Distributed Nash Equilibrium Seeking via the Alternating Direction
... in the context of finding an NE of a game. Here are the difficulties that we need to overcome: • A Nash game can be seen as a set of parallel optimization problems, each of them associated with the minimization of a player’s own cost function w.r.t. his variable. However, each optimization problem i ...
... in the context of finding an NE of a game. Here are the difficulties that we need to overcome: • A Nash game can be seen as a set of parallel optimization problems, each of them associated with the minimization of a player’s own cost function w.r.t. his variable. However, each optimization problem i ...
Chapter 12 - Arms-A
... test a positive numeric quantity that is decreased on each recursion, and to provide a stopping case for some small value. In the example write_vertical, the parameter value is the quantity mentioned above, and the "small value" is 10. General Form of a Recursive Function Definition The general outl ...
... test a positive numeric quantity that is decreased on each recursion, and to provide a stopping case for some small value. In the example write_vertical, the parameter value is the quantity mentioned above, and the "small value" is 10. General Form of a Recursive Function Definition The general outl ...
Answers11 - SIUE Computer Science
... Your method need not check that the string is a correct English phrase or word. Embed the method in a program, and test it. Notes: The algorithm for this Project is a bit tricky. The recursive algorithm leads to some inefficiency. For example, the problem statement asks for a method that takes a str ...
... Your method need not check that the string is a correct English phrase or word. Embed the method in a program, and test it. Notes: The algorithm for this Project is a bit tricky. The recursive algorithm leads to some inefficiency. For example, the problem statement asks for a method that takes a str ...
How to Ensure a Faithful Polynomial Evaluation with the
... We first provide an a priori sufficient criterion we summarize as follows. The compensated Horner algorithm provides a faithful rounding of the exact polynomial evaluation as long as its condition number is less than the upper bound we identify in Theorem 7; this bound only depends on the degree of ...
... We first provide an a priori sufficient criterion we summarize as follows. The compensated Horner algorithm provides a faithful rounding of the exact polynomial evaluation as long as its condition number is less than the upper bound we identify in Theorem 7; this bound only depends on the degree of ...
Comparison of Different Approaches to Automated Verification of
... Figure 4: Hyperedge replacement grammar for a list structure represented by a nonterminal L Juggrnaut then produces a state space where every state represents a heap configuration (via a hypergraph), and it is possible to verify properties on this state space using LTL model checking. Definition 1. ...
... Figure 4: Hyperedge replacement grammar for a list structure represented by a nonterminal L Juggrnaut then produces a state space where every state represents a heap configuration (via a hypergraph), and it is possible to verify properties on this state space using LTL model checking. Definition 1. ...
Recursion
... procedure itself. A procedure that goes through recursion is said to be 'recursive'. To understand recursion, one must recognize the distinction between a procedure and the running of a procedure. A procedure is a set of steps that are to be taken based on a set of rules. The running of a procedure ...
... procedure itself. A procedure that goes through recursion is said to be 'recursive'. To understand recursion, one must recognize the distinction between a procedure and the running of a procedure. A procedure is a set of steps that are to be taken based on a set of rules. The running of a procedure ...
Lecture Notes
... our discussion of linked lists from two weeks ago. What is the worst case complexity for appending N items on a linked list? For testing to see if the list contains X? What would be the best case complexity for these operations? If we were going to talk about O() complexity for a list, which of ...
... our discussion of linked lists from two weeks ago. What is the worst case complexity for appending N items on a linked list? For testing to see if the list contains X? What would be the best case complexity for these operations? If we were going to talk about O() complexity for a list, which of ...
A Market-Based Study of Optimal ATM`S Deployment Strategy
... The problem of ATM deployment is seen to be NP-complete problem (it is analogous to the file server placement problem) [3]. In order to solve this problem, three algorithms are designed and compared namely; Heuristic Approach using Convolution (HAC) [4], Rank Based Genetic Algorithm using Convolutio ...
... The problem of ATM deployment is seen to be NP-complete problem (it is analogous to the file server placement problem) [3]. In order to solve this problem, three algorithms are designed and compared namely; Heuristic Approach using Convolution (HAC) [4], Rank Based Genetic Algorithm using Convolutio ...
06_Recursion
... • When a program calls a subrutine, the current module suspends processing and the called subroutine takes over the control of the program. ...
... • When a program calls a subrutine, the current module suspends processing and the called subroutine takes over the control of the program. ...
Thomas L. Magnanti and Georgia Perakis
... then it is easy to see, as in the analysis of Proposition 2.1, that L 1 is scale invariant. The algorithms that we present in this paper compute an e-near optimal solution in a polynomial number of iterations (in terms of n and L 1 ). For notational convenience, in our analysis we use Definition 8. ...
... then it is easy to see, as in the analysis of Proposition 2.1, that L 1 is scale invariant. The algorithms that we present in this paper compute an e-near optimal solution in a polynomial number of iterations (in terms of n and L 1 ). For notational convenience, in our analysis we use Definition 8. ...
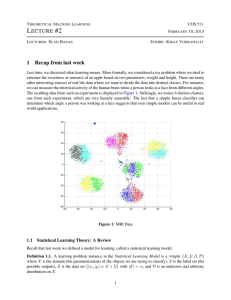
L #2 1 Recap from last week
... Definition 1.5. The generalization error errD (h) = Pr(x,y)∼D {h(x) 6= y} is the error the classifier h makes on all possible inputs according to the unknown distribution D. Typically, errD (h) should be chosen to have a low error on the sample set. To that effect, we define hERM : Definition 1.6. T ...
... Definition 1.5. The generalization error errD (h) = Pr(x,y)∼D {h(x) 6= y} is the error the classifier h makes on all possible inputs according to the unknown distribution D. Typically, errD (h) should be chosen to have a low error on the sample set. To that effect, we define hERM : Definition 1.6. T ...