Evaluates: MAX1711 MAX1711 Voltage Positioning Evaluation Kit General Description Features
... to sink current. If SKIP is held low (PFM mode), the circuit won’t sink current, so the output voltage will decrease only at the rate determined by the load current. This is often acceptable, but some applications require output voltage transitions to be completed within a set time limit. Powering C ...
... to sink current. If SKIP is held low (PFM mode), the circuit won’t sink current, so the output voltage will decrease only at the rate determined by the load current. This is often acceptable, but some applications require output voltage transitions to be completed within a set time limit. Powering C ...
Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computing and
... of M3 device which has negative temperature coefficient and the voltage drop across R2 i.e. the trimming resistors which gives positive temperature coefficient and the effects of positive temperature coefficient and negative coefficient cancels by adding in order to get stable output voltage referen ...
... of M3 device which has negative temperature coefficient and the voltage drop across R2 i.e. the trimming resistors which gives positive temperature coefficient and the effects of positive temperature coefficient and negative coefficient cancels by adding in order to get stable output voltage referen ...
FAN4931 Ultra-Low Cost, Rail-to-Rail I/O, CMOS Amplifier FAN4931 — Ultra-Lo
... above the recommended operating conditions and stressing the parts to these levels is not recommended. In addition, extended exposure to stresses above the recommended operating conditions may affect device reliability. The absolute maximum ratings are stress ratings only. Functional operation under ...
... above the recommended operating conditions and stressing the parts to these levels is not recommended. In addition, extended exposure to stresses above the recommended operating conditions may affect device reliability. The absolute maximum ratings are stress ratings only. Functional operation under ...
unit – ii applications of operational amplifiers
... Passive filters made of passive components like R, L, C works well for high frequencies. For audio frequencies inductors become problematic since they are large, heavy and expensive. For low frequency applications, more number of turns of wire must be used, which degrades inductor performance an ...
... Passive filters made of passive components like R, L, C works well for high frequencies. For audio frequencies inductors become problematic since they are large, heavy and expensive. For low frequency applications, more number of turns of wire must be used, which degrades inductor performance an ...
LMZ14202/LMZ14203 Demo Board SIMPLE
... control section switching cycle. The secondary function of the RON resistor is to create a nearly constant operating frequency over the input operating voltage range. If the output voltage of the regulator is changed by adjusting the feedback divider then it is generally required that the RON resist ...
... control section switching cycle. The secondary function of the RON resistor is to create a nearly constant operating frequency over the input operating voltage range. If the output voltage of the regulator is changed by adjusting the feedback divider then it is generally required that the RON resist ...
Buck Current/Voltage Fed Push-Pull PWM
... A bidirectional pin for the oscillator., used to synchronize several chips to the fastest oscillator. Its input synchronization threshold is 1.4 V. The SYNC voltage is 3.6 V when the oscillator capacitor, CT, is discharged. Otherwise it is 0 V. If the recommended synchronization circuit is not used, ...
... A bidirectional pin for the oscillator., used to synchronize several chips to the fastest oscillator. Its input synchronization threshold is 1.4 V. The SYNC voltage is 3.6 V when the oscillator capacitor, CT, is discharged. Otherwise it is 0 V. If the recommended synchronization circuit is not used, ...
HP 4145B Semiconductor Parameter Analyzer
... voltage. Tables 1 and 2 specify both the measuring and sourcing parameters. ...
... voltage. Tables 1 and 2 specify both the measuring and sourcing parameters. ...
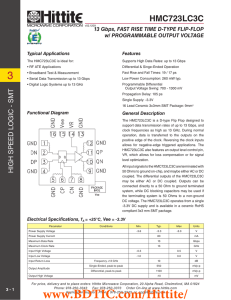
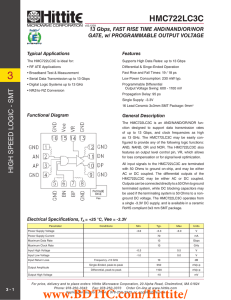
HMC723LC3C 数据资料DataSheet下载
... support data transmission rates of up to 13 Gbps, and clock frequencies as high as 13 GHz. During normal operation, data is transferred to the outputs on the positive edge of the clock. Reversing the clock inputs allows for negative-edge triggered applications. The HMC723LC3C also features an output ...
... support data transmission rates of up to 13 Gbps, and clock frequencies as high as 13 GHz. During normal operation, data is transferred to the outputs on the positive edge of the clock. Reversing the clock inputs allows for negative-edge triggered applications. The HMC723LC3C also features an output ...
Specifications - Lucas
... platform. The courses teach the theoretical building blocks and provide experiments to be carried out using the course-specific experiment hardware. The intelligent measurement interface supplies the analog and digital measuring and control I/O and represents, in combination with the system's virtua ...
... platform. The courses teach the theoretical building blocks and provide experiments to be carried out using the course-specific experiment hardware. The intelligent measurement interface supplies the analog and digital measuring and control I/O and represents, in combination with the system's virtua ...
9. Capacitor and Resistor Circuits
... the oscilloscope had better be something like this frequency f. If the oscilloscope is set at too high a frequency, the time will be too short to see the voltage rise. On the other hand, if the oscilloscope is set at too low a frequency, there will not be enough time to see the voltage rise across t ...
... the oscilloscope had better be something like this frequency f. If the oscilloscope is set at too high a frequency, the time will be too short to see the voltage rise. On the other hand, if the oscilloscope is set at too low a frequency, there will not be enough time to see the voltage rise across t ...
M43067982
... ballast. This ac-dc converter is implemented with two stages. In first stage, the ac voltage is converted into uncontrolled dc voltage by using the diode bridge rectifier circuits, followed by the second stage of dcdc converter using high frequency transformer. These two stages of power conversion h ...
... ballast. This ac-dc converter is implemented with two stages. In first stage, the ac voltage is converted into uncontrolled dc voltage by using the diode bridge rectifier circuits, followed by the second stage of dcdc converter using high frequency transformer. These two stages of power conversion h ...
Lab 2 - University of Colorado Boulder
... Part I. Measurement of resistance Each position should have 5 resistors: one 15, one 40, one 1500, and two 3000 resistors. These values for the resistances are given by the manufacturer and are approximate. Each resistor is mounted in a double-banana plug connector. Begin by carefully measuring ...
... Part I. Measurement of resistance Each position should have 5 resistors: one 15, one 40, one 1500, and two 3000 resistors. These values for the resistances are given by the manufacturer and are approximate. Each resistor is mounted in a double-banana plug connector. Begin by carefully measuring ...
living with the lab
... Kirchoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) Kirchoff’s Voltage Law says that the algebraic sum of voltages around any closed loop in a circuit is zero – we see that this is true for our circuit. It is also true for very complex circuits. ...
... Kirchoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) Kirchoff’s Voltage Law says that the algebraic sum of voltages around any closed loop in a circuit is zero – we see that this is true for our circuit. It is also true for very complex circuits. ...
Integrating ADC
An integrating ADC is a type of analog-to-digital converter that converts an unknown input voltage into a digital representation through the use of an integrator. In its most basic implementation, the unknown input voltage is applied to the input of the integrator and allowed to ramp for a fixed time period (the run-up period). Then a known reference voltage of opposite polarity is applied to the integrator and is allowed to ramp until the integrator output returns to zero (the run-down period). The input voltage is computed as a function of the reference voltage, the constant run-up time period, and the measured run-down time period. The run-down time measurement is usually made in units of the converter's clock, so longer integration times allow for higher resolutions. Likewise, the speed of the converter can be improved by sacrificing resolution.Converters of this type can achieve high resolution, but often do so at the expense of speed. For this reason, these converters are not found in audio or signal processing applications. Their use is typically limited to digital voltmeters and other instruments requiring highly accurate measurements.