HEMO-AEROBIC Culture medium for the isolation of fastidious
... isolated microorganism will indicate clinically significant infections. Take in consideration that it can be collected 2-3 quotes of blood sample in different points to increase the detection of bacteremia. LIMITS AND WARNINGS HEMO-AEROBIC can promote the growth of a wide variety of microorganisms. ...
... isolated microorganism will indicate clinically significant infections. Take in consideration that it can be collected 2-3 quotes of blood sample in different points to increase the detection of bacteremia. LIMITS AND WARNINGS HEMO-AEROBIC can promote the growth of a wide variety of microorganisms. ...
The Origin of Human “Races” and Blood Groups
... A human race most often is defined as a group of people with certain features in common that distinguish them from other groups of people. Currently there are three or four major “races” of humans, as the word race commonly is defined: (a) Caucasoid; (b) Mongoloid; (c) Negroid; and (d) Australoid. G ...
... A human race most often is defined as a group of people with certain features in common that distinguish them from other groups of people. Currently there are three or four major “races” of humans, as the word race commonly is defined: (a) Caucasoid; (b) Mongoloid; (c) Negroid; and (d) Australoid. G ...
Pathogen Inactivation Making Decisions About New
... 1994 when Dr. David Kessler urged blood banks to develop NAT for routine donor screening. His talk raised eyebrows and great skepticism; but because of his position of authority, it drove the system……, and resulted in the remarkably rapid development of practical NAT assays that have been an enormou ...
... 1994 when Dr. David Kessler urged blood banks to develop NAT for routine donor screening. His talk raised eyebrows and great skepticism; but because of his position of authority, it drove the system……, and resulted in the remarkably rapid development of practical NAT assays that have been an enormou ...
Blood Notes Packet
... response against the "invading" blood. This will cause coagulation of blood and death. ----- AGGLUTINATION (the clumping of red blood cells following a transfusion reaction; fatal ...
... response against the "invading" blood. This will cause coagulation of blood and death. ----- AGGLUTINATION (the clumping of red blood cells following a transfusion reaction; fatal ...
Powerpoint - Blood Journal
... Pretreatment with DEX does not affect the regulation of DC-antigen uptake machinery.Immature DCs were incubated in the absence or the presence of 10−6 mol/L DEX for 24 hours and further activated or not via CD40 with the CD8-CD40L fusion protein for 48 hours. ...
... Pretreatment with DEX does not affect the regulation of DC-antigen uptake machinery.Immature DCs were incubated in the absence or the presence of 10−6 mol/L DEX for 24 hours and further activated or not via CD40 with the CD8-CD40L fusion protein for 48 hours. ...
MD0853 A-1 APPENDIX GLOSSARY OF TERMS A Agranulocyte: A
... Sedimentation Rate, Erythrocyte (ESR): The rate at which red cells will settle out in their own plasma in a given time under controlled conditions. Serum: The fluid portion of the blood, after clot formation. Shift to the Left: A term used to designate that condition in which the immature forms of t ...
... Sedimentation Rate, Erythrocyte (ESR): The rate at which red cells will settle out in their own plasma in a given time under controlled conditions. Serum: The fluid portion of the blood, after clot formation. Shift to the Left: A term used to designate that condition in which the immature forms of t ...
Principles of Transfusion Medicine
... for RBC Transfusions (Revisited) • Lower limit (or “transfusion trigger”) for general medical and surgical patients remains at Hgb (Hct) levels of 7.0 g/dL (21%). • Some patient groups (e.g., elderly with acute MI’s) seem to have better outcomes when Hct is in 3033% range. “Current data suggest rest ...
... for RBC Transfusions (Revisited) • Lower limit (or “transfusion trigger”) for general medical and surgical patients remains at Hgb (Hct) levels of 7.0 g/dL (21%). • Some patient groups (e.g., elderly with acute MI’s) seem to have better outcomes when Hct is in 3033% range. “Current data suggest rest ...
Molecular mapping of the Cromer blood group Cra and Tca... of decay accelerating factor: toward the use of recombinant antigens
... The C f and Tc" antigens are the two highincidence Cromer antigens to which alloantibodies are most frequently identified, but they have not been previously characterized at the molecular level. Unlike the Dr(a-) phenotype, the Cr(a-) and Tc(a-) phenotypes have not been associated with weakened expr ...
... The C f and Tc" antigens are the two highincidence Cromer antigens to which alloantibodies are most frequently identified, but they have not been previously characterized at the molecular level. Unlike the Dr(a-) phenotype, the Cr(a-) and Tc(a-) phenotypes have not been associated with weakened expr ...
Prevalence of Antibodies to Syphilis among Blood Donors in Accra
... giving an overall syphilis prevalence rate of 7.5%. Three of the 536 samples screened were reactive as determined by the VDRL test (0.6%; 3/536), whilst 38 were reactive as determined by the TPPA test (7.1%; 38/536). Our sample of blood donors was comprised largely of male subjects (500 out of 536 d ...
... giving an overall syphilis prevalence rate of 7.5%. Three of the 536 samples screened were reactive as determined by the VDRL test (0.6%; 3/536), whilst 38 were reactive as determined by the TPPA test (7.1%; 38/536). Our sample of blood donors was comprised largely of male subjects (500 out of 536 d ...
Human Blood Type: Testing for ABO and Rh
... medically important. In the case of blood transfusions and organ transplants, it is critical that the blood type and Rh factor match. If a Type A person were given blood from a Type B person, the anti-B agglutinins in their own plasma would attack the Type B red blood cells resulting in clumping of ...
... medically important. In the case of blood transfusions and organ transplants, it is critical that the blood type and Rh factor match. If a Type A person were given blood from a Type B person, the anti-B agglutinins in their own plasma would attack the Type B red blood cells resulting in clumping of ...
Cell Quiz Review
... cephalic, basilic, and median cubital Obtain sample from below the IV site with ...
... cephalic, basilic, and median cubital Obtain sample from below the IV site with ...
Guidance manual on “ABO and Rh blood grouping”
... The Rh blood group is one of the most complex blood groups known in humans. From its discovery 60 years ago where it was named (in error) after the Rhesus monkey, it has become second in importance only to the ABO blood group in the field of transfusion medicine. The antigens of the Rh blood group a ...
... The Rh blood group is one of the most complex blood groups known in humans. From its discovery 60 years ago where it was named (in error) after the Rhesus monkey, it has become second in importance only to the ABO blood group in the field of transfusion medicine. The antigens of the Rh blood group a ...
Erythrocytes [Red Blood Cells]
... – Transferrin is carried to muscle fiber, liver cells and liver and spleen macrophages, where Fe detaches and is stored in ferritin and hemosiderin proteins. – Waste – non-iron part of heme converted to biliverdin(green) converted to bilirubin(yelloworange) – Bilirubin into blood to liver ...
... – Transferrin is carried to muscle fiber, liver cells and liver and spleen macrophages, where Fe detaches and is stored in ferritin and hemosiderin proteins. – Waste – non-iron part of heme converted to biliverdin(green) converted to bilirubin(yelloworange) – Bilirubin into blood to liver ...
Blood - Dr Magrann
... DIFFERENTIATE, which is to decide what system of cells it will belong to. A stem cell that matures in the bone marrow will become a blood cell. Adults don’t have too many stem cells that are so immature that they have not yet decided what system of cells to belong to. Most of our stem cells have ...
... DIFFERENTIATE, which is to decide what system of cells it will belong to. A stem cell that matures in the bone marrow will become a blood cell. Adults don’t have too many stem cells that are so immature that they have not yet decided what system of cells to belong to. Most of our stem cells have ...
Common Support Medications and Interventions During
... “Magic Mouth Wash” is a special mixture of substances used to treat mouth ulcers/sores (mucositis) as a result of chemotherapy. There are various formulations used, but we most often mix equal parts of liquid diphenhydramine (Benadryl), viscous lidocaine (Xylocaine), aluminum and magnesium hydroxide ...
... “Magic Mouth Wash” is a special mixture of substances used to treat mouth ulcers/sores (mucositis) as a result of chemotherapy. There are various formulations used, but we most often mix equal parts of liquid diphenhydramine (Benadryl), viscous lidocaine (Xylocaine), aluminum and magnesium hydroxide ...
Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human) RhoGAM® Ultra
... suspected exposure to Rh-positive red blood cells. There is little information concerning the effectiveness of Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human) when given beyond this 72 hour period. In one study, Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human) provided protection against Rh immunization in about 50% of subjects when ...
... suspected exposure to Rh-positive red blood cells. There is little information concerning the effectiveness of Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human) when given beyond this 72 hour period. In one study, Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human) provided protection against Rh immunization in about 50% of subjects when ...
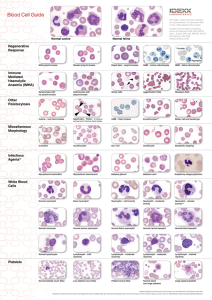
Blood Cell Guide
... parasite attachment and immune response by the host results in increased red blood cell (RBC) destruction and anaemia.2 There are three haemotropic mycoplasmas that have been identified in cats: Mycoplasma haemofelis, Candidatus Mycoplasma haemominutum and most recently Candidatus Mycoplasma turicen ...
... parasite attachment and immune response by the host results in increased red blood cell (RBC) destruction and anaemia.2 There are three haemotropic mycoplasmas that have been identified in cats: Mycoplasma haemofelis, Candidatus Mycoplasma haemominutum and most recently Candidatus Mycoplasma turicen ...
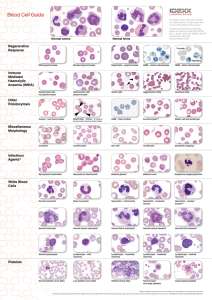
Blood Cell Guide - IDEXX Laboratories
... parasite attachment and immune response by the host results in increased red blood cell (RBC) destruction and anaemia. There are three haemotropic mycoplasmas that have been identified in cats: Mycoplasma haemofelis, Candidatus Mycoplasma haemominutum and most recently Candidatus Mycoplasma turicens ...
... parasite attachment and immune response by the host results in increased red blood cell (RBC) destruction and anaemia. There are three haemotropic mycoplasmas that have been identified in cats: Mycoplasma haemofelis, Candidatus Mycoplasma haemominutum and most recently Candidatus Mycoplasma turicens ...
G-6-PDH
... • When someone has G6PD deficiency, complications can arise; hemolytic anemia and prolonged neonatal jaundice are the two major pathologies associated with G6PD deficiency. • Both of these conditions are directly related to the inability of specific cell types to regenerate reduced nicotinamide ade ...
... • When someone has G6PD deficiency, complications can arise; hemolytic anemia and prolonged neonatal jaundice are the two major pathologies associated with G6PD deficiency. • Both of these conditions are directly related to the inability of specific cell types to regenerate reduced nicotinamide ade ...
Genetic Heterogeneity in Heterocellular Hereditary
... oligonucleotides were labeled by 3* end–tailing with a32P-dCTP using calf thymus deoxynucleotidyl terminal transferase and the terminal transferase kit from Boehringer Mannheim (Germany). Hybridizations were performed at 427C for 3 hours in 7% polyethylene glycol (PEG 6000 or 8000) and 10% sodium do ...
... oligonucleotides were labeled by 3* end–tailing with a32P-dCTP using calf thymus deoxynucleotidyl terminal transferase and the terminal transferase kit from Boehringer Mannheim (Germany). Hybridizations were performed at 427C for 3 hours in 7% polyethylene glycol (PEG 6000 or 8000) and 10% sodium do ...
Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase
... When someone has G6PD deficiency, complications can arise; hemolytic anemia and prolonged neonatal jaundice are the two major pathologies associated with G6PD deficiency. Both of these conditions are directly related to the inability of specific cell types to regenerate reduced nicotinamide adeni ...
... When someone has G6PD deficiency, complications can arise; hemolytic anemia and prolonged neonatal jaundice are the two major pathologies associated with G6PD deficiency. Both of these conditions are directly related to the inability of specific cell types to regenerate reduced nicotinamide adeni ...
Respiration and Circulation Blood Functions of Blood
... The ABO System You inherited your blood type from your parents. Blood type refers to the type of proteins, or antigens, on red blood cells. The table below shows the four human blood types: A, B, AB, and O. As you can see, type A blood cells have the A antigen. Type B blood cells have the B antigen. ...
... The ABO System You inherited your blood type from your parents. Blood type refers to the type of proteins, or antigens, on red blood cells. The table below shows the four human blood types: A, B, AB, and O. As you can see, type A blood cells have the A antigen. Type B blood cells have the B antigen. ...
Blood Collection Techniques and Limits
... This document outlines the preferred methods for collecting blood from animals and blood collection volume and frequency limits. Blood collection for experimental purposes must comply with the investigator’s Animal Care and Use Committee (ACUC) approved protocol, including approved collection techni ...
... This document outlines the preferred methods for collecting blood from animals and blood collection volume and frequency limits. Blood collection for experimental purposes must comply with the investigator’s Animal Care and Use Committee (ACUC) approved protocol, including approved collection techni ...
Blood Transfusion - Patient Education Institute
... emergencies when there is no time to test a person’s Rh type. Types of Blood Transfusions The blood used in blood transfusions typically comes from a blood bank. Blood banks collect, test, and store blood. They carefully screen all donated blood for possible problems, such as viruses that could make ...
... emergencies when there is no time to test a person’s Rh type. Types of Blood Transfusions The blood used in blood transfusions typically comes from a blood bank. Blood banks collect, test, and store blood. They carefully screen all donated blood for possible problems, such as viruses that could make ...
Blood AdministrationPPT
... Routine compatibility testing takes about 1 hour to identify recipient ABO and Rh type; in emergency O-negative RBC’s can be safely given to most without serologic testing. • Why can O-neg blood be safely given to most people? – *Universal RBC donor is O negative; universal recipient is AB positive ...
... Routine compatibility testing takes about 1 hour to identify recipient ABO and Rh type; in emergency O-negative RBC’s can be safely given to most without serologic testing. • Why can O-neg blood be safely given to most people? – *Universal RBC donor is O negative; universal recipient is AB positive ...










![Erythrocytes [Red Blood Cells]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/011997754_1-8692c5d89a78d41425c72abdd2615d43-300x300.png)