The Sampling Distribution of an Estimator
... A comparison of the two above figures shows that the bigger the sample size, the better the values in the underlying population are represented. It is also obvious that, for a fixed sample size, different sets of population values can be represented in the various samples that can possibly be drawn. ...
... A comparison of the two above figures shows that the bigger the sample size, the better the values in the underlying population are represented. It is also obvious that, for a fixed sample size, different sets of population values can be represented in the various samples that can possibly be drawn. ...
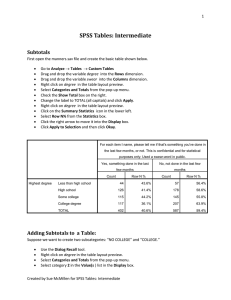
Adding Subtotals to a Table
... The table above means that there is a significant difference between the mean age in column (A) and the mean age in columns (B) and (C). There is also a significant difference between the mean in column (B) and the mean in column (C). However the mean age for column (D) does not differ significantly ...
... The table above means that there is a significant difference between the mean age in column (A) and the mean age in columns (B) and (C). There is also a significant difference between the mean in column (B) and the mean in column (C). However the mean age for column (D) does not differ significantly ...
View - CAUSEweb
... good estimator for evaluating the true mean of a distribution. But are there other estimators that can perform as well or better? It’s known that a trimmed mean (mean with a fixed number of extreme values removed) and the median (maximal amount of trimming) have been unbiased estimators for symmetri ...
... good estimator for evaluating the true mean of a distribution. But are there other estimators that can perform as well or better? It’s known that a trimmed mean (mean with a fixed number of extreme values removed) and the median (maximal amount of trimming) have been unbiased estimators for symmetri ...
Ch_ 8 Student Notes
... The following command was executed on their calculator: mean(randNorm(M,20,16)) The result was 240.79. This tells us the calculator chose an SRS of 16 observations from a Normal population with mean M and standard deviation 20. The resulting sample mean of those 16 values was 240.79. Your group must ...
... The following command was executed on their calculator: mean(randNorm(M,20,16)) The result was 240.79. This tells us the calculator chose an SRS of 16 observations from a Normal population with mean M and standard deviation 20. The resulting sample mean of those 16 values was 240.79. Your group must ...
SAMPLING TECHNIQUES INTRODUCTION
... fraction would be n/N = 20/100 = 20%. In this case, the interval size, k, is equal to N/n = 100/20 = 5. Now, select a random integer from 1 to 5. In our example, imagine that you chose 4. Now, to select the sample, start with the 4th unit in the list and take every k-th unit (every 5th, because k=5) ...
... fraction would be n/N = 20/100 = 20%. In this case, the interval size, k, is equal to N/n = 100/20 = 5. Now, select a random integer from 1 to 5. In our example, imagine that you chose 4. Now, to select the sample, start with the 4th unit in the list and take every k-th unit (every 5th, because k=5) ...