kernel-intro
... File System: Inode List • Inodes are used to access disk files. • Inodes maps the disk files • For each file there is an inode entry in the inode list block • Inode list also keeps track of directory structure ...
... File System: Inode List • Inodes are used to access disk files. • Inodes maps the disk files • For each file there is an inode entry in the inode list block • Inode list also keeps track of directory structure ...
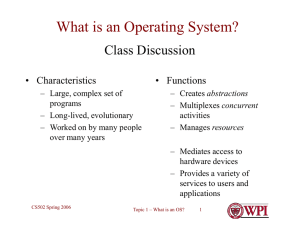
What is an Operating System
... sharing: how are resources shared across users? naming: how are resources named (by users or programs)? security: how is the integrity of the OS and its resources ensured? protection: how is one user/program protected from another? performance: how do we make it all go fast? reliability: what happen ...
... sharing: how are resources shared across users? naming: how are resources named (by users or programs)? security: how is the integrity of the OS and its resources ensured? protection: how is one user/program protected from another? performance: how do we make it all go fast? reliability: what happen ...
Operating Systems - Cardiff University
... – CPU operations take less time than I/O – When a process waits for I/O operation, OS swaps to another process. ...
... – CPU operations take less time than I/O – When a process waits for I/O operation, OS swaps to another process. ...
Chapter 2: Introduction to the Kernel
... File System: Inode List • Inodes are used to access disk files. • Inodes maps the disk files • For each file there is an inode entry in the inode list block • Inode list also keeps track of directory structure ...
... File System: Inode List • Inodes are used to access disk files. • Inodes maps the disk files • For each file there is an inode entry in the inode list block • Inode list also keeps track of directory structure ...
A Five-State Process Model (Review) The not
... Preempted means process was returning to user mode, but the kernel switched to another process instead ...
... Preempted means process was returning to user mode, but the kernel switched to another process instead ...
Cindy - Anatomy of a Window
... Computers can execute only one instruction at a time per processor or CPU The OS controls the order in which tasks or jobs are processed The OS acts as an intermediary between application software and physical hardware The OS uses device drivers to manage hardware devices ...
... Computers can execute only one instruction at a time per processor or CPU The OS controls the order in which tasks or jobs are processed The OS acts as an intermediary between application software and physical hardware The OS uses device drivers to manage hardware devices ...
Al- Balqa Applied University Al-huson University College Dept. of
... A) kernel is the program that constitutes the central core of the operating system B) kernel is the first part of operating system to load into memory during booting C) kernel is made of various modules which can not be loaded in running operating system D) kernel remains in the memory during the en ...
... A) kernel is the program that constitutes the central core of the operating system B) kernel is the first part of operating system to load into memory during booting C) kernel is made of various modules which can not be loaded in running operating system D) kernel remains in the memory during the en ...
Operating System
... • Load registers/ variables with arguments • TRAP instruction • Generates an interrupt • Automatic switch to kernel mode • Arguments tell OS what to do • Afterwards • “return” as from a function call • Force return to user mode ...
... • Load registers/ variables with arguments • TRAP instruction • Generates an interrupt • Automatic switch to kernel mode • Arguments tell OS what to do • Afterwards • “return” as from a function call • Force return to user mode ...
bt0070 - SMU Assignments
... Q1. What is an Operating System? Explain the functions of OS. Answer: Answer: Operating System is a System Software (Set of system programs) which provides an environment to help the user to execute the programs. An operating system (OS) is a software program that manages the hardware and software r ...
... Q1. What is an Operating System? Explain the functions of OS. Answer: Answer: Operating System is a System Software (Set of system programs) which provides an environment to help the user to execute the programs. An operating system (OS) is a software program that manages the hardware and software r ...
Page table
... Some implement user-level operating systems Some implement services crucial to all userlevel operating systems ...
... Some implement user-level operating systems Some implement services crucial to all userlevel operating systems ...
Greetings Hnoagain. D. O'Dell
... describes a software system designed to support building sophisticated, distributed applications in a network environment. The urgent need for such tools is, I believe, evidenced by the scarcity of large distributed software applications in spite of there being no shortage of large problems needing ...
... describes a software system designed to support building sophisticated, distributed applications in a network environment. The urgent need for such tools is, I believe, evidenced by the scarcity of large distributed software applications in spite of there being no shortage of large problems needing ...
2140702
... 7. Write a menu driven shell script which will print the following menu and execute the given task. 8. MENU 9. Display calendar of current month 10. Display today’s date and time 11. Display usernames those are currently logged in the system 12. Display your name at given x, y position 13. Display y ...
... 7. Write a menu driven shell script which will print the following menu and execute the given task. 8. MENU 9. Display calendar of current month 10. Display today’s date and time 11. Display usernames those are currently logged in the system 12. Display your name at given x, y position 13. Display y ...
Operating System
... interactive jobs • Processor’s time is shared among multiple users • Multiple users simultaneously access the system through terminals ...
... interactive jobs • Processor’s time is shared among multiple users • Multiple users simultaneously access the system through terminals ...
Unix Basics - Computer Science
... Multi-programmed: OS runs multiple processes simultaneously Process: running program Timeshared: multiple users share the system simultaneously ...
... Multi-programmed: OS runs multiple processes simultaneously Process: running program Timeshared: multiple users share the system simultaneously ...
KernelSec: An Authorization Model in the Operating System Kernel
... is a reflection of the set of actions that the process is allowed to perform. Traditionally, the set of privileges primarily depends on the user running the process The disadvantage is that all the processes of a user are executed with the entire set of user privileges. In KernelSec, the enforcement ...
... is a reflection of the set of actions that the process is allowed to perform. Traditionally, the set of privileges primarily depends on the user running the process The disadvantage is that all the processes of a user are executed with the entire set of user privileges. In KernelSec, the enforcement ...
What is an operating system? - KOVAN Research Lab
... System-call interface maintains a table indexed according to these numbers The system call interface invokes intended system call in OS kernel and returns status of the system call and any return values The caller need know nothing about how the system call is implemented Just needs to obey API and ...
... System-call interface maintains a table indexed according to these numbers The system call interface invokes intended system call in OS kernel and returns status of the system call and any return values The caller need know nothing about how the system call is implemented Just needs to obey API and ...
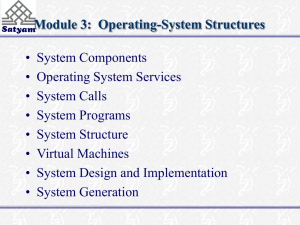
Module 3: Operating-System Structures
... volatile and too small to accommodate all data and programs permanently, the computer system must provide secondary storage to back up main memory. • Most modern computer systems use disks as the principle on-line storage medium, for both programs and data. • The operating system is responsible for ...
... volatile and too small to accommodate all data and programs permanently, the computer system must provide secondary storage to back up main memory. • Most modern computer systems use disks as the principle on-line storage medium, for both programs and data. • The operating system is responsible for ...
Operating System
... System Calls • A System Call is used by a process to request a service from the OS • Typical system calls – Open/read/write/close the file – Get the current time ...
... System Calls • A System Call is used by a process to request a service from the OS • Typical system calls – Open/read/write/close the file – Get the current time ...
CUSTOMER_CODE SMUDE DIVISION_CODE SMUDE
... applications. The user has access to the libraries and to the applications. These two components are what many users think of as UNIX, because together they constitute the UNIX interface. The part of UNIX that manages the hardware and the executing processes is called the kernel. In managing all har ...
... applications. The user has access to the libraries and to the applications. These two components are what many users think of as UNIX, because together they constitute the UNIX interface. The part of UNIX that manages the hardware and the executing processes is called the kernel. In managing all har ...
system programs
... reliably on common PC hardware, but also runs on a variety of other platforms. The core Linux operating-system kernel is entirely original, but it can run much existing free Unix software, resulting in an entire Unix-compatible operating system free from proprietary code. ...
... reliably on common PC hardware, but also runs on a variety of other platforms. The core Linux operating-system kernel is entirely original, but it can run much existing free Unix software, resulting in an entire Unix-compatible operating system free from proprietary code. ...
Module 3: Operating
... directly, the operating system must provide some means to perform I/O. • File-system manipulation – program capability to read, write, create, and delete files. • Communications – exchange of information between processes executing either on the same computer or on different systems tied together by ...
... directly, the operating system must provide some means to perform I/O. • File-system manipulation – program capability to read, write, create, and delete files. • Communications – exchange of information between processes executing either on the same computer or on different systems tied together by ...
Agenda - Seneca - School of Information & Communications
... The Unix OS was developed (based on Multics & CTSS operating systems) by Ken Thompson at the AT&T Bell Laboratories in 1969. He wanted to create an multi-user operating system to run “space wars” game. Ken’s philosophy was to create an operating system with commands or “utilities” that would do one ...
... The Unix OS was developed (based on Multics & CTSS operating systems) by Ken Thompson at the AT&T Bell Laboratories in 1969. He wanted to create an multi-user operating system to run “space wars” game. Ken’s philosophy was to create an operating system with commands or “utilities” that would do one ...
Slides 2 - USC Upstate: Faculty
... – Convenience: system calls are more difficult to work with than the API » Most programming languages provide a system call interface. The application programmers need to know nothing about how the system call is implemented or what it does during execution. ...
... – Convenience: system calls are more difficult to work with than the API » Most programming languages provide a system call interface. The application programmers need to know nothing about how the system call is implemented or what it does during execution. ...
slides - network systems lab @ sfu
... Performs diagnostic tests (Power-on Self Testing) Loads a small piece of code from a fixed location (block 0) on the disk into memory, which loads the rest of the loader from disk, which loads kernel itself ...
... Performs diagnostic tests (Power-on Self Testing) Loads a small piece of code from a fixed location (block 0) on the disk into memory, which loads the rest of the loader from disk, which loads kernel itself ...
History of Unix OS - Seneca
... The Unix OS was developed (based on Multics & CTSS operating systems) by Ken Thompson at the AT&T Bell Laboratories in 1969. He wanted to create an multi-user operating system to run “space wars” game. Ken’s philosophy was to create an operating system with commands or “utilities” that would do one ...
... The Unix OS was developed (based on Multics & CTSS operating systems) by Ken Thompson at the AT&T Bell Laboratories in 1969. He wanted to create an multi-user operating system to run “space wars” game. Ken’s philosophy was to create an operating system with commands or “utilities” that would do one ...