Science 9: Unit D – Electrical Principles and Technologies
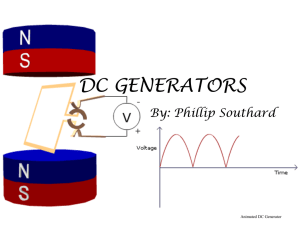
... Generators work by taking in some kind of mechanical energy and changing and storing it as electrical energy. A generator basically works in reverse order from an electric motor. Moving energy is supplied which causes permanent magnets to move which cause an electric current to run through the wire. ...
... Generators work by taking in some kind of mechanical energy and changing and storing it as electrical energy. A generator basically works in reverse order from an electric motor. Moving energy is supplied which causes permanent magnets to move which cause an electric current to run through the wire. ...
What is energy
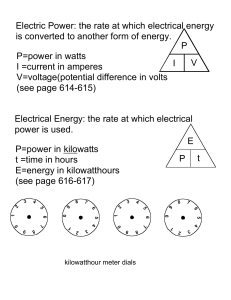
... What units are used measure power? What units are used to measure current? What units are used to measure voltage? What units are used to measure current? What is static electricity? Electric companies use what unit of measure to bill their customers for energy use? ...
... What units are used measure power? What units are used to measure current? What units are used to measure voltage? What units are used to measure current? What is static electricity? Electric companies use what unit of measure to bill their customers for energy use? ...
Electro-magnetics Electro
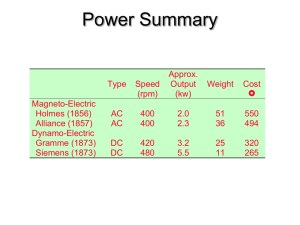
... Sources Of Electrical Energy u Mechanical Generators Of Electricity u Dynamo-Electric Generators u Gramme Armature & Successors u Alternator u Electric Lighting u Power Stations u Batteries ...
... Sources Of Electrical Energy u Mechanical Generators Of Electricity u Dynamo-Electric Generators u Gramme Armature & Successors u Alternator u Electric Lighting u Power Stations u Batteries ...
Basic Principles of Electricity
... electric current in the coil itself. The electro-magnet used in power stations is made of many turns of covered copper wire wound around an iron core. The magnet is referred to as the rotor and the coil as the stator. Some form of mechanical energy such as the movement of steam, water, gas or wind i ...
... electric current in the coil itself. The electro-magnet used in power stations is made of many turns of covered copper wire wound around an iron core. The magnet is referred to as the rotor and the coil as the stator. Some form of mechanical energy such as the movement of steam, water, gas or wind i ...
High voltage - Ysgol John Bright
... Why would the electricity company want to transmit electricity at high voltage? ...
... Why would the electricity company want to transmit electricity at high voltage? ...
Electricity 101 - Learn the Basics on Production | GE Power
... Fuel types include fossil (coal, oil, natural gas), nuclear, and renewable (such as solar power, wind power, falling water for hydro generation, and even garbage and agricultural waste products). Renewables also reduce emissions during power generation. 1. Turbine and generator convert energy. In a ...
... Fuel types include fossil (coal, oil, natural gas), nuclear, and renewable (such as solar power, wind power, falling water for hydro generation, and even garbage and agricultural waste products). Renewables also reduce emissions during power generation. 1. Turbine and generator convert energy. In a ...
Electromagnetism Cloze - Science
... example, uses the energy of flowing water to generate electricity. As water flows from a high place to a low place, it pushes on _________________ blades causing them to spin. Coils of wire are attached to the spinning turbine and placed next to magnets. As the coil _________________ in the magnetic ...
... example, uses the energy of flowing water to generate electricity. As water flows from a high place to a low place, it pushes on _________________ blades causing them to spin. Coils of wire are attached to the spinning turbine and placed next to magnets. As the coil _________________ in the magnetic ...
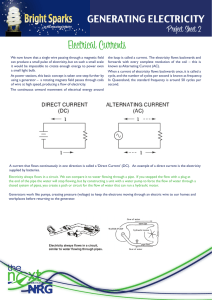
Electrical Currents - NRG Gladstone Power Station
... We now know that a single wire passing through a magnetic field can produce a small pulse of electricity, but on such a small scale it would be impossible to create enough energy to power even a small light bulb. At power stations, this basic concept is taken one step further by using a generator – ...
... We now know that a single wire passing through a magnetic field can produce a small pulse of electricity, but on such a small scale it would be impossible to create enough energy to power even a small light bulb. At power stations, this basic concept is taken one step further by using a generator – ...
Step 3: Electricity
... Electricity Science of Energy Station Six Teaches Students About The Relationship Between Magnetism and Electricity Shows Electricity Can Be Changed To Other Forms Of Energy Demonstrates How We Use Various Sources of Energy to Generate Electricity in A Power Plant ...
... Electricity Science of Energy Station Six Teaches Students About The Relationship Between Magnetism and Electricity Shows Electricity Can Be Changed To Other Forms Of Energy Demonstrates How We Use Various Sources of Energy to Generate Electricity in A Power Plant ...
Vocabulary Terms
... is generated by passing a wire through a magnetic field or by rotating a magnet past a wire. There are two basic kinds of electricity-static and current; Static: Build up of electrons and then passing them on Current: Steady flow of electrons from a source, through a conductor to an appliance and ba ...
... is generated by passing a wire through a magnetic field or by rotating a magnet past a wire. There are two basic kinds of electricity-static and current; Static: Build up of electrons and then passing them on Current: Steady flow of electrons from a source, through a conductor to an appliance and ba ...
Electricity and Resources Study Guide Answers
... by spinning a coil of wire inside a magnet 6. What is the most common fuel for electric power plants? burning fossil fuels (mainly coal) 7. How does the thickness of a wire affect its resistance? The thicker the wire the less resistance so the more current can flow 8. What does a transformer do? A t ...
... by spinning a coil of wire inside a magnet 6. What is the most common fuel for electric power plants? burning fossil fuels (mainly coal) 7. How does the thickness of a wire affect its resistance? The thicker the wire the less resistance so the more current can flow 8. What does a transformer do? A t ...
Electrification

Electrification is the process of powering by electricity and is usually associated with changing over from another power source. The broad meaning of the term, such as in the history of technology and economic history, usually applies to a region or national economy. Broadly speaking, electrification was the build out of the electrical generating and distribution systems which occurred in Britain, the United States, and other countries from the mid-1880s until around 1950 and is in progress in rural areas in some developing countries. This included the change over from line shaft and belt drive using steam engines and water power to electric motors.The electrification of particular sectors of the economy is called by terms such as factory electrification, household electrification, rural electrification or railway electrification. It may also apply to changing industrial processes such as smelting, melting, separating or refining from coal or coke heating or chemical processes to some type of electric process such as electric arc furnace, electric induction or resistance heating or electrolysis or electrolytic separating.Electrification was called ""the greatest engineering achievement of the 20th Century"" by the National Academy of Engineering.