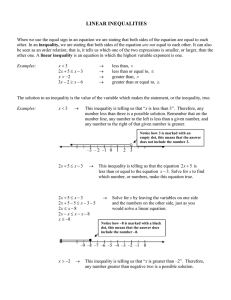
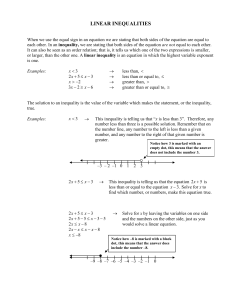
Expected Uses of Probability
... The first two problems are somewhat straightforward applications of the methods described above. Problem 2.4 (AHSME 1989). Suppose that 7 boys and 13 girls line up in a row. Let S be the number of places in the row where a boy and a girl are standing next to each other. For example, for the row GBBG ...
... The first two problems are somewhat straightforward applications of the methods described above. Problem 2.4 (AHSME 1989). Suppose that 7 boys and 13 girls line up in a row. Let S be the number of places in the row where a boy and a girl are standing next to each other. For example, for the row GBBG ...
finalReview (compile..
... 9. Monty is bored (Spring 2008) Tired of hosting the same game year after year, Monty Hall decided to make some changes to his game. There are still three doors, but now one contains 1000 dollars, one contains 500 dollars, and one contains nothing (0 dollars), with the order of the prizes randomly p ...
... 9. Monty is bored (Spring 2008) Tired of hosting the same game year after year, Monty Hall decided to make some changes to his game. There are still three doors, but now one contains 1000 dollars, one contains 500 dollars, and one contains nothing (0 dollars), with the order of the prizes randomly p ...
5 - Web4students
... b) Is this probability low enough so that overbooking is not a real concern for passengers? Is it unusual to find that there are not enough sits available? According to the answer given in part (c), it’s not unusual for 15 people to show up, then overbooking is a real concern. c) Now use a feature i ...
... b) Is this probability low enough so that overbooking is not a real concern for passengers? Is it unusual to find that there are not enough sits available? According to the answer given in part (c), it’s not unusual for 15 people to show up, then overbooking is a real concern. c) Now use a feature i ...