04. Physical-chemical essence of surface phenomenon
... to break film and is defined as the force in dynes acting upon а line one cm long on the surface of the liquid. Surface tension is typically measured in dynes/cm, the force in dynes required to break a film of length 1 cm. Equivalently, it can be stated as surface energy in ergs per square centimete ...
... to break film and is defined as the force in dynes acting upon а line one cm long on the surface of the liquid. Surface tension is typically measured in dynes/cm, the force in dynes required to break a film of length 1 cm. Equivalently, it can be stated as surface energy in ergs per square centimete ...
Effect of negative substrate bias voltage on the CrN film deposition
... saturation of both the peak and mean Isub was observed as the Vb was higher than -50 V. The structure and properties of the CrNx coatings deposited at different Vb voltages were characterized using electron probe micro-analysis, x-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, nanoindentation, and b ...
... saturation of both the peak and mean Isub was observed as the Vb was higher than -50 V. The structure and properties of the CrNx coatings deposited at different Vb voltages were characterized using electron probe micro-analysis, x-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, nanoindentation, and b ...
Phenomena at curved surfaces
... 3.Liquid-gas and liquid-liquid Interface 4. Adsorption and desorption 5. Surface reactions and heterogeneous catalysis 6.Surface spectroscopy 7. Preparation of colloids 8. Kinetic properties of colloids 9. Optical properties of colloids 10. Charged interfaces & Electro-kinetic phenomena 11. Colloid ...
... 3.Liquid-gas and liquid-liquid Interface 4. Adsorption and desorption 5. Surface reactions and heterogeneous catalysis 6.Surface spectroscopy 7. Preparation of colloids 8. Kinetic properties of colloids 9. Optical properties of colloids 10. Charged interfaces & Electro-kinetic phenomena 11. Colloid ...
Format Download
... Super-hydrophobic surface has a contact angle greater than 150°. Due to the high contact angle, very small amount of water droplet comes into contact with the surface. So super-hydrophobic properties have attracted much interested for both fundamental research and applications. The applications incl ...
... Super-hydrophobic surface has a contact angle greater than 150°. Due to the high contact angle, very small amount of water droplet comes into contact with the surface. So super-hydrophobic properties have attracted much interested for both fundamental research and applications. The applications incl ...
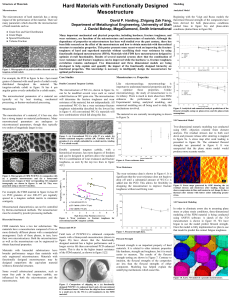
Hard Materials with Functionally Designed Mesostructure
... typically set by heat treating, mechanical will determine the fracture toughness and wear processing, or thermo-mechanical processing. resistance of the material, but not independently. All conventional WC-Co has a wear resistance-fracture toughness relationship described by the lowest line Mesostru ...
... typically set by heat treating, mechanical will determine the fracture toughness and wear processing, or thermo-mechanical processing. resistance of the material, but not independently. All conventional WC-Co has a wear resistance-fracture toughness relationship described by the lowest line Mesostru ...
Fundamentals of Adhesion
... Consider an automobile that has not been waxed for a long time. When water contacts the surface it spreads in large puddles. The unwaxed car surface exhibits high surface energy — the molecular attraction allows the water to flow. In comparison, water beads up into small spheres on freshly waxed car ...
... Consider an automobile that has not been waxed for a long time. When water contacts the surface it spreads in large puddles. The unwaxed car surface exhibits high surface energy — the molecular attraction allows the water to flow. In comparison, water beads up into small spheres on freshly waxed car ...
resonant material processing using (ultra-)short
... the properties of the material, modes develop. If now the material is excited resonantly (i.e. with a frequency that is specific to said material) these modes create standing waves leading to a local increase or decrease of the electromagnetic field on the surface. Hills are represented by nodes, va ...
... the properties of the material, modes develop. If now the material is excited resonantly (i.e. with a frequency that is specific to said material) these modes create standing waves leading to a local increase or decrease of the electromagnetic field on the surface. Hills are represented by nodes, va ...
Abrasive Jet Machining (AJM)
... MRR, machining accuracy, surface roughness and nozzle wear are influenced by Size and distance of the nozzle. Composition, strength, size, and shape of abrasives Flow rate Composition, pressure, and velocity of the carrier gas. MRR is mainly dependent on the flow rate and size of abrasiv ...
... MRR, machining accuracy, surface roughness and nozzle wear are influenced by Size and distance of the nozzle. Composition, strength, size, and shape of abrasives Flow rate Composition, pressure, and velocity of the carrier gas. MRR is mainly dependent on the flow rate and size of abrasiv ...
Classes of materials
... In order to select the correct material of construction, the process environment to which the material will be exposed must be clearly defined. In addition to the main corrosive chemicals present, the following factors must be considered: 1. Temperature—affects corrosion rate and mechanical properti ...
... In order to select the correct material of construction, the process environment to which the material will be exposed must be clearly defined. In addition to the main corrosive chemicals present, the following factors must be considered: 1. Temperature—affects corrosion rate and mechanical properti ...
AFM267
... This project aims to improve process efficiency and minimise the material usage in the vertical formfill-seal operation. More specifically, the overarching scientific challenge is to obtain a fundamental understanding of machine-material interaction and the design rules necessary for the creation of ...
... This project aims to improve process efficiency and minimise the material usage in the vertical formfill-seal operation. More specifically, the overarching scientific challenge is to obtain a fundamental understanding of machine-material interaction and the design rules necessary for the creation of ...
Effect of SiC Grain Refining on Wear Resistance of Mg
... widen the usage of these materials in different applications [5]. Wear damage is one of the main problems for moving parts in automotive production. In general magnesium and its alloys show poor wear resistance [6]. There are different ways to increase wear resistance of Mg alloys like plasma electr ...
... widen the usage of these materials in different applications [5]. Wear damage is one of the main problems for moving parts in automotive production. In general magnesium and its alloys show poor wear resistance [6]. There are different ways to increase wear resistance of Mg alloys like plasma electr ...
Bedrijf - Lindor
... Is injection of liquid(s) required? Name of liquid 1 (L1) to be injected L1: Amount as weight % of mix L1: Density [kg/l] L1: Dynamic viscosity [cP] L1: Specific characteristics1) Name of liquid 2 (L2) to be injected L2: Amount as weight % of mix L2: Density [kg/l] L2: Dynamic viscosity [cP] L2: Spe ...
... Is injection of liquid(s) required? Name of liquid 1 (L1) to be injected L1: Amount as weight % of mix L1: Density [kg/l] L1: Dynamic viscosity [cP] L1: Specific characteristics1) Name of liquid 2 (L2) to be injected L2: Amount as weight % of mix L2: Density [kg/l] L2: Dynamic viscosity [cP] L2: Spe ...
Protein sorption on soft contact lenses: a comparison between
... Above all, in the last years, numerous studies have been done on the adhesion of proteic deposits on soft contact lenses. This because the accumulation of lachrymal components, until today, renains a problem not totally solved that may lead to intolerance of the wearer and hence to a consequent drop ...
... Above all, in the last years, numerous studies have been done on the adhesion of proteic deposits on soft contact lenses. This because the accumulation of lachrymal components, until today, renains a problem not totally solved that may lead to intolerance of the wearer and hence to a consequent drop ...
Chapter 2 Materials Selection and Design Problems
... 1. Cartridge brass is an alloy of two metals: 70 wt % copper and 30 wt % zinc. Discuss the nature of the bonds between copper and zinc in this alloy. 2. Pure aluminum is a ductile metal with low tensile strength and hardness. Its oxide (alumina) is extremely strong, hard, and brittle. Can you explai ...
... 1. Cartridge brass is an alloy of two metals: 70 wt % copper and 30 wt % zinc. Discuss the nature of the bonds between copper and zinc in this alloy. 2. Pure aluminum is a ductile metal with low tensile strength and hardness. Its oxide (alumina) is extremely strong, hard, and brittle. Can you explai ...
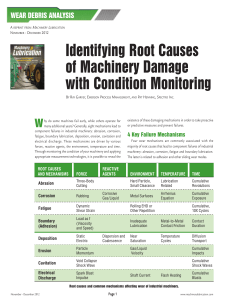
wear debris analysis
... harder metal. This is akin to the process by which sandpaper cuts steel. The lubricating fluid minimizes friction and adhesion, effectively improving the cutting efficiency of the abrasive particles during subsequent revolutions of the machine components. Abrasion involves localized friction, which ...
... harder metal. This is akin to the process by which sandpaper cuts steel. The lubricating fluid minimizes friction and adhesion, effectively improving the cutting efficiency of the abrasive particles during subsequent revolutions of the machine components. Abrasion involves localized friction, which ...
Wear modeling and material testing of elastomers
... Erosion testing at Tampere Wear Center using centrifugal accelerator produces impacts with lower loads but higher volume. The amount of abrasive is up to 10 kg. However, the particle size of the abrasive is smaller than 1 mm. The samp- ...
... Erosion testing at Tampere Wear Center using centrifugal accelerator produces impacts with lower loads but higher volume. The amount of abrasive is up to 10 kg. However, the particle size of the abrasive is smaller than 1 mm. The samp- ...
HW4 Problem 1 and 2.docx
... an increase in force will cause an increase in the volume of material removal. This results in course particle wear. Finally, the very large applied normal load causes a high amount of friction. This increase in friction can cause the materials to heat up and become brittle and harder. It can be see ...
... an increase in force will cause an increase in the volume of material removal. This results in course particle wear. Finally, the very large applied normal load causes a high amount of friction. This increase in friction can cause the materials to heat up and become brittle and harder. It can be see ...
Wear

In materials science, wear is erosion or sideways displacement of material from its ""derivative"" and original position on a solid surface performed by the action of another surface.Wear is related to interactions between surfaces and specifically the removal and deformation of material on a surface as a result of mechanical action of the opposite surface. The need for relative motion between two surfaces and initial mechanical contact between asperities is an important distinction between mechanical wear compared to other processes with similar outcomes.The definition of wear may include loss of dimension from plastic deformation if it is originated at the interface between two sliding surfaces.However, plastic deformation such as yield stress is excluded from the wear definition if it doesn't incorporate a relative sliding motion and contact against another surface despite the possibility for material removal, because it then lacks the relative sliding action of another surface.Impact wear is in reality a short sliding motion where two solid bodies interact at an exceptional short time interval. Previously due to the fast execution, the contact found in impact wear was referred to as an impulse contact by the nomenclature. Impulse can be described as a mathematical model of a synthesised average on the energy transport between two travelling solids in opposite converging contact. Cavitation wear is a form of wear where the erosive medium or counter-body is a fluid.Corrosion may be included in wear phenomenons, but the damage is amplified and performed by chemical reactions rather than mechanical action.Wear can also be defined as a process where interaction between two surfaces or bounding faces of solids within the working environment results in dimensional loss of one solid, with or without any actual decoupling and loss of material. Aspects of the working environment which affect wear include loads and features such as unidirectional sliding, reciprocating, rolling, and impact loads, speed, temperature, but also different types of counter-bodies such as solid, liquid or gas and type of contact ranging between single phase or multiphase, in which the last multiphase may combine liquid with solid particles and gas bubbles.