Linear Equations in One Variable
... Solutions of Equations • To solve an equation in x means to find all values of x for which the equation is true. Such values are called solutions. • For instance, x = 4 is the solution of the equation 3x – 5 = 7 since replacing x with 4 makes a true statement. ...
... Solutions of Equations • To solve an equation in x means to find all values of x for which the equation is true. Such values are called solutions. • For instance, x = 4 is the solution of the equation 3x – 5 = 7 since replacing x with 4 makes a true statement. ...
continued
... Read and reread the problem. We are going to propose a solution. Suppose the measure of the smallest angle is 30º. Then the largest angle is 30º + 90º = 120º (90º more than the smallest), and the remaining angle is 30º + 30º = 60º (30º more than the smallest). In a triangle, the sum of the measures ...
... Read and reread the problem. We are going to propose a solution. Suppose the measure of the smallest angle is 30º. Then the largest angle is 30º + 90º = 120º (90º more than the smallest), and the remaining angle is 30º + 30º = 60º (30º more than the smallest). In a triangle, the sum of the measures ...
File
... iii. Use Distributive Property a second time to factor a common binomial factor: (4y + 3)(3y2 + 2). d. A polynomial will sometimes factor to include binomials that are additive inverses (e.g., (x − 2) and (2 − x); rewriting the additive inverse as the original term times −1 may allow factoring by gr ...
... iii. Use Distributive Property a second time to factor a common binomial factor: (4y + 3)(3y2 + 2). d. A polynomial will sometimes factor to include binomials that are additive inverses (e.g., (x − 2) and (2 − x); rewriting the additive inverse as the original term times −1 may allow factoring by gr ...
parametric equations
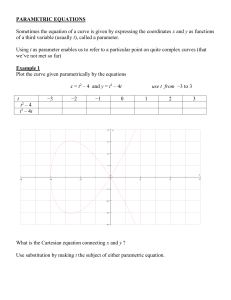
... PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS Sometimes the equation of a curve is given by expressing the coordinates x and y as functions of a third variable (usually t), called a parameter. Using t as parameter enables us to refer to a particular point on quite complex curves (that we’ve not met so far) Example 1 Plot th ...
... PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS Sometimes the equation of a curve is given by expressing the coordinates x and y as functions of a third variable (usually t), called a parameter. Using t as parameter enables us to refer to a particular point on quite complex curves (that we’ve not met so far) Example 1 Plot th ...
An Insight into Division Algorithm, Remainder and Factor Theorem
... A polynomial is an algebraic expression of the form an x n + an −1 x n −1 + .......... + a1 x + a0 , where a0 , a1 ,......an are real numbers and n is a positive integer. When a polynomial P( x) is divided by another polynomial D( x) , we stop the division when the remainder has degree less than the ...
... A polynomial is an algebraic expression of the form an x n + an −1 x n −1 + .......... + a1 x + a0 , where a0 , a1 ,......an are real numbers and n is a positive integer. When a polynomial P( x) is divided by another polynomial D( x) , we stop the division when the remainder has degree less than the ...
File - PROJECT MATHS REVISION
... let the real parts equal to each other and separately, let the imaginary parts equal to each other, therefore creating two equations. Example 1 If a bi c di Then we can say that a c and b d Please note, that when equating complex numbers, we never use the i part of the questions; we just u ...
... let the real parts equal to each other and separately, let the imaginary parts equal to each other, therefore creating two equations. Example 1 If a bi c di Then we can say that a c and b d Please note, that when equating complex numbers, we never use the i part of the questions; we just u ...