24.02.2015 - Erwin Sitompul
... Consider positive and negative charges moving horizontally through four different pieces of a conductor. (a) Determine the current (a) and (c) rightward, direction of each piece. (b) and (d) leftward (b) Rank the current from a, b and c tie, d highest to lowest. ...
... Consider positive and negative charges moving horizontally through four different pieces of a conductor. (a) Determine the current (a) and (c) rightward, direction of each piece. (b) and (d) leftward (b) Rank the current from a, b and c tie, d highest to lowest. ...
FML9
... No technical content pages of this document may be reproduced in any form or transmitted by any means without prior permission of ROHM CO.,LTD. The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference only. Up ...
... No technical content pages of this document may be reproduced in any form or transmitted by any means without prior permission of ROHM CO.,LTD. The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference only. Up ...
EE 466: VLSI Design
... QI at x=0=-Cox(VGS-VT0) and the inversion layer charge at the drain end of the channel is expressed as: QI at x=L=-Cox(VGS-VT0-VDS) At the edge of saturation when the drain-to-source voltage reaches saturation (VDS=VDSAT=VGS-VT0) the inversion layer charge at the drain end becomes zero. ...
... QI at x=0=-Cox(VGS-VT0) and the inversion layer charge at the drain end of the channel is expressed as: QI at x=L=-Cox(VGS-VT0-VDS) At the edge of saturation when the drain-to-source voltage reaches saturation (VDS=VDSAT=VGS-VT0) the inversion layer charge at the drain end becomes zero. ...
Series-Parallel Circuits
... Circuit: A conducting path for current from one side of a source of voltage and current -- the positive side of a battery, for example -- to the other -- or the negative side of the same battery in the following example: i. To preface the example: When apply Ohm’s law you often must think of a large ...
... Circuit: A conducting path for current from one side of a source of voltage and current -- the positive side of a battery, for example -- to the other -- or the negative side of the same battery in the following example: i. To preface the example: When apply Ohm’s law you often must think of a large ...
Precision High Side Current Sense Amplifiers
... The LT1999 accurately measures fast switching currents in H-bridge motor controls, switching power supplies, solenoids and battery chargers. It features a –5V to 80V input common mode voltage range, 2MHz bandwidth, less than 1.5mV offset voltage and 0.5% gain error over temperature. With more than 8 ...
... The LT1999 accurately measures fast switching currents in H-bridge motor controls, switching power supplies, solenoids and battery chargers. It features a –5V to 80V input common mode voltage range, 2MHz bandwidth, less than 1.5mV offset voltage and 0.5% gain error over temperature. With more than 8 ...
sdf - Milwaukee School of Engineering
... Consider also using Multisim to simulate and check any of your homework problems – but only after you have solved or attempted to solve them manually. It will be great practice and further help reinforce your understanding of basic circuit principles. ...
... Consider also using Multisim to simulate and check any of your homework problems – but only after you have solved or attempted to solve them manually. It will be great practice and further help reinforce your understanding of basic circuit principles. ...
Chapter 8 Constant Current Sources
... A load connected to a voltage source or its equivalent current Should have same voltage and current for either source ...
... A load connected to a voltage source or its equivalent current Should have same voltage and current for either source ...
chapter 23: electromagnetic induction, ac circuits, and electrical
... completed.” Thus, the final current is given by: I = I 0 ⎛⎜1 − e τ ⎞⎟ , where t = 3τ so that: ...
... completed.” Thus, the final current is given by: I = I 0 ⎛⎜1 − e τ ⎞⎟ , where t = 3τ so that: ...
In this new setup, the current flowing across the Pt100/polysilicon...
... a very stable 10 V voltage (±25 mV) was obtained from a precision REF102 voltage reference (Burr-Brown). A 10 kΩ 0.1% precision resistor was then placed in the current path to force a 1 mA current through the sensing element. Instead of monitoring the passing current, the ground source of the voltag ...
... a very stable 10 V voltage (±25 mV) was obtained from a precision REF102 voltage reference (Burr-Brown). A 10 kΩ 0.1% precision resistor was then placed in the current path to force a 1 mA current through the sensing element. Instead of monitoring the passing current, the ground source of the voltag ...
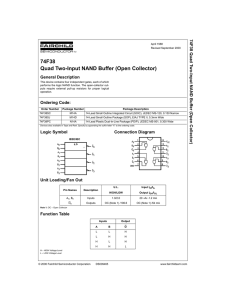
74F38 Quad Two-Input NAND Buffer (Open Collector)
... 14-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300 Wide Package Number N14A ...
... 14-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300 Wide Package Number N14A ...
New P4 P5 P6 Revision
... energy is transferred by the charge flowing through a large resistance than through a small one The current is smallest through the component with the largest resistance, because the same battery voltage causes more current through a smaller resistance than a bigger one ...
... energy is transferred by the charge flowing through a large resistance than through a small one The current is smallest through the component with the largest resistance, because the same battery voltage causes more current through a smaller resistance than a bigger one ...
Chapter 7 Notes
... ohms when the current in it is 2 amperes. What voltage is required to produce this current? ...
... ohms when the current in it is 2 amperes. What voltage is required to produce this current? ...
Second Term Test
... Draw in the diagram to show how to measure the voltage of bulb B. (1 mark) Calculate the total amount of current being drawn from the battery. (1 mark) If bulb B burns out, what happens to bulb A? (1 mark) ...
... Draw in the diagram to show how to measure the voltage of bulb B. (1 mark) Calculate the total amount of current being drawn from the battery. (1 mark) If bulb B burns out, what happens to bulb A? (1 mark) ...
Door-Opening Alarm
... the numbers 05, 12 represent the required output voltage levels. The L78xx series of threeterminal positive regulators is available in TO-220, TO-220FP, TO-3, D2PAK and DPAK packages and several fixed output voltages, making it useful in a wide range of applications. These regulators can provide loc ...
... the numbers 05, 12 represent the required output voltage levels. The L78xx series of threeterminal positive regulators is available in TO-220, TO-220FP, TO-3, D2PAK and DPAK packages and several fixed output voltages, making it useful in a wide range of applications. These regulators can provide loc ...