Viscosity
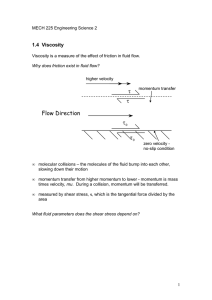
... is the flow velocity, and y is the distance from the plate, across the flow. Near the surface, the rate of change of velocity is high, but further away from the plate the velocity changes more slowly, and may become constant, so du/dy gets smaller. The shear stress is proportional to the rate of cha ...
... is the flow velocity, and y is the distance from the plate, across the flow. Near the surface, the rate of change of velocity is high, but further away from the plate the velocity changes more slowly, and may become constant, so du/dy gets smaller. The shear stress is proportional to the rate of cha ...
Study of shear thinning and shear thickening in 2D fluids
... stress is also close to zero, such fluids are called Newtonian fluids. In other words, once the temperature and density of the fluid is fixed, the viscosity of the fluid does not dependent on how fast or slow the fluid is made to flow. However, there exists a class of fluids called Complex Fluids wh ...
... stress is also close to zero, such fluids are called Newtonian fluids. In other words, once the temperature and density of the fluid is fixed, the viscosity of the fluid does not dependent on how fast or slow the fluid is made to flow. However, there exists a class of fluids called Complex Fluids wh ...
Stokes Polarimetry - Hinds Instruments
... With a PEM, there are at least two ways of accomplishing this. The first method is to provide a means of rotating the entire polarimeter apparatus (Figure 2) through 45 degrees. A measurement in each of the two positions must be made. This is an acceptable and straightforward method provided that th ...
... With a PEM, there are at least two ways of accomplishing this. The first method is to provide a means of rotating the entire polarimeter apparatus (Figure 2) through 45 degrees. A measurement in each of the two positions must be made. This is an acceptable and straightforward method provided that th ...
Viscosity Measurement - Northern Illinois University
... are controlled to some degree by fluid viscosity. Viscosity is defined as the internal friction of a fluid. The microscopic nature of internal friction in a fluid is analogous to the macroscopic concept of mechanical friction in the system of an object moving on a stationary planar surface. Energy m ...
... are controlled to some degree by fluid viscosity. Viscosity is defined as the internal friction of a fluid. The microscopic nature of internal friction in a fluid is analogous to the macroscopic concept of mechanical friction in the system of an object moving on a stationary planar surface. Energy m ...
MOVING BUBBLES, DROPS, AND OTHER FLUID BLOBS
... volumes, except for the miscible cases that are unsteady for all volumes. The initial conditions of the experiment consist of only two fluids and a blob volume. We might expect that such fluid fields could be explained quantitatively with a very few characteristic non-dimensional numbers; attempts t ...
... volumes, except for the miscible cases that are unsteady for all volumes. The initial conditions of the experiment consist of only two fluids and a blob volume. We might expect that such fluid fields could be explained quantitatively with a very few characteristic non-dimensional numbers; attempts t ...
Cone-Plate Viscometer
... above; however, the torque is still proportional to angular velocity. Hence provided calibration is performed, the end effects will not cause error. ...
... above; however, the torque is still proportional to angular velocity. Hence provided calibration is performed, the end effects will not cause error. ...
8. Gauss` and Stokes` Theorems
... This is called the integral form of Gauss’ law and it shows how the electric field on the surface of any region is related to the charge contained in that region. Let us apply (8.5) to the boxshaped region R with surface S shown in Fig. 8.7. Suppose that the bottom and top of the box have area A and ...
... This is called the integral form of Gauss’ law and it shows how the electric field on the surface of any region is related to the charge contained in that region. Let us apply (8.5) to the boxshaped region R with surface S shown in Fig. 8.7. Suppose that the bottom and top of the box have area A and ...
Fluid Dynamics
... So far, we have considered ideal fluids: • They coast along with no difference in pressure • An ideal milk shake would be as easy to drink as a watery soda ...
... So far, we have considered ideal fluids: • They coast along with no difference in pressure • An ideal milk shake would be as easy to drink as a watery soda ...
Jamie Kohl
... nature. After gravity comes mirrors. A mirror is a device whose surface has good specular reflection. Specular reflection is the perfect mirror-like reflection of light. The most familiar type of mirror is the plane mirror, which has a flat surface. Curved mirrors are also used to produce magnified ...
... nature. After gravity comes mirrors. A mirror is a device whose surface has good specular reflection. Specular reflection is the perfect mirror-like reflection of light. The most familiar type of mirror is the plane mirror, which has a flat surface. Curved mirrors are also used to produce magnified ...
ENIAC`s Problem 1 Discussion
... Immediately following the war, computers were quietly built for code breaking and publicly built for nuclear weapon calculations. The business world (and hence IBM) was initially not much interested in duplicating the expensive, fragile, one-of-a-kind computers that were the immediate descendants of ...
... Immediately following the war, computers were quietly built for code breaking and publicly built for nuclear weapon calculations. The business world (and hence IBM) was initially not much interested in duplicating the expensive, fragile, one-of-a-kind computers that were the immediate descendants of ...
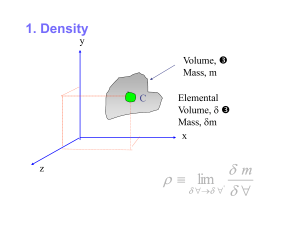
fluid_pr
... In some sense measures fluidity of a fluid. Actually it is the resistance offered by a layer of fluid to the motion of an adjacent one. Consider the two-plate experiment. In case of a fluid in between them, we know that the upper plate moves with a speed U whereas the lower plate does not move. This ...
... In some sense measures fluidity of a fluid. Actually it is the resistance offered by a layer of fluid to the motion of an adjacent one. Consider the two-plate experiment. In case of a fluid in between them, we know that the upper plate moves with a speed U whereas the lower plate does not move. This ...
Boundary induced streaming
... The efficiency compares well with other known strategies. But … are the required frequencies biologically feasible? ...
... The efficiency compares well with other known strategies. But … are the required frequencies biologically feasible? ...
Lines of Force
... We should thus obtain a geometrical model of the physical phenomena, which would tell us the direction of the force, but we should still require some method of indicating the intensity of the force at ...
... We should thus obtain a geometrical model of the physical phenomena, which would tell us the direction of the force, but we should still require some method of indicating the intensity of the force at ...
Motion with Air Resistance
... tendency of a fluid to resist shearing stresses. It is often denoted by the Greek letter η (eta). In a few simple cases, the value of α can be computed analytically. For example, in the case of a sphere of radius r moving slowly through a fluid, it can be shown that fdiss = 6πrηv . Usually, however, ...
... tendency of a fluid to resist shearing stresses. It is often denoted by the Greek letter η (eta). In a few simple cases, the value of α can be computed analytically. For example, in the case of a sphere of radius r moving slowly through a fluid, it can be shown that fdiss = 6πrηv . Usually, however, ...
Interaction of light with gravitational waves
... subject started with Plebanski’s article on the scattering of electromagnetic waves by weak gravitational fields [4]. Electromagnetic waves in the field of a gravitational wave were studied by Mashhoon and Grishchuk [5] in a general context. Exact but purely formal solutions of Einstein’s equations ...
... subject started with Plebanski’s article on the scattering of electromagnetic waves by weak gravitational fields [4]. Electromagnetic waves in the field of a gravitational wave were studied by Mashhoon and Grishchuk [5] in a general context. Exact but purely formal solutions of Einstein’s equations ...
Chap-7
... Raman scattering is a two-photon linear inelastic light scattering process. The elastic counterpart is the well-known Rayleigh scattering process. In spontaneous Raman scattering the light is emitted in random directions (although for polarized light there may be preferred directions, depending also ...
... Raman scattering is a two-photon linear inelastic light scattering process. The elastic counterpart is the well-known Rayleigh scattering process. In spontaneous Raman scattering the light is emitted in random directions (although for polarized light there may be preferred directions, depending also ...
Millikan Oil Drop Experiment
... are all contained in one unit. A small video camera has been attached to the microscope to allow recording of videos of the drops’ motion to the computer. The “Grabbee” software or Windows Video Maker can be used to make such recordings. The videos can then be analyzed using Movie Maker or ImageJ. N ...
... are all contained in one unit. A small video camera has been attached to the microscope to allow recording of videos of the drops’ motion to the computer. The “Grabbee” software or Windows Video Maker can be used to make such recordings. The videos can then be analyzed using Movie Maker or ImageJ. N ...
Lithography - Chemical Engineering IIT Madras
... Light from 200 to 800 nm (Deuterium and W or Halogen lamps) Reflected light intensity vs wavelength detected Film stack quality must be known Not as accurate as ellipsometery Also cannot be used (accurately) to determine refractive index real and imaginary quantities Refractive index, ...
... Light from 200 to 800 nm (Deuterium and W or Halogen lamps) Reflected light intensity vs wavelength detected Film stack quality must be known Not as accurate as ellipsometery Also cannot be used (accurately) to determine refractive index real and imaginary quantities Refractive index, ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2014 Semester Lecture 39 – Review
... (b) Calculate the intensity of transmitted light if the incident light is unpolarized (c) Calculate the intensity of transmitted light if the incident light is left circular polarized (d) Is the system symmetric? That is, is the intensity of transmitted light the same if the paths of all light rays ...
... (b) Calculate the intensity of transmitted light if the incident light is unpolarized (c) Calculate the intensity of transmitted light if the incident light is left circular polarized (d) Is the system symmetric? That is, is the intensity of transmitted light the same if the paths of all light rays ...
Adjusting the Brillouin spectrum in optical fibers for slow and fast
... If the bandwidth of the gain is narrow the time delay is high but the pulses experience a strong distortion which leads to a broadening. The natural Brillouin bandwidth would result in data rates which could be delayed of only 15Mbit/s. To enhance the bandwidth the gain can be broadened by a direct ...
... If the bandwidth of the gain is narrow the time delay is high but the pulses experience a strong distortion which leads to a broadening. The natural Brillouin bandwidth would result in data rates which could be delayed of only 15Mbit/s. To enhance the bandwidth the gain can be broadened by a direct ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2014 Semester
... • What is the polarization state of light that initially had right-circular polarization but passed through a horizontal polarizer? ...
... • What is the polarization state of light that initially had right-circular polarization but passed through a horizontal polarizer? ...
Stokes` Theorem
... Oriented surface with unit normal vector n. The orientation of S induces the positive orientation of the boundary curve C. If you walk in the positive direction around C with your head pointing in the direction of n, the surface will always be on your left. ...
... Oriented surface with unit normal vector n. The orientation of S induces the positive orientation of the boundary curve C. If you walk in the positive direction around C with your head pointing in the direction of n, the surface will always be on your left. ...
WHY IS AN EINSTEIN RING BLUE? Jonathan Blackledge Stokes Professorship: Annual
... ‘high frequency (space-time) wavefields’ (matter waves) of the other. ...
... ‘high frequency (space-time) wavefields’ (matter waves) of the other. ...
Sir George Stokes, 1st Baronet

Sir George Gabriel Stokes, 1st Baronet, PRS (/stoʊks/; 13 August 1819 – 1 February 1903), was a mathematician, physicist, politician and theologian. Born in Ireland, Stokes spent all of his career at University of Cambridge, where he served as the Lucasian Professor of Mathematics from 1849 until his death in 1903. Stokes made seminal contributions to fluid dynamics (including the Navier–Stokes equations), optics, and mathematical physics (including the first version of what is now known as Stokes' theorem). He was secretary, then president, of the Royal Society.