Emergent properties of coupled human-environment sy
... subsystem recovers while the environmental subsystem does not. This may reflect the inherent fact that humans are more dependent on the environment than the environment is dependent on humans. Jim Heffernan and the Cambridge Group Students Jim and the Cambridge Students brought forth three main que ...
... subsystem recovers while the environmental subsystem does not. This may reflect the inherent fact that humans are more dependent on the environment than the environment is dependent on humans. Jim Heffernan and the Cambridge Group Students Jim and the Cambridge Students brought forth three main que ...
5.1.3 Net Price and User Cost Applications
... prescription (see Section 4). While a welfare emphasis may stress efficient resource use, an explicit focus on sustainability might require us to account for whether or not reductions in natural capital are being made up for by increases in other forms of capital by the reinvestment of resource rent ...
... prescription (see Section 4). While a welfare emphasis may stress efficient resource use, an explicit focus on sustainability might require us to account for whether or not reductions in natural capital are being made up for by increases in other forms of capital by the reinvestment of resource rent ...
PDF
... prescription (see Section 4). While a welfare emphasis may stress efficient resource use, an explicit focus on sustainability might require us to account for whether or not reductions in natural capital are being made up for by increases in other forms of capital by the reinvestment of resource rent ...
... prescription (see Section 4). While a welfare emphasis may stress efficient resource use, an explicit focus on sustainability might require us to account for whether or not reductions in natural capital are being made up for by increases in other forms of capital by the reinvestment of resource rent ...
Characterizing sustainability: The converse of Hartwick`s rule
... In a one consumption good economy endowed with two stocks — a stock of an exhaustible non-renewable resource and a stock of man-made capital — Hartwick’s rule means that if the accumulation of man-made capital always exactly compensates in value for the resource depletion, then consumption remains c ...
... In a one consumption good economy endowed with two stocks — a stock of an exhaustible non-renewable resource and a stock of man-made capital — Hartwick’s rule means that if the accumulation of man-made capital always exactly compensates in value for the resource depletion, then consumption remains c ...
chapter 3 review of literature on natural resource accounting
... Economists worldwide do not ascribe to one single theory of capital growth (Victor, 1991). There are two main components of sustainability differing in their treatment of the substitutability relationship between manufactured and natural capital: weak and strong sustainability. (De Groot et al., 200 ...
... Economists worldwide do not ascribe to one single theory of capital growth (Victor, 1991). There are two main components of sustainability differing in their treatment of the substitutability relationship between manufactured and natural capital: weak and strong sustainability. (De Groot et al., 200 ...
View/Open
... covers four different environmental functions, from which two are directly connected to production process. The first is the supply of resources required for production, that is, raw materials that are used for producing food, fuel, etc. The second is the absorption of waste produced during producti ...
... covers four different environmental functions, from which two are directly connected to production process. The first is the supply of resources required for production, that is, raw materials that are used for producing food, fuel, etc. The second is the absorption of waste produced during producti ...
Sustainability: Virtuous or Vulgar?
... possible harvestable surplus of ungulates. That is, population health is defined in terms of human needs or desires. However, other reasonable notions for population health of an ungulate population entail “more natural” conditions, such as balanced sex ratios, age structures, and abundances that ar ...
... possible harvestable surplus of ungulates. That is, population health is defined in terms of human needs or desires. However, other reasonable notions for population health of an ungulate population entail “more natural” conditions, such as balanced sex ratios, age structures, and abundances that ar ...
Canton of Berne Sustainability Compass
... According to the Swiss definition a distinction is made between three equally important dimensions of sustainable development, namely the ecologic, the economic and the social dimension. In addition the principle of fairness within one generation and towards future generations (intragenerational and ...
... According to the Swiss definition a distinction is made between three equally important dimensions of sustainable development, namely the ecologic, the economic and the social dimension. In addition the principle of fairness within one generation and towards future generations (intragenerational and ...
Economic analysis of sustainability.
... In the contributions included in this book I (and my co-authors) limit the discussion by considering sustainability to be a requirement for inter generational justice. The included articles present models where an infinite number of generations follows in sequence, and where distributional issues wi ...
... In the contributions included in this book I (and my co-authors) limit the discussion by considering sustainability to be a requirement for inter generational justice. The included articles present models where an infinite number of generations follows in sequence, and where distributional issues wi ...
PDF
... Points out that sustainability as such does not provide a clearcut guide to policy. First one has to decide what is to be sustained. If this is agreed, it must be in an operational from. However, difficulties may still emerge since opinions may differ about how to achieve. This is illustrated by dif ...
... Points out that sustainability as such does not provide a clearcut guide to policy. First one has to decide what is to be sustained. If this is agreed, it must be in an operational from. However, difficulties may still emerge since opinions may differ about how to achieve. This is illustrated by dif ...
Economic sustainability of the economy: concepts and
... comparability as there is simply no functional equivalent for water, communication or decision making in these disciplines; see e.g., Ehrlich et al., 1999). Thus they seem to be more characteristic for the challenge that sustainability poses to economics than the economic challenges of sustainable d ...
... comparability as there is simply no functional equivalent for water, communication or decision making in these disciplines; see e.g., Ehrlich et al., 1999). Thus they seem to be more characteristic for the challenge that sustainability poses to economics than the economic challenges of sustainable d ...
natural values - Ducks Unlimited Canada
... Natural Values: Linking the Environment to the Economy was developed to improve the environmental and economic understanding of natural systems. In Canada, policy, legislation and regulation efforts must accelerate to protect Canada’s important resources. To view other installments in this series, v ...
... Natural Values: Linking the Environment to the Economy was developed to improve the environmental and economic understanding of natural systems. In Canada, policy, legislation and regulation efforts must accelerate to protect Canada’s important resources. To view other installments in this series, v ...
Document
... controversial topic within the discipline. Economy is based on utility and this utility comes with the consumption. However, as it occurs in all social science, there is a return in economics, return maybe the ancient understanding of interrelatedness of all branches of science. For instance, econom ...
... controversial topic within the discipline. Economy is based on utility and this utility comes with the consumption. However, as it occurs in all social science, there is a return in economics, return maybe the ancient understanding of interrelatedness of all branches of science. For instance, econom ...
Natural Resources, Eonomic Growth and Sustainability
... study by the Club of Rome examined a global economy dependent upon a nonrenewable resource and damaged by the accumulation of pollution. It found rather dire outcomes –overexpansion and collapse of the economy – if economic and population growth were not significantly curtailed. The two oil crises i ...
... study by the Club of Rome examined a global economy dependent upon a nonrenewable resource and damaged by the accumulation of pollution. It found rather dire outcomes –overexpansion and collapse of the economy – if economic and population growth were not significantly curtailed. The two oil crises i ...
Ecological Economics
... resources using systems of property rights and transfers. . ……… Third, once the scale and distribution problems are solved, market-based mechanisms can be used to allocate resources efficiently. ...
... resources using systems of property rights and transfers. . ……… Third, once the scale and distribution problems are solved, market-based mechanisms can be used to allocate resources efficiently. ...
Chapter 6 The Forms of Capital
... ** Academic ability/talent is itself the product of an investment of time and cultural capital ** Scholastic yield from education cultural capital invested by family mobilized by Social Capital ...
... ** Academic ability/talent is itself the product of an investment of time and cultural capital ** Scholastic yield from education cultural capital invested by family mobilized by Social Capital ...
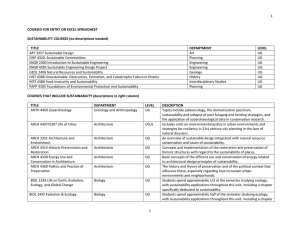
courses for entry on excel spreadheet
... relationships between humans and the environment. This includes a focus on how the spatial organization of human activities (e.g., urbanization, global trade, agriculture, governance) influences the ways in which sustainability is practiced and policies of sustainable development are constructed. Gl ...
... relationships between humans and the environment. This includes a focus on how the spatial organization of human activities (e.g., urbanization, global trade, agriculture, governance) influences the ways in which sustainability is practiced and policies of sustainable development are constructed. Gl ...
12 Resources & Natural Capital
... What caused the collapse Decades of unsustainable harvest Magnuson Act of 1976 supported unprecedented growth of the fishing fleet 570 boats to 900 Bigger boats with more technology to catch fish ...
... What caused the collapse Decades of unsustainable harvest Magnuson Act of 1976 supported unprecedented growth of the fishing fleet 570 boats to 900 Bigger boats with more technology to catch fish ...
Sustainable Development: Between Moral Injunctions and Natural
... notion of development during the past century, in such a way that today the adjective ―sustainable‖ is almost always associated with it, referring to the promotion of economic growth that takes account of its environmental and social impacts on both present and future generations. In Section 3, we s ...
... notion of development during the past century, in such a way that today the adjective ―sustainable‖ is almost always associated with it, referring to the promotion of economic growth that takes account of its environmental and social impacts on both present and future generations. In Section 3, we s ...
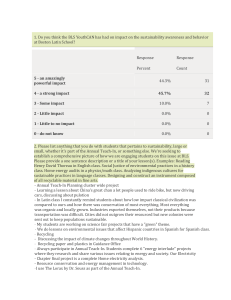
Education_files/Results BLS Teacher Survey
... compared to ours and how there was conservation of most everything. Most everything was organic and locally grown. Industries exported themselves, not their products because transportation was difficult. Cities did not outgrow their resourced but new colonies were sent out to keep populations sustai ...
... compared to ours and how there was conservation of most everything. Most everything was organic and locally grown. Industries exported themselves, not their products because transportation was difficult. Cities did not outgrow their resourced but new colonies were sent out to keep populations sustai ...
growth, development and sustainability
... (Turner R.K., p. 11). That is, the VS continues to permit the substitution of one form of capital with another in order to allow at least maintaining the overall value of the total capital, but this substitutability is not the most perfect, recognizing that it is actually possible only within certai ...
... (Turner R.K., p. 11). That is, the VS continues to permit the substitution of one form of capital with another in order to allow at least maintaining the overall value of the total capital, but this substitutability is not the most perfect, recognizing that it is actually possible only within certai ...
paper or powerpoint - University of Denver
... • The Correlation between the 2001 ESI and the EcoDeficit of Wackernagel is not significant (R2 = 0.03) • The 2001 ESI incorporates more cultural and Institutional elements of sustainability along the lines of those described by Courtland Smith in a critique of the I=P*A*T formulation. And is conseq ...
... • The Correlation between the 2001 ESI and the EcoDeficit of Wackernagel is not significant (R2 = 0.03) • The 2001 ESI incorporates more cultural and Institutional elements of sustainability along the lines of those described by Courtland Smith in a critique of the I=P*A*T formulation. And is conseq ...
PPT Resources and Natural Capital
... What caused the collapse Decades of unsustainable harvest Magnuson Act of 1976 supported unprecedented growth of the fishing fleet 570 boats to 900 Bigger boats with more technology to catch fish ...
... What caused the collapse Decades of unsustainable harvest Magnuson Act of 1976 supported unprecedented growth of the fishing fleet 570 boats to 900 Bigger boats with more technology to catch fish ...
Strong Sustainability
... δKm - Depreciation of manufactured capital δKn - Depreciation of natural capital (resource depletion + environmental degradation) Sustainable Energy Systems ...
... δKm - Depreciation of manufactured capital δKn - Depreciation of natural capital (resource depletion + environmental degradation) Sustainable Energy Systems ...