Geometry 2016-17 ~ Unit 2 Lines, Angles, and Triangles *CISD
... Hypotenuse-Leg (SSS) - only true for right triangle bc since it has a right angle you can use the Pythagorean theorem. it only will give you one possible value for the 3rd side. ...
... Hypotenuse-Leg (SSS) - only true for right triangle bc since it has a right angle you can use the Pythagorean theorem. it only will give you one possible value for the 3rd side. ...
Slides for Nov. 12, 2014, lecture
... manifold; the collection of all possible physical colors is as well, since an individual physical color can be uniquely identified by the values (modes of specification) of its hue, saturation and brightness, all of which vary continuously ...
... manifold; the collection of all possible physical colors is as well, since an individual physical color can be uniquely identified by the values (modes of specification) of its hue, saturation and brightness, all of which vary continuously ...
Geometry Fundamentals - Art of Problem Solving
... 2. Let BD be the angle bisector of angle B in triangle ABC with D on side AC. The circumcircle of triangle BDC meets AB at E, while the circumcircle of triangle ABD meets BC at F . Prove that AE = CF . 3. Draw tangents OA and OB from a point O to a given circle. Through A is drawn a chord AC paralle ...
... 2. Let BD be the angle bisector of angle B in triangle ABC with D on side AC. The circumcircle of triangle BDC meets AB at E, while the circumcircle of triangle ABD meets BC at F . Prove that AE = CF . 3. Draw tangents OA and OB from a point O to a given circle. Through A is drawn a chord AC paralle ...
Hyperbolic
... Note. (From Non-Euclidean Geometry by Roberto Bonola, Dover Publications, 1955.) Historically, it is recognized that there are three founders of hyperbolic geometry: Carl Frederick Gauss (1777–1855), Nicolai Lobachevsky (1793–1856), and Johann Bolyai (1802–1860). Historical documents (primarily in t ...
... Note. (From Non-Euclidean Geometry by Roberto Bonola, Dover Publications, 1955.) Historically, it is recognized that there are three founders of hyperbolic geometry: Carl Frederick Gauss (1777–1855), Nicolai Lobachevsky (1793–1856), and Johann Bolyai (1802–1860). Historical documents (primarily in t ...
Geometry Curriculum - Oneonta City School District
... volume equals the product of the area of the base and the altitude lateral area of a right circular cylinder equals the product of an altitude and the circumference of the base ...
... volume equals the product of the area of the base and the altitude lateral area of a right circular cylinder equals the product of an altitude and the circumference of the base ...
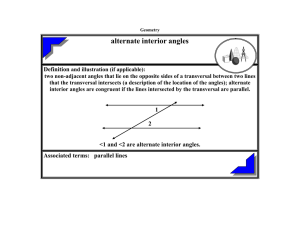
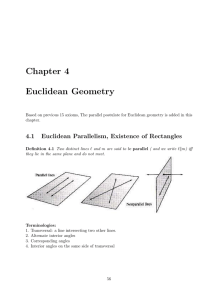
alternate interior angles
... the usual theorems in geometry. One of the five postulates Euclid used was Parallel Postulate: Through a point not on a given line, there is exactly one line parallel to the given line. In the eighteenth century, mathematicians began to explore two different parallel postulates: Spherical Geometry-- ...
... the usual theorems in geometry. One of the five postulates Euclid used was Parallel Postulate: Through a point not on a given line, there is exactly one line parallel to the given line. In the eighteenth century, mathematicians began to explore two different parallel postulates: Spherical Geometry-- ...
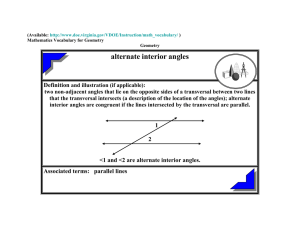
Geometry Vocabulary
... the usual theorems in geometry. One of the five postulates Euclid used was Parallel Postulate: Through a point not on a given line, there is exactly one line parallel to the given line. In the eighteenth century, mathematicians began to explore two different parallel postulates: Spherical Geometry-- ...
... the usual theorems in geometry. One of the five postulates Euclid used was Parallel Postulate: Through a point not on a given line, there is exactly one line parallel to the given line. In the eighteenth century, mathematicians began to explore two different parallel postulates: Spherical Geometry-- ...