Technical Overview
... optimization, quality of service and security at that time. This automatically builds redundancy into the system and as with the other nodes multiple Edge Nodes are deployed to ensure availability. Each Edge Node can manage up to hundred thousand end users and additional nodes can be added in order ...
... optimization, quality of service and security at that time. This automatically builds redundancy into the system and as with the other nodes multiple Edge Nodes are deployed to ensure availability. Each Edge Node can manage up to hundred thousand end users and additional nodes can be added in order ...
The concept of operating system
... Many systems include both CLI and GUI interfaces Microsoft Windows is GUI with CLI “command” shell Apple Mac OS X as “Aqua” GUI interface with UNIX kernel underneath and shells available Solaris is CLI with optional GUI interfaces (Java Desktop, KDE) ...
... Many systems include both CLI and GUI interfaces Microsoft Windows is GUI with CLI “command” shell Apple Mac OS X as “Aqua” GUI interface with UNIX kernel underneath and shells available Solaris is CLI with optional GUI interfaces (Java Desktop, KDE) ...
Reconfigurable Computing for Signal Processing Applications
... Structure Adaptive RTR : Self Adaptive Software • Digital signal processing system can modify its own structure (i.e. the composition of the signal flow) while it is running. • Software synthesis tool creates the executable version of SFG. • Run-time kernel schedules the computational blocks as dic ...
... Structure Adaptive RTR : Self Adaptive Software • Digital signal processing system can modify its own structure (i.e. the composition of the signal flow) while it is running. • Software synthesis tool creates the executable version of SFG. • Run-time kernel schedules the computational blocks as dic ...
Unit-5 - Ipemgzb.ac.in
... associates named environment variables with arbitrary textual values. Passing environment variables among processes and inheriting variables by a process’s children are flexible means of passing information to components of the user-mode system software. The environment-variable mechanism provides a ...
... associates named environment variables with arbitrary textual values. Passing environment variables among processes and inheriting variables by a process’s children are flexible means of passing information to components of the user-mode system software. The environment-variable mechanism provides a ...
Operating Systems
... decision-making process. This not only includes the costs of obtaining and installing the OS, but also all costs associated with supporting it. Another factor that might come into play in the decision-making process is the availability of the operating system. Some countries and/or businesses have m ...
... decision-making process. This not only includes the costs of obtaining and installing the OS, but also all costs associated with supporting it. Another factor that might come into play in the decision-making process is the availability of the operating system. Some countries and/or businesses have m ...
Network Organization Concepts
... – Users aware of specific computers and resources in network – Access resources • Log on to remote host • Data transfer from remote host ...
... – Users aware of specific computers and resources in network – Access resources • Log on to remote host • Data transfer from remote host ...
Operating Systems Concepts Resource Abstraction
... is or how to load that kernel? – Use a bootstrap program or loader – Execution starts at a predefined memory ...
... is or how to load that kernel? – Use a bootstrap program or loader – Execution starts at a predefined memory ...
CPU-Scheduling
... • Provides reasonable response times and prevents the system being held up by processes in infinite loops. ...
... • Provides reasonable response times and prevents the system being held up by processes in infinite loops. ...
7.3. Computer System Structures
... In MS-DOS, the interfaces and levels of functionality are not well separated. For instance, application programs are able to access the basic I/O routines to write directly to the display and disk drives. Such freedom leaves MS-DOS vulnerable to errant (or malicious) programs, causing entire system ...
... In MS-DOS, the interfaces and levels of functionality are not well separated. For instance, application programs are able to access the basic I/O routines to write directly to the display and disk drives. Such freedom leaves MS-DOS vulnerable to errant (or malicious) programs, causing entire system ...
Document
... This technique is used iteratively to assign these nodes ID numbers ranging from 1 to N. This assignment is anonymous in that the identities received are unknown to the other members of the group. Resistance to collusion among other members is verified in an information theoretic sense when private ...
... This technique is used iteratively to assign these nodes ID numbers ranging from 1 to N. This assignment is anonymous in that the identities received are unknown to the other members of the group. Resistance to collusion among other members is verified in an information theoretic sense when private ...
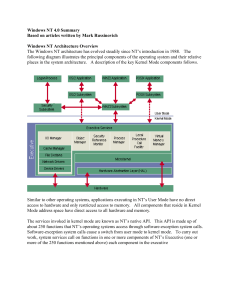
Windows_NT_4
... The Virtual Memory Manager creates and manages address maps for processes. The Virtual Memory Manager also does all physical memory allocation. To improve performance, the VMM implements file memory mapping, memory sharing, and copy-on-write page protection. File memory mapping involves the automati ...
... The Virtual Memory Manager creates and manages address maps for processes. The Virtual Memory Manager also does all physical memory allocation. To improve performance, the VMM implements file memory mapping, memory sharing, and copy-on-write page protection. File memory mapping involves the automati ...
Introduction
... Most computer systems today are based on the principles of a “stored-program computer” formulated by mathematician John von Neumann and others in the late 1940s. The basic components of a computer and their interconnections are shown schematically in Figure 1-1 in the form of a high-level block diag ...
... Most computer systems today are based on the principles of a “stored-program computer” formulated by mathematician John von Neumann and others in the late 1940s. The basic components of a computer and their interconnections are shown schematically in Figure 1-1 in the form of a high-level block diag ...
Presentazione di PowerPoint - Micrel Lab @ DEIS
... Each CPU execute the same program. Basing upon the CPU id we separate portions of code to be executed by master and slaves. Master CPU executes serial code, initializes synchronization structures in shared memory, etc.. Slave CPUs only execute the parallel regions of code, behaving like the typical ...
... Each CPU execute the same program. Basing upon the CPU id we separate portions of code to be executed by master and slaves. Master CPU executes serial code, initializes synchronization structures in shared memory, etc.. Slave CPUs only execute the parallel regions of code, behaving like the typical ...
Operating-System Structures
... OS is responsible for all file management activities: file creation and deletion. directory creation and deletion. support of primitives for manipulating files and directories. mapping files onto secondary storage. file backup on stable (nonvolatile) storage media. CSC 4103: Operating Sy ...
... OS is responsible for all file management activities: file creation and deletion. directory creation and deletion. support of primitives for manipulating files and directories. mapping files onto secondary storage. file backup on stable (nonvolatile) storage media. CSC 4103: Operating Sy ...
Introduction - UW Courses Web Server
... Job: program + the data + control info Programmers pass their jobs to an operator The operator batches together jobs OS transfers control from one job to another Job output is sent back to the programmer ...
... Job: program + the data + control info Programmers pass their jobs to an operator The operator batches together jobs OS transfers control from one job to another Job output is sent back to the programmer ...
Processes and System Calls
... • Kernel code runs at a higher level of execution privilege than application code – privilege levels are implemented by the CPU • The kernel’s higher privilege level allows it to do things that the CPU prevents less-privileged (application) programs from doing. For example: – application programs ca ...
... • Kernel code runs at a higher level of execution privilege than application code – privilege levels are implemented by the CPU • The kernel’s higher privilege level allows it to do things that the CPU prevents less-privileged (application) programs from doing. For example: – application programs ca ...
Processes and System Calls
... • Kernel code runs at a higher level of execution privilege than application code – privilege levels are implemented by the CPU • The kernel’s higher privilege level allows it to do things that the CPU prevents less-privileged (application) programs from doing. For example: – application programs ca ...
... • Kernel code runs at a higher level of execution privilege than application code – privilege levels are implemented by the CPU • The kernel’s higher privilege level allows it to do things that the CPU prevents less-privileged (application) programs from doing. For example: – application programs ca ...
theGuard! ApplicationManager System Windows Data
... user mode. Elementary operating system processes with high privileges run in protected kernel mode. These processes can impact the stability of the entire operating system when an error occurs (blue screen). Nonelementary operating system processes and user applications with low privileges run in un ...
... user mode. Elementary operating system processes with high privileges run in protected kernel mode. These processes can impact the stability of the entire operating system when an error occurs (blue screen). Nonelementary operating system processes and user applications with low privileges run in un ...
Distributed operating system
A distributed operating system is a software over a collection of independent, networked, communicating, and physically separate computational nodes. Each individual node holds a specific software subset of the global aggregate operating system. Each subset is a composite of two distinct service provisioners. The first is a ubiquitous minimal kernel, or microkernel, that directly controls that node’s hardware. Second is a higher-level collection of system management components that coordinate the node's individual and collaborative activities. These components abstract microkernel functions and support user applications.The microkernel and the management components collection work together. They support the system’s goal of integrating multiple resources and processing functionality into an efficient and stable system. This seamless integration of individual nodes into a global system is referred to as transparency, or single system image; describing the illusion provided to users of the global system’s appearance as a single computational entity.