conditions necessary for an electric current Electric current through wires is in many ways very similar to water current through pipes. Why does water flow through a pipe? One way of looking at it is in terms of water pressure: water always flows from places of high pressure to places of low pressu ...
... Conditions necessary for an electric current Electric current through wires is in many ways very similar to water current through pipes. Why does water flow through a pipe? One way of looking at it is in terms of water pressure: water always flows from places of high pressure to places of low pressu ...
Parallel and Serial Circuits
... be hard for students to differentiate with clarity. • Units of measurement are varied from Tera to nano. Conversions are needed frequently. • Terminology is dense. Embracing many concepts Polarity, DC/AC, resistance and capacitance. • Distinguishing between electron flow (negative to positive), and ...
... be hard for students to differentiate with clarity. • Units of measurement are varied from Tera to nano. Conversions are needed frequently. • Terminology is dense. Embracing many concepts Polarity, DC/AC, resistance and capacitance. • Distinguishing between electron flow (negative to positive), and ...
Slide 1
... MC_HI(STANBY); MC_LO(LEFT0); MC_LO(LEFT1); MC_LO(RIGHT0); MC_LO(RIGHT1); int speed = 1000; ...
... MC_HI(STANBY); MC_LO(LEFT0); MC_LO(LEFT1); MC_LO(RIGHT0); MC_LO(RIGHT1); int speed = 1000; ...