A Survey of Context-Aware Mobile Computing Research
... Introducing the rules related to data aggregation, attributebased naming, and clustering to the sensor nodes Exchanging data related to the location finding algorithms Time synchronization of the sensor nodes Moving sensor nodes Turning sensor nodes on and off Querying the sensor network ...
... Introducing the rules related to data aggregation, attributebased naming, and clustering to the sensor nodes Exchanging data related to the location finding algorithms Time synchronization of the sensor nodes Moving sensor nodes Turning sensor nodes on and off Querying the sensor network ...
第二章 进程与调度 (Processes and Scheduling)
... Reasons for Process Suspension (Table 3.4 p116) Swapping: OS needs to release sufficient main memory to bring in a process that is ready to execute. Other OS reason: OS may suspend a background or utility process or a process that is suspected of causing a problem. Interactive user request: A us ...
... Reasons for Process Suspension (Table 3.4 p116) Swapping: OS needs to release sufficient main memory to bring in a process that is ready to execute. Other OS reason: OS may suspend a background or utility process or a process that is suspected of causing a problem. Interactive user request: A us ...
Proceedings of the General Track: 2003 USENIX Annual Technical Conference
... is no longer being referenced. For example, to swing the head pointer of a linked list from one chain of nodes to another, one can divide the accesses to the list into two epochs. The first epoch includes all threads in the system that were active before the swing, and the second epoch includes any ...
... is no longer being referenced. For example, to swing the head pointer of a linked list from one chain of nodes to another, one can divide the accesses to the list into two epochs. The first epoch includes all threads in the system that were active before the swing, and the second epoch includes any ...
CS-703 Advance Operating Systems
... OS in this class are Win2K, XP and flavors of UNIX. • Multiprocessor operating systems OS is basically a variation to server operating systems with special provisions for connectivity and communication management between different CPUs. • PC operating systems OS provides a nice interface to a si ...
... OS in this class are Win2K, XP and flavors of UNIX. • Multiprocessor operating systems OS is basically a variation to server operating systems with special provisions for connectivity and communication management between different CPUs. • PC operating systems OS provides a nice interface to a si ...
Active Names: Flexible Location and Transport of Wide-Area Resources.
... and DNS [33] enhancements to this basic mapping abstraction. More broadly, academic and industrial researchers have proposed a bewildering array of new services for mediating between clients and servers, including dynamic redistribution of replicas over the wide area [49], compression and distillati ...
... and DNS [33] enhancements to this basic mapping abstraction. More broadly, academic and industrial researchers have proposed a bewildering array of new services for mediating between clients and servers, including dynamic redistribution of replicas over the wide area [49], compression and distillati ...
ch5
... Suppose that we wanted to provide a solution to the consumer-producer problem that fills all the buffers. We can do so by having an integer counter that keeps track of the number of full buffers. Initially, counter is set to 0. It is incremented by the producer after it produces a new buffer and is ...
... Suppose that we wanted to provide a solution to the consumer-producer problem that fills all the buffers. We can do so by having an integer counter that keeps track of the number of full buffers. Initially, counter is set to 0. It is incremented by the producer after it produces a new buffer and is ...
Device management. I/O system organisation. Direct I/O. Memory
... – Create an API that implements the I/O functions available to the device, still compliant with interfaces implemented by other drivers; this is called device driver interface – Achieve correct coordination among the application processes, drivers and device controllers – Optimize the overall machin ...
... – Create an API that implements the I/O functions available to the device, still compliant with interfaces implemented by other drivers; this is called device driver interface – Achieve correct coordination among the application processes, drivers and device controllers – Optimize the overall machin ...
On-demand loop-free routing with link vectors
... find a given destination records its traversed route, and a route reply (RREP) sent by a node in response to the RREQ specifies the complete route between the node and the destination. Routers store the discovered routes in a route cache. The basic scheme in DSR is for the header of every data packet ...
... find a given destination records its traversed route, and a route reply (RREP) sent by a node in response to the RREQ specifies the complete route between the node and the destination. Routers store the discovered routes in a route cache. The basic scheme in DSR is for the header of every data packet ...
Multithreaded Programming
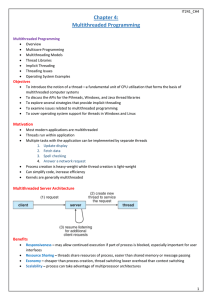
... To examine issues related to multithreaded programming To cover operating system support for threads in Windows and Linux ...
... To examine issues related to multithreaded programming To cover operating system support for threads in Windows and Linux ...
slides.02.pdf
... • Associated with each I/O device is a memory location where execution continues when that device generates an interrupt (interrupt vector). • The interrupt vector contains the start address of an operating-system provided procedure (interrupt handler). Execution continues with that procedure. ...
... • Associated with each I/O device is a memory location where execution continues when that device generates an interrupt (interrupt vector). • The interrupt vector contains the start address of an operating-system provided procedure (interrupt handler). Execution continues with that procedure. ...
A C T I V E N A... TR A N S P O R T ... W I D E - A R E A ...
... and DNS [33] enhancements to this basic mapping abstraction. More broadly, academic and industrial researchers have proposed a bewildering array of new services for mediating between clients and servers, including dynamic redistribution of replicas over the wide area [49], compression and distillati ...
... and DNS [33] enhancements to this basic mapping abstraction. More broadly, academic and industrial researchers have proposed a bewildering array of new services for mediating between clients and servers, including dynamic redistribution of replicas over the wide area [49], compression and distillati ...
ppt
... • Active networks makes such applications easy to develop and deploy © Srinivasan Seshan, 2001 ...
... • Active networks makes such applications easy to develop and deploy © Srinivasan Seshan, 2001 ...
Tapestry: A Resilient Global-scale Overlay for Service Deployment
... messages to a live node that has responsibility for the destination key. They can also support higher level interfaces such as a distributed hash table (DHT) or a decentralized object location and routing (DOLR) layer [3]. These systems scale well, and guarantee that queries find existing objects un ...
... messages to a live node that has responsibility for the destination key. They can also support higher level interfaces such as a distributed hash table (DHT) or a decentralized object location and routing (DOLR) layer [3]. These systems scale well, and guarantee that queries find existing objects un ...
Proceedings of the 5th Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation USENIX Association
... service or the underlying protection system. Additionally, performance isolation is required to bound each service’s resource consumption. Finally, the degree of information sharing between these multiplexed services will be small, or entirely non-existent. Because of this, it is reasonable to stren ...
... service or the underlying protection system. Additionally, performance isolation is required to bound each service’s resource consumption. Finally, the degree of information sharing between these multiplexed services will be small, or entirely non-existent. Because of this, it is reasonable to stren ...
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE)
... Abstract: Mobile ad hoc network (MANET) is an autonomous system of mobile nodes connected by wireless links. Each node operates not only as an end system, but also as a router to forward packets. The nodes are free to move about and organize themselves into a network. In either case, the proliferati ...
... Abstract: Mobile ad hoc network (MANET) is an autonomous system of mobile nodes connected by wireless links. Each node operates not only as an end system, but also as a router to forward packets. The nodes are free to move about and organize themselves into a network. In either case, the proliferati ...
Chap05
... Suppose that we wanted to provide a solution to the consumer-producer problem that fills all the buffers. We can do so by having an integer counter that keeps track of the number of full buffers. Initially, counter is set to 0. It is incremented by the producer after it produces a new buffer and is ...
... Suppose that we wanted to provide a solution to the consumer-producer problem that fills all the buffers. We can do so by having an integer counter that keeps track of the number of full buffers. Initially, counter is set to 0. It is incremented by the producer after it produces a new buffer and is ...
A modeling framework for gossip-based information spread
... system. The mean-field framework can be combined with our framework, as it is shown in [5] for Shuffle. There is previous work [18] on a simple gossip-based membership protocol with nonatomic protocol actions in the presence of message loss of up to 1%. The authors proposed to use a push-based gossi ...
... system. The mean-field framework can be combined with our framework, as it is shown in [5] for Shuffle. There is previous work [18] on a simple gossip-based membership protocol with nonatomic protocol actions in the presence of message loss of up to 1%. The authors proposed to use a push-based gossi ...
OPERATING SYSTEMS Lecture Notes
... allocated to each of them Many types of resources - Some (such as CPU cycles, main memory, and file storage) may have special allocation code, others (such as I/O devices) may have general request and release code Accounting - To keep track of which users use how much and what kinds of computer reso ...
... allocated to each of them Many types of resources - Some (such as CPU cycles, main memory, and file storage) may have special allocation code, others (such as I/O devices) may have general request and release code Accounting - To keep track of which users use how much and what kinds of computer reso ...
NetVM: High Performance and Flexible Networking Using
... and multi-level memory systems, all of which tend to increase the penalty paid by an interrupt in terms of cycles [12, 13]. When the packet reception rate increases further, the achieved (receive) throughput can drop dramatically in such systems [14]. Second, existing operating systems typically rea ...
... and multi-level memory systems, all of which tend to increase the penalty paid by an interrupt in terms of cycles [12, 13]. When the packet reception rate increases further, the achieved (receive) throughput can drop dramatically in such systems [14]. Second, existing operating systems typically rea ...
T R ECHNICAL ESEARCH
... When a node is unable to admit a ow, either due to its inability to give the ow the requested minimum bandwidth or due to congestion at a node, it is not able to allocate the minimum bandwidth BWmin required by the ow, the Admission Control Failure messages as in the coarse-feedback scheme descri ...
... When a node is unable to admit a ow, either due to its inability to give the ow the requested minimum bandwidth or due to congestion at a node, it is not able to allocate the minimum bandwidth BWmin required by the ow, the Admission Control Failure messages as in the coarse-feedback scheme descri ...
Large-scale Virtualization in the Emulab Network Testbed
... Network emulation is valuable largely because of its ability to study applications running on real hosts and “somewhat real” networks. However, conservatively allocating a physical host or network link for each corresponding virtual entity is costly and limits scale. We present a system that can fai ...
... Network emulation is valuable largely because of its ability to study applications running on real hosts and “somewhat real” networks. However, conservatively allocating a physical host or network link for each corresponding virtual entity is costly and limits scale. We present a system that can fai ...
Distributed operating system
A distributed operating system is a software over a collection of independent, networked, communicating, and physically separate computational nodes. Each individual node holds a specific software subset of the global aggregate operating system. Each subset is a composite of two distinct service provisioners. The first is a ubiquitous minimal kernel, or microkernel, that directly controls that node’s hardware. Second is a higher-level collection of system management components that coordinate the node's individual and collaborative activities. These components abstract microkernel functions and support user applications.The microkernel and the management components collection work together. They support the system’s goal of integrating multiple resources and processing functionality into an efficient and stable system. This seamless integration of individual nodes into a global system is referred to as transparency, or single system image; describing the illusion provided to users of the global system’s appearance as a single computational entity.