Summary: OS Concepts System Calls
... • to link is to create a new entry with the inumber of existing file ...
... • to link is to create a new entry with the inumber of existing file ...
Slides - Dr. Choong
... Silberschatz, Galvin, and Gagne, Operating Systems Concepts, Seventh Edition, John Wiley and Sons, 2005. ...
... Silberschatz, Galvin, and Gagne, Operating Systems Concepts, Seventh Edition, John Wiley and Sons, 2005. ...
Slide 1
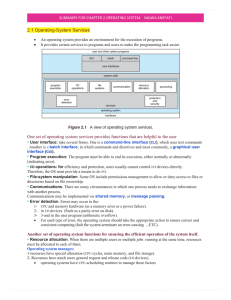
... controls how the hardware of a computer works… It is the means of communication between the user and the computer, deals with the loading and running of application programs and manages the transfer of data and files to and from the peripheral devices. ...
... controls how the hardware of a computer works… It is the means of communication between the user and the computer, deals with the loading and running of application programs and manages the transfer of data and files to and from the peripheral devices. ...
Summary for chapter 2 OPERATING SYSTEM nAJWA kNEFATI
... A programmer accesses an API via a library of code provided by the operating system (In C language, the library is called libc). Each operating system has its own name for each system call. The functions that make up an API typically invoke the actual system calls . EX: Function CreateProcess () (cr ...
... A programmer accesses an API via a library of code provided by the operating system (In C language, the library is called libc). Each operating system has its own name for each system call. The functions that make up an API typically invoke the actual system calls . EX: Function CreateProcess () (cr ...
Judul - Binus Repository
... – The OS that runs on Apple Macintosh computers – Pioneered the easy-to-use GUI – Proprietary OS • System 9 is OS from 1999, but still popular • Mac OS X is based on BSD Unix kernel • Tiger is 2005 release of Mac OS X; features include – Spotlight – a desktop search engine for locating files on loca ...
... – The OS that runs on Apple Macintosh computers – Pioneered the easy-to-use GUI – Proprietary OS • System 9 is OS from 1999, but still popular • Mac OS X is based on BSD Unix kernel • Tiger is 2005 release of Mac OS X; features include – Spotlight – a desktop search engine for locating files on loca ...
10B17CI307: UNIX Programming Lab
... Introduction to Unix Operating System and comparing it with Windows OS. Overview to Open Source Software. Writing and studying about how to execute C program in Unix environment using GCC compiler along with phases of compilation. Executing simple Hello World C program in UNIX environment using ed / ...
... Introduction to Unix Operating System and comparing it with Windows OS. Overview to Open Source Software. Writing and studying about how to execute C program in Unix environment using GCC compiler along with phases of compilation. Executing simple Hello World C program in UNIX environment using ed / ...
Operating System
... • Arguments tell OS what to do • Afterwards • “return” as from a function call • Force return to user mode ...
... • Arguments tell OS what to do • Afterwards • “return” as from a function call • Force return to user mode ...
Tools: Compilers and Operating Systems
... Traditional (centralized) operating systems for uniprocessors have the luxury of perfect knowledge of the state of the machine. Operating systems for parallel computers usually do not have an up-to-date knowledge of the state of the parallel machine. Their primary goal is to integrate the computing ...
... Traditional (centralized) operating systems for uniprocessors have the luxury of perfect knowledge of the state of the machine. Operating systems for parallel computers usually do not have an up-to-date knowledge of the state of the parallel machine. Their primary goal is to integrate the computing ...
Operating Systems
... • Buffering - store data in memory while transferring between devices – To cope with device speed mismatch – To cope with device transfer size mismatch – To maintain “copy semantics” ...
... • Buffering - store data in memory while transferring between devices – To cope with device speed mismatch – To cope with device transfer size mismatch – To maintain “copy semantics” ...
Windows NT Operating System
... because each one resides in a separate process whose memory is protected from other processes by the NT executive’s virtual memory system. They communicate with each other by passing messages. • The NT executive is capable of supporting any number of server processes. The servers give the NT executi ...
... because each one resides in a separate process whose memory is protected from other processes by the NT executive’s virtual memory system. They communicate with each other by passing messages. • The NT executive is capable of supporting any number of server processes. The servers give the NT executi ...
Design of OSes
... • Typically written in a high-level language (C or C++) • Mostly accessed by programs using APIs • Three most common APIs: – Win32 API for Windows – POSIX API for POSIX-based systems (UNIX, Linux, Mac OS X) – Java API for the Java virtual machine (JVM) ...
... • Typically written in a high-level language (C or C++) • Mostly accessed by programs using APIs • Three most common APIs: – Win32 API for Windows – POSIX API for POSIX-based systems (UNIX, Linux, Mac OS X) – Java API for the Java virtual machine (JVM) ...
Lecture Overview Operating System Components
... its own address; it is a quickly accessible storage repository shared by the CPU and I/O devices • Main memory is a volatile storage device; it loses its contents in the case of system failure • The operating system is responsible for – Keeping track of which parts of memory are currently being used ...
... its own address; it is a quickly accessible storage repository shared by the CPU and I/O devices • Main memory is a volatile storage device; it loses its contents in the case of system failure • The operating system is responsible for – Keeping track of which parts of memory are currently being used ...
Introduction to Operating Systems - Seneca
... Let more than one program run at once Support multiple users Make hardware transparent so that all disk drives look alike even if made by different companies ...
... Let more than one program run at once Support multiple users Make hardware transparent so that all disk drives look alike even if made by different companies ...
Underlying computer system = hardware + software
... Kernel sends interrupt to a process to give another process a turn to use the CPU z Processes can give up CPU when they don’t need it (e.g. waiting on I/O device) z ...
... Kernel sends interrupt to a process to give another process a turn to use the CPU z Processes can give up CPU when they don’t need it (e.g. waiting on I/O device) z ...
Overview of Operating Systems
... ❚ Some operating systems do not have well-defined structures. Often, they started as simple systems and grew beyond their original scope. ❚ MS-DOS – written to provide the most functionality in the least space Ø not divided into modules Ø Although MS-DOS has some structure, its interfaces and le ...
... ❚ Some operating systems do not have well-defined structures. Often, they started as simple systems and grew beyond their original scope. ❚ MS-DOS – written to provide the most functionality in the least space Ø not divided into modules Ø Although MS-DOS has some structure, its interfaces and le ...
Chapter 8 Operating Systems and Utility Programs
... program you are using • Background contains programs that are running but are not in use ...
... program you are using • Background contains programs that are running but are not in use ...
Operating Systems
... • Before: machine waits for I/O to complete • New approach: more work by the OS – Allow CPU to execute while waiting – Add buffering • Data fills “buffer” and then output ...
... • Before: machine waits for I/O to complete • New approach: more work by the OS – Allow CPU to execute while waiting – Add buffering • Data fills “buffer” and then output ...
Introduction To Operating Systems
... – A general device-driver interface – Drivers for specific hardware devices ...
... – A general device-driver interface – Drivers for specific hardware devices ...
Chapter 4
... System software includes programs that manage the basic operations of a computer such as starting up and saving and printing files. ...
... System software includes programs that manage the basic operations of a computer such as starting up and saving and printing files. ...
Telecommunications
... System software includes programs that manage the basic operations of a computer such as starting up and saving and printing files. ...
... System software includes programs that manage the basic operations of a computer such as starting up and saving and printing files. ...
CENG334 Introduction to Operating Systems
... your own. We have a zero tolerance policy on cheating and plagiarism. Your work will be ...
... your own. We have a zero tolerance policy on cheating and plagiarism. Your work will be ...
Language Based Operating Systems
... that is compiled to some intermediate language for execution or interpretation by a VM. Such languages are usually very high level (abstract) and provide expressive features. ...
... that is compiled to some intermediate language for execution or interpretation by a VM. Such languages are usually very high level (abstract) and provide expressive features. ...
Section 10: Intro to I/O and File Systems
... Otherwise, the referenced bit is cleared, the page is inserted at the back of the queue and the process is repeated until a page is swapped out. • Clock Algorithm Clock is a more efficient version of FIFO than Second-chance because pages don’t have to be constantly pushed to the back of the list. Th ...
... Otherwise, the referenced bit is cleared, the page is inserted at the back of the queue and the process is repeated until a page is swapped out. • Clock Algorithm Clock is a more efficient version of FIFO than Second-chance because pages don’t have to be constantly pushed to the back of the list. Th ...
Module 3: Operating
... Traditionally written in assembly language, operating systems can now be written in higher-level languages. Code written in a high-level language: can be written faster. is more compact. is easier to understand and debug. An operating system is far easier to port (move to some other hard ...
... Traditionally written in assembly language, operating systems can now be written in higher-level languages. Code written in a high-level language: can be written faster. is more compact. is easier to understand and debug. An operating system is far easier to port (move to some other hard ...