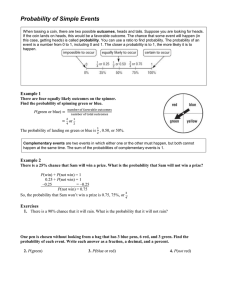
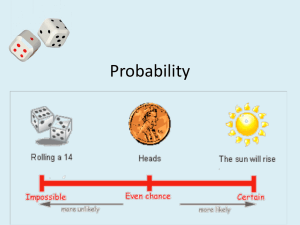
5-2 Random Variables
... either a finite number of values or countable number of values, where “countable” refers to the fact that there might be infinitely many values, but they result from a counting process Continuous random variable infinitely many values, and those values can be associated with measurements on a cont ...
... either a finite number of values or countable number of values, where “countable” refers to the fact that there might be infinitely many values, but they result from a counting process Continuous random variable infinitely many values, and those values can be associated with measurements on a cont ...
Solution - Math User Home Pages
... Do all your work in the space provided on these sheets. If you need additional paper, attach it to these sheets. On the multiple choice questions, clearly indicate the answer that you choose. If your selection is not clear, you will not earn any points for that problem. Partial credit will be reward ...
... Do all your work in the space provided on these sheets. If you need additional paper, attach it to these sheets. On the multiple choice questions, clearly indicate the answer that you choose. If your selection is not clear, you will not earn any points for that problem. Partial credit will be reward ...
Section 6.2: Possibility Trees and the Multiplication Rule
... placing these numbers as one of the digits in the number. First, for 2, there are 5 places, for 3, there will be four, for 4 there will be three and for 5 there will be two remaining places. For the last digit, we can choose any of 0, 1, 6, 7, 8, 9, so there will be six total choices. Thus, there ar ...
... placing these numbers as one of the digits in the number. First, for 2, there are 5 places, for 3, there will be four, for 4 there will be three and for 5 there will be two remaining places. For the last digit, we can choose any of 0, 1, 6, 7, 8, 9, so there will be six total choices. Thus, there ar ...