Chapter 2 – outline
... o System software works with end users, application software, and computer hardware to handle the majority of technical details. o It is a collection or a system of programs that handle hundreds of technical details with little or no user intervention. o There are four types of programs that makeup ...
... o System software works with end users, application software, and computer hardware to handle the majority of technical details. o It is a collection or a system of programs that handle hundreds of technical details with little or no user intervention. o There are four types of programs that makeup ...
Commercial Real-Time Operating Systems
... run on them. The Lynx microkernel is 28KBytes in size and provides the essential services in scheduling, interrupt dispatch, and synchronization. The other services are provided as kernel plug-ins (KPIs). By adding KPIs to the microkernel, the system can be configured to support I/O, file systems, s ...
... run on them. The Lynx microkernel is 28KBytes in size and provides the essential services in scheduling, interrupt dispatch, and synchronization. The other services are provided as kernel plug-ins (KPIs). By adding KPIs to the microkernel, the system can be configured to support I/O, file systems, s ...
Proceedings of the First Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation
... other words, rather than have a single privileged application controlling a particular aspect of the OS, the PlanetLab OS potentially supports many such management services. One implication of this interface being sharable is that it must be well-defined, explicitly exposing the state of the underly ...
... other words, rather than have a single privileged application controlling a particular aspect of the OS, the PlanetLab OS potentially supports many such management services. One implication of this interface being sharable is that it must be well-defined, explicitly exposing the state of the underly ...
process control block
... Process state. The state may be new, ready running, waiting, halted, and so on. Program counter. The counter indicates the address of the next instruction to be executed for this process. CPU registers. The registers vary in number and type, depending on the computer architecture. They include accum ...
... Process state. The state may be new, ready running, waiting, halted, and so on. Program counter. The counter indicates the address of the next instruction to be executed for this process. CPU registers. The registers vary in number and type, depending on the computer architecture. They include accum ...
Introduction - McMaster Computing and Software
... The basic unit of computer storage is the bit. A bit can contain one of two values, 0 and 1. All other storage in a computer is based on collections of bits. Given enough bits, it is amazing how many things a computer can represent: numbers, letters, images, movies, sounds, documents, and programs, ...
... The basic unit of computer storage is the bit. A bit can contain one of two values, 0 and 1. All other storage in a computer is based on collections of bits. Given enough bits, it is amazing how many things a computer can represent: numbers, letters, images, movies, sounds, documents, and programs, ...
Ch 1 PowerPoint Slides
... • Technique for sharing the CPU among runnable processes – Process may be blocked on I/O – Process may be blocked waiting for other resource, including the CPU ...
... • Technique for sharing the CPU among runnable processes – Process may be blocked on I/O – Process may be blocked waiting for other resource, including the CPU ...
Discussion #05
... exhibit a parent-child (creator-created) relationship with another process. The process control block may contain pointers to other processes to support these structures. ...
... exhibit a parent-child (creator-created) relationship with another process. The process control block may contain pointers to other processes to support these structures. ...
Document
... It should focus mainly on Windows and Linux, should address I/O communication techniques focusing on interrupts and DMA and should briefly describe memory hierarchy. In addition please provide a summation of which operating system you believe could apply to your current business ...
... It should focus mainly on Windows and Linux, should address I/O communication techniques focusing on interrupts and DMA and should briefly describe memory hierarchy. In addition please provide a summation of which operating system you believe could apply to your current business ...
Orf467F10Networks
... as the tail node and j (“B” node) as the head node. Arc (i,j) emenates from i and terminates at j. Arc (i,j) is incident to nodes i and j. It is outgoing from i and incoming to j. Whenever an arc (i,j) ∈ A, then node j is adjacent to i. Degrees: The indegree of a node is the number on incoming arcs ...
... as the tail node and j (“B” node) as the head node. Arc (i,j) emenates from i and terminates at j. Arc (i,j) is incident to nodes i and j. It is outgoing from i and incoming to j. Whenever an arc (i,j) ∈ A, then node j is adjacent to i. Degrees: The indegree of a node is the number on incoming arcs ...
p2p-unstructured - Computer Science and Engineering
... Implications: High tolerance to random node failure but low reliability ...
... Implications: High tolerance to random node failure but low reliability ...
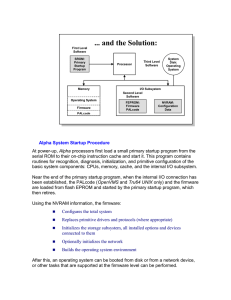
Alpha System Startup Procedure
... some systems with AlphaBIOS have EISA and PCI expansion slots, others have ISA and PCI expansion slots, and some new Compaq AlphaServer systems such as DS10 and ES40 have PCI expansion slots only. As a result, EISA setup options appear in the AlphaBIOS screens for the systems with EISA slots, and no ...
... some systems with AlphaBIOS have EISA and PCI expansion slots, others have ISA and PCI expansion slots, and some new Compaq AlphaServer systems such as DS10 and ES40 have PCI expansion slots only. As a result, EISA setup options appear in the AlphaBIOS screens for the systems with EISA slots, and no ...
Chapter 3 Operating-System Structures 2
... • A virtual-machine system is a perfect vehicle for operating-systems research and development. System development is done on the virtual machine, instead of on a physical machine and so does not disrupt normal system operation. • The virtual machine concept is difficult to implement due to the effo ...
... • A virtual-machine system is a perfect vehicle for operating-systems research and development. System development is done on the virtual machine, instead of on a physical machine and so does not disrupt normal system operation. • The virtual machine concept is difficult to implement due to the effo ...
1.01 - UCSB Computer Science
... Symmetric clustering has multiple nodes running applications, monitoring each other ...
... Symmetric clustering has multiple nodes running applications, monitoring each other ...
Slide 1
... Step 0: Join the network Step 1: Determining who is on the network • "Ping" packet is used to announce your presence on the network. • Other peers respond with a "Pong" packet. • Also forwards your Ping to other connected peers ...
... Step 0: Join the network Step 1: Determining who is on the network • "Ping" packet is used to announce your presence on the network. • Other peers respond with a "Pong" packet. • Also forwards your Ping to other connected peers ...
P2P_Computing
... Then sends a PING message to discover other nodes PONG message are sent in reply from hosts offering connections with the new node ...
... Then sends a PING message to discover other nodes PONG message are sent in reply from hosts offering connections with the new node ...
Slides: Monitoring.
... of information to the network administrator (i.e., (1) which nodes are queried by x, and (2) through which type of message, and finally (3) which type of information x can return); • Goal: Compute a minimum-size subset of sentinel nodes SV allowing to monitor G with respect to the simultaneous fail ...
... of information to the network administrator (i.e., (1) which nodes are queried by x, and (2) through which type of message, and finally (3) which type of information x can return); • Goal: Compute a minimum-size subset of sentinel nodes SV allowing to monitor G with respect to the simultaneous fail ...
LAB - ECE233
... terminal nodes determines the number of voltage levels that will occur. If there are N input terminal nodes, the number of voltage levels that can be obtained is equal to 2 N. The smallest of these voltage levels is equal to zero where as the highest of them will be equal to 2N 1 VS . Thus, the inc ...
... terminal nodes determines the number of voltage levels that will occur. If there are N input terminal nodes, the number of voltage levels that can be obtained is equal to 2 N. The smallest of these voltage levels is equal to zero where as the highest of them will be equal to 2N 1 VS . Thus, the inc ...
Peer-to-Peer
... For concurrent operations and failures, each Chord node runs a stabilization algorithm periodically to update the finger tables and successor lists to reflect addition/failure of nodes. If lookups fail during the stabilization process, the higher layer can lookup again. Chord provides guarantees tha ...
... For concurrent operations and failures, each Chord node runs a stabilization algorithm periodically to update the finger tables and successor lists to reflect addition/failure of nodes. If lookups fail during the stabilization process, the higher layer can lookup again. Chord provides guarantees tha ...
PDF
... clients of these systems benefit significantly from being directed to blacklists to exclude probing specific clients. Currently, this effort the nearest suitable service component. Selecting a close-by server must be repeated for each new service. is critical in order to ensure that the services pro ...
... clients of these systems benefit significantly from being directed to blacklists to exclude probing specific clients. Currently, this effort the nearest suitable service component. Selecting a close-by server must be repeated for each new service. is critical in order to ensure that the services pro ...
Presentación de PowerPoint
... The OS is the interface user-machine that provides the management of different resources: ...
... The OS is the interface user-machine that provides the management of different resources: ...
FileStore - Symantec
... Directories are not supported as shares (1 share per fs) Multiple file systems can be used for home directories For regular (non home-directory) shares – User visible share is a proxy share w/ single target DFS referral – Load balancing is done by moving a VIP w/ its shares to another node For home- ...
... Directories are not supported as shares (1 share per fs) Multiple file systems can be used for home directories For regular (non home-directory) shares – User visible share is a proxy share w/ single target DFS referral – Load balancing is done by moving a VIP w/ its shares to another node For home- ...
9-SystemSoftware - Systems and Computer Engineering
... – It takes far less time to create a new thread in an existing process than to create a brand-new process (Unix, factor of 10) – It takes less time to terminate a thread – It takes less time to switch between two threads within the same process – They also enhance communication efficiency between di ...
... – It takes far less time to create a new thread in an existing process than to create a brand-new process (Unix, factor of 10) – It takes less time to terminate a thread – It takes less time to switch between two threads within the same process – They also enhance communication efficiency between di ...
Distributed operating system
A distributed operating system is a software over a collection of independent, networked, communicating, and physically separate computational nodes. Each individual node holds a specific software subset of the global aggregate operating system. Each subset is a composite of two distinct service provisioners. The first is a ubiquitous minimal kernel, or microkernel, that directly controls that node’s hardware. Second is a higher-level collection of system management components that coordinate the node's individual and collaborative activities. These components abstract microkernel functions and support user applications.The microkernel and the management components collection work together. They support the system’s goal of integrating multiple resources and processing functionality into an efficient and stable system. This seamless integration of individual nodes into a global system is referred to as transparency, or single system image; describing the illusion provided to users of the global system’s appearance as a single computational entity.