321-12-taxa-Diatoms2005
... Photosynthetic, productive even in cold nutrient-rich water (Antarctic, etc.) Base of the food chain = “Grass of the sea” (Account for up to 25% total world primary food production by phytoplankton. Some species harvested for food for shellfish industry.) ...
... Photosynthetic, productive even in cold nutrient-rich water (Antarctic, etc.) Base of the food chain = “Grass of the sea” (Account for up to 25% total world primary food production by phytoplankton. Some species harvested for food for shellfish industry.) ...
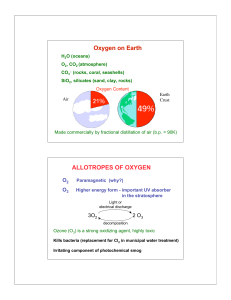
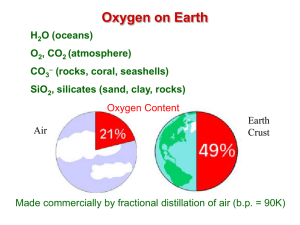
Chapter 11: The rise of oxygen and ozone – ppt
... the their ration can be used as evidence of methanogenic activity. But this requires a little bit extra: IF the CH4 thus produced is used by other organisms, which died and eventually made it to the sediments (the ‘preserved geological record’ which is analyzed), then the record will show low 13C co ...
... the their ration can be used as evidence of methanogenic activity. But this requires a little bit extra: IF the CH4 thus produced is used by other organisms, which died and eventually made it to the sediments (the ‘preserved geological record’ which is analyzed), then the record will show low 13C co ...
Air pollution
... A. Acidic deposition = the deposition of acid, or acid-forming pollutants, from the atmosphere onto Earth’s surface 1. Acid rain = precipitation of acid 2. Atmospheric deposition = the wet or dry deposition on land of pollutants 3. Acid rain is considered to be precipitation with a pH of less than 5 ...
... A. Acidic deposition = the deposition of acid, or acid-forming pollutants, from the atmosphere onto Earth’s surface 1. Acid rain = precipitation of acid 2. Atmospheric deposition = the wet or dry deposition on land of pollutants 3. Acid rain is considered to be precipitation with a pH of less than 5 ...
Environmental Science
... 1. When sugar is “burnt” for energy, CO2 is left over and exhaled. 2. Carbon can also be released by decomposers after the organism dies. III. Fossil Fuel and the Carbon Cycle A. Sometimes, instead of breaking down, organisms get buried in the ground. B. Over millions of years, their bodies become o ...
... 1. When sugar is “burnt” for energy, CO2 is left over and exhaled. 2. Carbon can also be released by decomposers after the organism dies. III. Fossil Fuel and the Carbon Cycle A. Sometimes, instead of breaking down, organisms get buried in the ground. B. Over millions of years, their bodies become o ...
Harmful microalgal episodes in Greek coastal waters
... a few thousands cells can at times cause harm to humans and to marine ecosystems. The negative effects of harmful algae are many and diverse, ranging from economical losses in aquaculture, fisheries and tourism industry to major environmental and human impacts. Attending the problems that they cause ...
... a few thousands cells can at times cause harm to humans and to marine ecosystems. The negative effects of harmful algae are many and diverse, ranging from economical losses in aquaculture, fisheries and tourism industry to major environmental and human impacts. Attending the problems that they cause ...
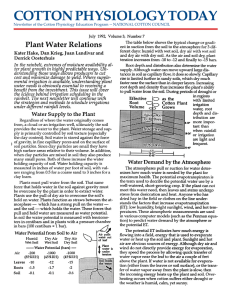
Plant Water Relations - National Cotton Council
... water flow. When the soil surface is wet, the resistance for evaporation is very low and most of the water flow is from the surface soil, but as the soil surface dries, resistance to evaporative water flow increases and plant transpiration becomes the dominant route. The transpiration process relies ...
... water flow. When the soil surface is wet, the resistance for evaporation is very low and most of the water flow is from the surface soil, but as the soil surface dries, resistance to evaporative water flow increases and plant transpiration becomes the dominant route. The transpiration process relies ...
Chemistry Notes - The Bored of Studies Community
... of synthesising ammonia. Increasing demands for nitrogenous fertiliser to grow food for increasing world populations were placing strains on the supply of naturally-occurring Chile saltpetre (sodium nitrate), the main ‘artificial’ fertiliser at that time. In addition the growing militancy of Germany ...
... of synthesising ammonia. Increasing demands for nitrogenous fertiliser to grow food for increasing world populations were placing strains on the supply of naturally-occurring Chile saltpetre (sodium nitrate), the main ‘artificial’ fertiliser at that time. In addition the growing militancy of Germany ...
Eutrophication
Eutrophication (Greek: eutrophia—healthy, adequate nutrition, development; German: Eutrophie) or more precisely hypertrophication, is the ecosystem's response to the addition of artificial or natural substances, mainly phosphates, through detergents, fertilizers, or sewage, to an aquatic system. One example is the ""bloom"" or great increase of phytoplankton in a water body as a response to increased levels of nutrients. Negative environmental effects include hypoxia, the depletion of oxygen in the water, which may cause death to aquatic animals.