OPTICS
... 1. A real image can be projected on a screen when placed where the image is formed. a. Lenses in a slide projector or a camera produce real images C. Virtual Image-formed when the light rays from a common point pass through or are reflected by an optical system that causes them to diverge and appea ...
... 1. A real image can be projected on a screen when placed where the image is formed. a. Lenses in a slide projector or a camera produce real images C. Virtual Image-formed when the light rays from a common point pass through or are reflected by an optical system that causes them to diverge and appea ...
d - Madison Public Schools
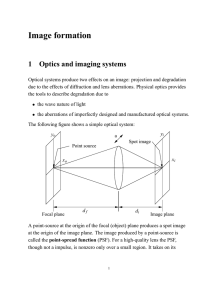
... Although principal rays help guide us to locate the image, we cannot forget the important fact that each point on the object emits rays in all directions. The lens is completely filled with rays from every point of the object! ...
... Although principal rays help guide us to locate the image, we cannot forget the important fact that each point on the object emits rays in all directions. The lens is completely filled with rays from every point of the object! ...
lab9 - University of Puget Sound
... What happens to a well-focused image when a portion of the lens is blocked? Does the left side of the image disappear when the left half of the lens is covered? Or the right half, or what? Explain your observations. Describe what happens when the object distance is less than the focal length. Can yo ...
... What happens to a well-focused image when a portion of the lens is blocked? Does the left side of the image disappear when the left half of the lens is covered? Or the right half, or what? Explain your observations. Describe what happens when the object distance is less than the focal length. Can yo ...
Lens Types
... from the object to the lens, z2 is the length from the lens to the focal point, and f is the focal length the equation to find the magnification is , M=-(z2/z1) You would place a sensor at the focal point to get a focused image Convex have a + focal length (image is on the other side of light) Conca ...
... from the object to the lens, z2 is the length from the lens to the focal point, and f is the focal length the equation to find the magnification is , M=-(z2/z1) You would place a sensor at the focal point to get a focused image Convex have a + focal length (image is on the other side of light) Conca ...
lecture1
... to eliminate some of the peripheral rays but results in decrease aperture angle and therefore resolution This is Cs programs for image processing 2.0 mm in 2100, constant Bizzola Electron Microscopy 1999 ...
... to eliminate some of the peripheral rays but results in decrease aperture angle and therefore resolution This is Cs programs for image processing 2.0 mm in 2100, constant Bizzola Electron Microscopy 1999 ...
Transmission Electron Microscopy -TEM
... waves. Ruska was aware that magnetic fields affect electron trajectories, possibly focusing them as optical lenses do to light. After confirming these principles he set out to design the electron microscope, which he knew would be much more powerful than an ordinary optical microscope since electron ...
... waves. Ruska was aware that magnetic fields affect electron trajectories, possibly focusing them as optical lenses do to light. After confirming these principles he set out to design the electron microscope, which he knew would be much more powerful than an ordinary optical microscope since electron ...
PHYSICS 504 OPTICS REVIEW: Important things to remember: 1
... calculations, explain how it is possible for Marlin and Nemo to see each other from their present positions. Justify your answer. Air ...
... calculations, explain how it is possible for Marlin and Nemo to see each other from their present positions. Justify your answer. Air ...
PHYSICS 504 OPTICS REVIEW: Important things to remember
... calculations, explain how it is possible for Marlin and Nemo to see each other from their present positions. Justify your answer. Air ...
... calculations, explain how it is possible for Marlin and Nemo to see each other from their present positions. Justify your answer. Air ...
PDF - Bridgend Astronomical Society
... determines the magnification of the optical system. Magnification is simply the Focal Length of the telescope divided by the Focal Length of the ocular. There are many types of ocular, each having it’s good and bad points. Eye Relief is important for many observers, especially if spectacles are worn ...
... determines the magnification of the optical system. Magnification is simply the Focal Length of the telescope divided by the Focal Length of the ocular. There are many types of ocular, each having it’s good and bad points. Eye Relief is important for many observers, especially if spectacles are worn ...
explanation
... nature of the material and on the frequency of the incident light. If some of the light is reflected or transmitted, it will reach the retina in our eyes which is sensitive to light and then sent as impulses to our brain. As sunlight is a mixture of various frequencies, some frequencies will be abso ...
... nature of the material and on the frequency of the incident light. If some of the light is reflected or transmitted, it will reach the retina in our eyes which is sensitive to light and then sent as impulses to our brain. As sunlight is a mixture of various frequencies, some frequencies will be abso ...
Stop Faking It! Light
... Electromagnetic waves are arranged by the degree of frequency, from radio waves to gamma waves. They are waves that don’t require a medium (can travel through space) E-waves all travel at the speed of light The energy of the e-wave moves/ is transferred by radiation ...
... Electromagnetic waves are arranged by the degree of frequency, from radio waves to gamma waves. They are waves that don’t require a medium (can travel through space) E-waves all travel at the speed of light The energy of the e-wave moves/ is transferred by radiation ...
Light Microscopy
... Light as electromagnetic wave with mutually perpendicular E, B components characterized by wavelength,λ, and frequency, ν, in cycles/s. Wave velocity = ν x λ. [λ=500nm--> ν=6x1014 cycles/s] ...
... Light as electromagnetic wave with mutually perpendicular E, B components characterized by wavelength,λ, and frequency, ν, in cycles/s. Wave velocity = ν x λ. [λ=500nm--> ν=6x1014 cycles/s] ...
SP212 Lab: Nine→ Thin Lenses Version: April, 2014 Page 1 of 2
... a laser on the lab jack as your instructor demonstrates. It is necessary to adjust the laser so that the laser beam lies on the lens’s optical axis. Note the position of the image of the ...
... a laser on the lab jack as your instructor demonstrates. It is necessary to adjust the laser so that the laser beam lies on the lens’s optical axis. Note the position of the image of the ...
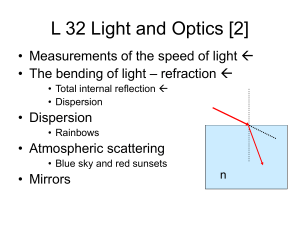
L32
... • The water and ice scatter the sunlight • Scattering by water and ice (particles) is very different from scattering by molecules • The atoms are smaller than the wavelength of light, but the ice and water particles are larger • Scattering by particles does not favor any particular wavelength so the ...
... • The water and ice scatter the sunlight • Scattering by water and ice (particles) is very different from scattering by molecules • The atoms are smaller than the wavelength of light, but the ice and water particles are larger • Scattering by particles does not favor any particular wavelength so the ...
CP Physics - Ms. Lisa Cole-
... 2. The area of the eye on which light is focused is called the ____________________ 3. As a ray of light passes from air into the lens, the speed of light ____________. 4. A diverging lens ____________________________ 5. A magnifying glass is usually a ____________________________. 6. If a person’s ...
... 2. The area of the eye on which light is focused is called the ____________________ 3. As a ray of light passes from air into the lens, the speed of light ____________. 4. A diverging lens ____________________________ 5. A magnifying glass is usually a ____________________________. 6. If a person’s ...
Plane Mirrors
... Homework: ALL answers must be written on looseleaf paper. No answers placed on this sheet will be accepted. 1) A plane mirror produces a real / virtual (choose one) image. This is known as the image’s TYPE. 2) A plane mirror produces an upright / inverted (choose one) image. This is known as the im ...
... Homework: ALL answers must be written on looseleaf paper. No answers placed on this sheet will be accepted. 1) A plane mirror produces a real / virtual (choose one) image. This is known as the image’s TYPE. 2) A plane mirror produces an upright / inverted (choose one) image. This is known as the im ...
Physics 212 HW17 - University of St. Thomas
... M01. An object 0.600 cm tall is placed 16.5 cm to the left of the vertex of a converging spherical mirror having a radius of curvature of 22.0 cm. a) Draw a principal-ray diagram showing formation of the image. b) Determine the position, size, orientation, and nature (real or virtual) of the image. ...
... M01. An object 0.600 cm tall is placed 16.5 cm to the left of the vertex of a converging spherical mirror having a radius of curvature of 22.0 cm. a) Draw a principal-ray diagram showing formation of the image. b) Determine the position, size, orientation, and nature (real or virtual) of the image. ...
name
... 1. Cut the filter paper into an oblong strip wide enough to fit into the test tube without touching the sides of the test tube. The strip should be 5 cm longer than the length of the test tube. Cut one end into a point. Using a pencil, draw a light line across the strip about 2 cm from the tip of th ...
... 1. Cut the filter paper into an oblong strip wide enough to fit into the test tube without touching the sides of the test tube. The strip should be 5 cm longer than the length of the test tube. Cut one end into a point. Using a pencil, draw a light line across the strip about 2 cm from the tip of th ...
clicker questions 2
... Consider two light fields in vacuum, one at 532 nm (green), the other at 400 nm wavelength (blue). If you multiply the wavelength of each light field with the corresponding frequency , the result will be … (A) … a larger number for the green light field than for the blue ...
... Consider two light fields in vacuum, one at 532 nm (green), the other at 400 nm wavelength (blue). If you multiply the wavelength of each light field with the corresponding frequency , the result will be … (A) … a larger number for the green light field than for the blue ...
2 Reflection
... where the line OA’ and the mirror intersect. Draw a solid line (representing the reflected ray of light) over the portion IO of the line. No real ray travels between A’ and I. ...
... where the line OA’ and the mirror intersect. Draw a solid line (representing the reflected ray of light) over the portion IO of the line. No real ray travels between A’ and I. ...
PochPHYS104-Obj_Chapt23Sp13
... solve for the magnification using the information in (d). identify the basic principles of how a microscope magnifies light, solve for the magnification knowing me and mo, plus apply to explain a practical example. ...
... solve for the magnification using the information in (d). identify the basic principles of how a microscope magnifies light, solve for the magnification knowing me and mo, plus apply to explain a practical example. ...
pupil function - UCT Digital Image Processing
... Note that as the aperture size a increases, the PSF becomes narrower. This allows objects to be imaged with higher resolution, and is (part of) the reason for telescopes having such a large diameter. (They also have a large aperture to capture a larger portion of the incoming light.) Synthetic apert ...
... Note that as the aperture size a increases, the PSF becomes narrower. This allows objects to be imaged with higher resolution, and is (part of) the reason for telescopes having such a large diameter. (They also have a large aperture to capture a larger portion of the incoming light.) Synthetic apert ...
Image intensifier

An image intensifier or image intensifier tube is a vacuum tube device for increasing the intensity of available light in an optical system to allow use under low-light conditions, such as at night, to facilitate visual imaging of low-light processes, such as fluorescence of materials in x-rays or gamma rays (x-ray image intensifier), or for conversion of non-visible light sources, such as near-infrared or short wave infrared to visible. They operate by converting photons of light into electrons, amplifying the electrons (usually with a microchannel plate), and then converting the amplified electrons back into photons for viewing. They are used in devices such as night vision goggles.