a system of quadrics describing the orbit of the highest weight vector
... First, % is a union of G-orbits, and, if x E Vx is any Vector with G-orbit 6X, then ^(0^) contains tr(vx) in its closure. [Since Vx is irreducible, every orbit 6X spans Vx, so we may assume x = cvx + y with c ¥= 0 and y a linear combination of weight vectors of weight less than A. Now choose H Eb su ...
... First, % is a union of G-orbits, and, if x E Vx is any Vector with G-orbit 6X, then ^(0^) contains tr(vx) in its closure. [Since Vx is irreducible, every orbit 6X spans Vx, so we may assume x = cvx + y with c ¥= 0 and y a linear combination of weight vectors of weight less than A. Now choose H Eb su ...
Chapter 2 - Cartesian Vectors and Tensors: Their Algebra Definition
... Conversely, if the relative velocity between any pair of points is described by the above equation with the same value of angular velocity, then the motion is due to a rigid body rotation. Triple scalar product The triple scalar product is the scalar product of the first vector with the vector produ ...
... Conversely, if the relative velocity between any pair of points is described by the above equation with the same value of angular velocity, then the motion is due to a rigid body rotation. Triple scalar product The triple scalar product is the scalar product of the first vector with the vector produ ...
u · v
... vectors. To provide maximum geometric insight, we concentrate on vectors in two-space and three-space. Later, in Chapter 3, we will generalize many of the ideas developed in this chapter and apply them to a study of vectors in n-space, that is, to vectors in Rn. A major emphasis in Chapter 3 is on c ...
... vectors. To provide maximum geometric insight, we concentrate on vectors in two-space and three-space. Later, in Chapter 3, we will generalize many of the ideas developed in this chapter and apply them to a study of vectors in n-space, that is, to vectors in Rn. A major emphasis in Chapter 3 is on c ...
Unit 8 Corrective
... the angle formed by a horizontal line and a line of sight to a point below in a right triangle, the ratio of the length of the leg opposite the angle to the length of the hypotenuse in a right triangle, the ratio of the length of the leg adjacent to the angle to the length of the hypotenuse a ratio ...
... the angle formed by a horizontal line and a line of sight to a point below in a right triangle, the ratio of the length of the leg opposite the angle to the length of the hypotenuse in a right triangle, the ratio of the length of the leg adjacent to the angle to the length of the hypotenuse a ratio ...
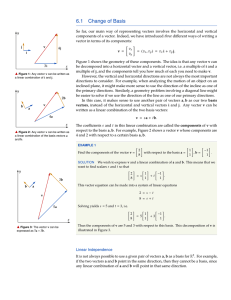
4.3 Linear Combinations and Spanning Sets
... From the last line, we see that the system has no solution. So, v cannot be expressed as a linear combination of u1 ; u2 and u3 . In general, given v 2 V and u1 ; u2 ; :::; un in V , determining if v is a linear combination of the vectors u1 ; u2 ; :::; un is simply a matter of solving the system of ...
... From the last line, we see that the system has no solution. So, v cannot be expressed as a linear combination of u1 ; u2 and u3 . In general, given v 2 V and u1 ; u2 ; :::; un in V , determining if v is a linear combination of the vectors u1 ; u2 ; :::; un is simply a matter of solving the system of ...
Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line Position, Displacement
... Note that it traveled to the right for a total of 15 meters in 5 seconds. We say that the ball’s velocity is +3 m/s (+15 m / 5 s). The (+) sign signifies it moved in the positive x-direction. Now consider the following motion that takes 4 seconds. x/m Note that it traveled to the left for a total ...
... Note that it traveled to the right for a total of 15 meters in 5 seconds. We say that the ball’s velocity is +3 m/s (+15 m / 5 s). The (+) sign signifies it moved in the positive x-direction. Now consider the following motion that takes 4 seconds. x/m Note that it traveled to the left for a total ...