Balaji-opt-lecture2
... Introduce the concept of slack variables. To illustrate, use the first functional constraint, x1 ≤ 4, in the Wyndor Glass Co. problem as an example. x1 ≤ 4 is equivalent to x1 + x2=4 where x2 ≥ 0. The variable x2 is called a slack variable. (3) Some functional constraints with a greater-than-or-equa ...
... Introduce the concept of slack variables. To illustrate, use the first functional constraint, x1 ≤ 4, in the Wyndor Glass Co. problem as an example. x1 ≤ 4 is equivalent to x1 + x2=4 where x2 ≥ 0. The variable x2 is called a slack variable. (3) Some functional constraints with a greater-than-or-equa ...
Unconstrained Univariate Optimization
... Quasi-Newton Methods A major drawback of Newton’s method is that it requires us to have analytically determined both the first and second derivatives of our objective function. Often this is considered onerous, particularly in the case of the second derivative. The large family of optimization algo ...
... Quasi-Newton Methods A major drawback of Newton’s method is that it requires us to have analytically determined both the first and second derivatives of our objective function. Often this is considered onerous, particularly in the case of the second derivative. The large family of optimization algo ...
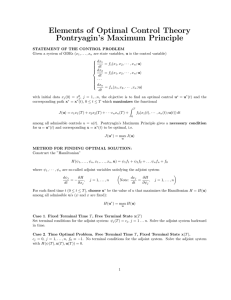
Elements of Optimal Control Theory Pontryagin’s Maximum Principle
... consciously, but is determined by complex genetic characteristics of the insects. We may hypothesize, however, that those colonies that adopt nearly optimal policies of production will have an advantage over their competitors who do not. Thus, it is expected that through continued natural selection, ...
... consciously, but is determined by complex genetic characteristics of the insects. We may hypothesize, however, that those colonies that adopt nearly optimal policies of production will have an advantage over their competitors who do not. Thus, it is expected that through continued natural selection, ...
Swarm Intelligence
... The systems are robust because agents are simple in design, the reliance on individual agents is small, and failure of a single agents has little impact on the system’s performance The systems are able to adapt to new situations ...
... The systems are robust because agents are simple in design, the reliance on individual agents is small, and failure of a single agents has little impact on the system’s performance The systems are able to adapt to new situations ...