File System Maintenance (continued)
... Installation • Software Installation checklist – provided on pages 518 and 519 ...
... Installation • Software Installation checklist – provided on pages 518 and 519 ...
I/O Systems & Mass-Storage Structure
... Performance depends on the number and types of requests. Requests for disk service can be influenced by the fileallocation method. The disk-scheduling algorithm should be written as a separate module of the operating system, allowing it to be replaced with a different algorithm if necessary. Either ...
... Performance depends on the number and types of requests. Requests for disk service can be influenced by the fileallocation method. The disk-scheduling algorithm should be written as a separate module of the operating system, allowing it to be replaced with a different algorithm if necessary. Either ...
OperatingSystemDesign_SP16_Ch_1_4
... Download PuTTY PuTTY is an SSH and telnet client, developed originally by Simon Tatham for the Windows platform. PuTTY is open source software that is available with source code and is developed and supported by a group of volunteers. You can download PuTTY here. ...
... Download PuTTY PuTTY is an SSH and telnet client, developed originally by Simon Tatham for the Windows platform. PuTTY is open source software that is available with source code and is developed and supported by a group of volunteers. You can download PuTTY here. ...
Adopting and Commenting the Old Kernel Source Code for Education
... first read into the cache area from the block device. When a task needs to output the data to a block device, the data is put into the cache area first and then is written into the block device by the hardware driver in due time. The last part of the physical memory is the main area used dynamically ...
... first read into the cache area from the block device. When a task needs to output the data to a block device, the data is put into the cache area first and then is written into the block device by the hardware driver in due time. The last part of the physical memory is the main area used dynamically ...
The Case for VOS: The Vector Operating System Abstract Carnegie Mellon University,
... 1. Application-agnostic changes: One way to provide opportunities for making vector calls without application support is to introduce system call queues to coalesce similar requests. An application issues a system call through libc, which inserts the call into a syscall queue while the application w ...
... 1. Application-agnostic changes: One way to provide opportunities for making vector calls without application support is to introduce system call queues to coalesce similar requests. An application issues a system call through libc, which inserts the call into a syscall queue while the application w ...
L4_L6_System_Structu..
... Resource allocation - When multiple users or multiple jobs running concurrently, resources must be allocated to each of them ...
... Resource allocation - When multiple users or multiple jobs running concurrently, resources must be allocated to each of them ...
Process Migration in Distributed Systems
... postpone state transfer until page faults occur (e.g. Accent). This type of implementation incurs run-time penalty only. Other possibilities that go between the two extremes (e.g. Sprite) incur both initial and run-time cost. Runtime cost can also be appeared as a consequence of residual dependencie ...
... postpone state transfer until page faults occur (e.g. Accent). This type of implementation incurs run-time penalty only. Other possibilities that go between the two extremes (e.g. Sprite) incur both initial and run-time cost. Runtime cost can also be appeared as a consequence of residual dependencie ...
Self-Assessment Interactive Topic 1
... _ Medium-term - used especially with time-sharing systems as an intermediate scheduling level. A swapping scheme is implemented to remove partially run programs from memory and reinstate them later to continue where they left off. _ Long-term (job scheduler) - determines which jobs are brought into ...
... _ Medium-term - used especially with time-sharing systems as an intermediate scheduling level. A swapping scheme is implemented to remove partially run programs from memory and reinstate them later to continue where they left off. _ Long-term (job scheduler) - determines which jobs are brought into ...
Figure 15.1 A distributed multimedia system
... • Programs can manage threads in groups. It is useful when several applications coexist on the same JVM. In the example of security, one group is not allowed to access the methods in other group. Thread groups facilitate control of the relative priorities of threads. This is useful for browsers ...
... • Programs can manage threads in groups. It is useful when several applications coexist on the same JVM. In the example of security, one group is not allowed to access the methods in other group. Thread groups facilitate control of the relative priorities of threads. This is useful for browsers ...
Module 4: Processes
... When CPU switches to another process, the system must save the state of the old process and load the saved state for the new process ...
... When CPU switches to another process, the system must save the state of the old process and load the saved state for the new process ...
Operating System Structures
... Virtual disks with virtual file systems on physical disk / file system A normal user time-sharing terminal serves as the virtual machine ...
... Virtual disks with virtual file systems on physical disk / file system A normal user time-sharing terminal serves as the virtual machine ...
Module 6: CPU Scheduling
... Lowest priority has round-robin scheduling. Is it possible for processes in the lowest class to starve? Explain your answer. What advantage does First Come First Served scheduling over Round ...
... Lowest priority has round-robin scheduling. Is it possible for processes in the lowest class to starve? Explain your answer. What advantage does First Come First Served scheduling over Round ...
Operating System Tutorial
... hardware. An operating system is a software which performs all the basic tasks like file management, memory management, process management, handling input and output, and controlling peripheral devices such as disk drives and printers. Some popular Operating Systems include Linux Operating System, W ...
... hardware. An operating system is a software which performs all the basic tasks like file management, memory management, process management, handling input and output, and controlling peripheral devices such as disk drives and printers. Some popular Operating Systems include Linux Operating System, W ...
Process Scheduling
... One solution is to have the server run as a single process that accepts requests. When the server receives a request, it creates a separate process to service that request. In fact, this process-creation method was in common use before threads became popular. Benefits The benefits of multithreaded p ...
... One solution is to have the server run as a single process that accepts requests. When the server receives a request, it creates a separate process to service that request. In fact, this process-creation method was in common use before threads became popular. Benefits The benefits of multithreaded p ...
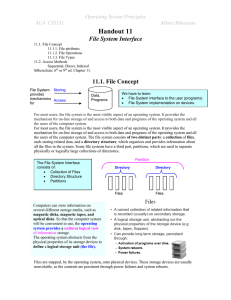
H 10.1. File-System Interface
... formatted rigidly. In general, a file is a sequence of bits, bytes, lines, or records, the meaning of which is defined by the file's creator and user. The concept of a file is thus extremely general. The information in a file is defined by its creator. Many different types of information may be stor ...
... formatted rigidly. In general, a file is a sequence of bits, bytes, lines, or records, the meaning of which is defined by the file's creator and user. The concept of a file is thus extremely general. The information in a file is defined by its creator. Many different types of information may be stor ...
No Slide Title
... each process gets 1/n of the CPU time in chunks of at most q time units at once. No process waits more than (n-1)q time units before next execution. Timer interrupts every quantum to schedule next process ...
... each process gets 1/n of the CPU time in chunks of at most q time units at once. No process waits more than (n-1)q time units before next execution. Timer interrupts every quantum to schedule next process ...
The Abstraction: The Process
... Time sharing is one of the most basic techniques used by an OS to share a resource. By allowing the resource to be used for a little while by one entity, and then a little while by another, and so forth, the resource in question (e.g., the CPU, or a network link) can be shared by many. The natural c ...
... Time sharing is one of the most basic techniques used by an OS to share a resource. By allowing the resource to be used for a little while by one entity, and then a little while by another, and so forth, the resource in question (e.g., the CPU, or a network link) can be shared by many. The natural c ...
Module 4: Processes
... memory, ready and waiting to execute. Device queues – set of processes waiting for an I/O ...
... memory, ready and waiting to execute. Device queues – set of processes waiting for an I/O ...
lecture1423726024
... 4. Distributed System/Loosely Coupled Systems: In contrast to tightly coupled systems, the processors do not share memory or a clock. Instead, each processor has its own local memory. The processors communicate with each other by various communication lines such as high speed buses or telephone line ...
... 4. Distributed System/Loosely Coupled Systems: In contrast to tightly coupled systems, the processors do not share memory or a clock. Instead, each processor has its own local memory. The processors communicate with each other by various communication lines such as high speed buses or telephone line ...
Operation Systems
... Demand paging gives rise the concept of virtual memory. Only a small part of a process needs to be in main memory at one time. Programs which require bigger memory that main memory can still be executed. Impression of a bigger computer memory. This concept of the main memory is called virtual memory ...
... Demand paging gives rise the concept of virtual memory. Only a small part of a process needs to be in main memory at one time. Programs which require bigger memory that main memory can still be executed. Impression of a bigger computer memory. This concept of the main memory is called virtual memory ...
mod13_Process Management
... The life cycle of a process can be generalized by the above slide. When a process is born (or starts), its text must be paged in from the file system on disk (on demand). In addition, space must be reserved on the swap partition for the process in the event it may need to page portions out to swap. ...
... The life cycle of a process can be generalized by the above slide. When a process is born (or starts), its text must be paged in from the file system on disk (on demand). In addition, space must be reserved on the swap partition for the process in the event it may need to page portions out to swap. ...