solution
... Reading: Practical Electronics for Inventors: p 1-80, 159-164. 1) The circuit shown to the right is a “voltage divider.” a) Show that the voltage, V, from the supply splits across the two resistors according to the fraction of the total resistance R1 in each segment. In particular: V1 = V. R1 + R2 L ...
... Reading: Practical Electronics for Inventors: p 1-80, 159-164. 1) The circuit shown to the right is a “voltage divider.” a) Show that the voltage, V, from the supply splits across the two resistors according to the fraction of the total resistance R1 in each segment. In particular: V1 = V. R1 + R2 L ...
AC Circuits Summary
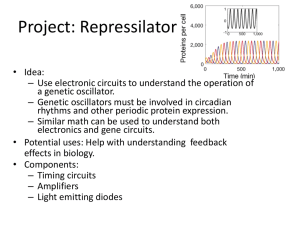
... Approach 1: Remember the spring and mass oscillator. When the mass is at the maximum or minimum spring extension, the stored potential energy in the spring is a maximum and the mass is momentarily at rest. When the mass passes through the equilibrium position, the velocity is at maximum and the pote ...
... Approach 1: Remember the spring and mass oscillator. When the mass is at the maximum or minimum spring extension, the stored potential energy in the spring is a maximum and the mass is momentarily at rest. When the mass passes through the equilibrium position, the velocity is at maximum and the pote ...
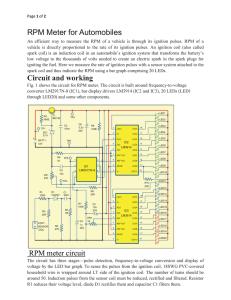
RPM Meter for Automobiles
... corresponding to the frequency of pulses is available at pin 4 of IC1. The level of this output voltage can be controlled by preset VR1. LM2917N-8 (IC1) is available in 8-pin and 14-pin versions; we have used 8-pin version here. The output of IC1 is fed at pins 5 of IC2 and IC3 through a filter form ...
... corresponding to the frequency of pulses is available at pin 4 of IC1. The level of this output voltage can be controlled by preset VR1. LM2917N-8 (IC1) is available in 8-pin and 14-pin versions; we have used 8-pin version here. The output of IC1 is fed at pins 5 of IC2 and IC3 through a filter form ...
DN339 - An Autoranging True RMS Converter
... voltage divided by the PGA gain. For example, if the output voltage is 64mV and the digital code is 0111, then the input voltage in RMS is equal to 64mV divided by 64. The circuit’s conversion error is less than 1% for an LTC1966 input voltage range of 50mVRMS to 1.5VRMS and increases to 5% for the ...
... voltage divided by the PGA gain. For example, if the output voltage is 64mV and the digital code is 0111, then the input voltage in RMS is equal to 64mV divided by 64. The circuit’s conversion error is less than 1% for an LTC1966 input voltage range of 50mVRMS to 1.5VRMS and increases to 5% for the ...
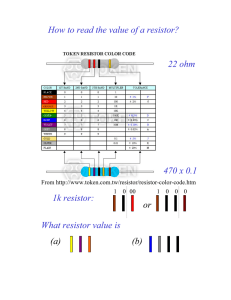
How to read the value of a resistor? 22 ohm 1k resistor:
... How to read the value of a resistor? ...
... How to read the value of a resistor? ...
Lab1
... Measure the threshold voltages at which a NOT gate switches from Logical “1” to Logical “0” and vice versa. Use Fig. 2 and connect the input of Inverter U1A to a voltage between 0 to +5 V using Agilent Power Supply (0 to +6V but limit it to +5V) or through a potentiometer and the +5V Power supply av ...
... Measure the threshold voltages at which a NOT gate switches from Logical “1” to Logical “0” and vice versa. Use Fig. 2 and connect the input of Inverter U1A to a voltage between 0 to +5 V using Agilent Power Supply (0 to +6V but limit it to +5V) or through a potentiometer and the +5V Power supply av ...
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM Existing System
... light load while the traditional interleaving control is used to keep better performance in heavy load. The boundary condition for swapping between APS and traditional interleaving PWM control is derived. Based on the aforementioned analysis, a full power range control combining APS and traditional ...
... light load while the traditional interleaving control is used to keep better performance in heavy load. The boundary condition for swapping between APS and traditional interleaving PWM control is derived. Based on the aforementioned analysis, a full power range control combining APS and traditional ...
LUCIA® 60/1-70
... installation and easy setup. The supplied wall-mount bracket enables discreet on-wall location (such as behind video displays), but the ultra-compact form factor also allows easy placement virtually anyplace – whether next to a projector or integrated into a reception counter, podium & lectern or ba ...
... installation and easy setup. The supplied wall-mount bracket enables discreet on-wall location (such as behind video displays), but the ultra-compact form factor also allows easy placement virtually anyplace – whether next to a projector or integrated into a reception counter, podium & lectern or ba ...
EE 42/100 Lecture 10: Op-Amp Based Circuits
... The most common application is to increase the noise immunity of a circuit. In a comparator, there is only a signal threshold voltage. If the input is noisy, then the output will bounce if the noise causes the input to cross the threshold. In a Schmitt Trigger, though, once the output transitions (s ...
... The most common application is to increase the noise immunity of a circuit. In a comparator, there is only a signal threshold voltage. If the input is noisy, then the output will bounce if the noise causes the input to cross the threshold. In a Schmitt Trigger, though, once the output transitions (s ...
Summing Amplifier
... are another op amp, some kind of sensor circuit, or an initial constant value. Since we don't have the first two available at this time, we'll use the third source for this experiment. • The point of using an op amp to add multiple input signals is to avoid interaction between them, so that any chan ...
... are another op amp, some kind of sensor circuit, or an initial constant value. Since we don't have the first two available at this time, we'll use the third source for this experiment. • The point of using an op amp to add multiple input signals is to avoid interaction between them, so that any chan ...
hw3
... Assume nCox=20uA/V2, W/L=10,000/1, Vth=1V, =0.01V. You should be able to do all of the calculations by hand (without calculators). One-ish significant digits is fine. a. Write an expression for ID as a function of output bias point. How much does ID change as the output voltage varies from 9V to 1 ...
... Assume nCox=20uA/V2, W/L=10,000/1, Vth=1V, =0.01V. You should be able to do all of the calculations by hand (without calculators). One-ish significant digits is fine. a. Write an expression for ID as a function of output bias point. How much does ID change as the output voltage varies from 9V to 1 ...
File
... to the circuit and what dangers or loss they may cause. I learnt from this project that understanding the concept of components is far not enough; we also need to know how to effectively implement them and combine them in different structures so as to make different effects as we want. The error we ...
... to the circuit and what dangers or loss they may cause. I learnt from this project that understanding the concept of components is far not enough; we also need to know how to effectively implement them and combine them in different structures so as to make different effects as we want. The error we ...
Part 2 – Operational Transconductance Amplifier
... Project 4 – Differential Pairs and OTAs Objective To understand the operation of differential pairs and how they are used to construct operational transconductance amplifiers. Simulation Models As will be standard with all projects involving circuit simulations, we will be using the 0.5μm EKV model ...
... Project 4 – Differential Pairs and OTAs Objective To understand the operation of differential pairs and how they are used to construct operational transconductance amplifiers. Simulation Models As will be standard with all projects involving circuit simulations, we will be using the 0.5μm EKV model ...
Integrating ADC
An integrating ADC is a type of analog-to-digital converter that converts an unknown input voltage into a digital representation through the use of an integrator. In its most basic implementation, the unknown input voltage is applied to the input of the integrator and allowed to ramp for a fixed time period (the run-up period). Then a known reference voltage of opposite polarity is applied to the integrator and is allowed to ramp until the integrator output returns to zero (the run-down period). The input voltage is computed as a function of the reference voltage, the constant run-up time period, and the measured run-down time period. The run-down time measurement is usually made in units of the converter's clock, so longer integration times allow for higher resolutions. Likewise, the speed of the converter can be improved by sacrificing resolution.Converters of this type can achieve high resolution, but often do so at the expense of speed. For this reason, these converters are not found in audio or signal processing applications. Their use is typically limited to digital voltmeters and other instruments requiring highly accurate measurements.