A generalized reciprocal theorem for predicting the force
... bubbles because the boundary layer induced by the shear-free condition at a bubble surface only induces secondary changes in the flow field. The work described in this communication summarizes the main findings of a recent investigation [1] in which the above goal has been pursued with the objective ...
... bubbles because the boundary layer induced by the shear-free condition at a bubble surface only induces secondary changes in the flow field. The work described in this communication summarizes the main findings of a recent investigation [1] in which the above goal has been pursued with the objective ...
Lecture 14c - TTU Physics
... volume flow rate or flux. Av = constant says that the volume that enters one end of the pipe in a given time equals the volume leaving the other end in the same time (If no leaks are present!) ...
... volume flow rate or flux. Av = constant says that the volume that enters one end of the pipe in a given time equals the volume leaving the other end in the same time (If no leaks are present!) ...
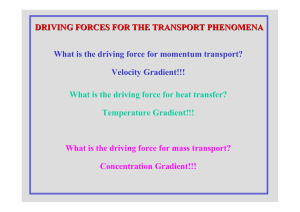
DRIVING FORCES FOR THE TRANSPORT PHENOMENA What is
... What is the driving force for heat transfer? Temperature Gradient!!! ...
... What is the driving force for heat transfer? Temperature Gradient!!! ...
umax
... 2. Water flows through a horizontal, 180o pipe bend as illustrated in Figure. The flow cross-sectional area is constant at a value of 0.1 ft2 through the bend. The flow velocity everywhere in the bend is axial and 50 ft/s. The absolute pressures at the entrance and exit of the bend are 30 psia and ...
... 2. Water flows through a horizontal, 180o pipe bend as illustrated in Figure. The flow cross-sectional area is constant at a value of 0.1 ft2 through the bend. The flow velocity everywhere in the bend is axial and 50 ft/s. The absolute pressures at the entrance and exit of the bend are 30 psia and ...
Introduction to Fluid Mechanics
... of thermodynamics, Newton’s laws of motion, and careful experiments. 4. Gases have weak intermolecular attractions and expand without limit. Liquids have much stronger intermolecular attractions and can expand very little. With increasing temperature and pressure, the differences between liquids and ...
... of thermodynamics, Newton’s laws of motion, and careful experiments. 4. Gases have weak intermolecular attractions and expand without limit. Liquids have much stronger intermolecular attractions and can expand very little. With increasing temperature and pressure, the differences between liquids and ...
Newtonian, Non-Newtonian Fluids and Viscosity
... Vector Relationships Q.15) what is the physical meaning of .V, divergence velocity component? a. .V = volumetric rate of expansion of a differential element of fluid per unit volume of that element b. .V > 0 for expanding gas c. .V < 0 for a gas being compressed d. all of the above e. none o ...
... Vector Relationships Q.15) what is the physical meaning of .V, divergence velocity component? a. .V = volumetric rate of expansion of a differential element of fluid per unit volume of that element b. .V > 0 for expanding gas c. .V < 0 for a gas being compressed d. all of the above e. none o ...
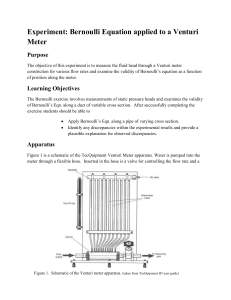
Experiment: Bernoulli Equation applied to a Venturi Meter Purpose
... 6) Once steady state is reached you may notice air bubbles trapped in the manometers. These need to be removed. Tilt the entire Venturi meter and gently pluck each manometer to dislodge the bubbles. Repeat until all the bubbles have risen to the top. 7) Increase the flow rate (to about 10gpm) until ...
... 6) Once steady state is reached you may notice air bubbles trapped in the manometers. These need to be removed. Tilt the entire Venturi meter and gently pluck each manometer to dislodge the bubbles. Repeat until all the bubbles have risen to the top. 7) Increase the flow rate (to about 10gpm) until ...
Lecture Notes for First Quiz - Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences
... airplane wings introduce paired vorticity into flow, related to lift and contrail formation Sports balls curve when the spin drags the boundary layer with medium pressure to one side, but low pressure remains on the other side, with a PGF perpendicular to the direction of motion ...
... airplane wings introduce paired vorticity into flow, related to lift and contrail formation Sports balls curve when the spin drags the boundary layer with medium pressure to one side, but low pressure remains on the other side, with a PGF perpendicular to the direction of motion ...
Where is the blood?
... • Resistance in parallel will always be less than resistance in a series. • Fact: Total resistance for all vessels is far less than the resistance of any single blood vessel • Implications: Varicose veins, amputation, thrombosis…all increase Resistance ...
... • Resistance in parallel will always be less than resistance in a series. • Fact: Total resistance for all vessels is far less than the resistance of any single blood vessel • Implications: Varicose veins, amputation, thrombosis…all increase Resistance ...
Here
... The saltwater oscillator denotes a non-linear phenomenon that can be observed when vertically neighboring liquids of different densities are periodically exchanged in a small orifice. For a conventional saltwater oscillator, a liquid with a larger density is placed above another liquid with a smalle ...
... The saltwater oscillator denotes a non-linear phenomenon that can be observed when vertically neighboring liquids of different densities are periodically exchanged in a small orifice. For a conventional saltwater oscillator, a liquid with a larger density is placed above another liquid with a smalle ...