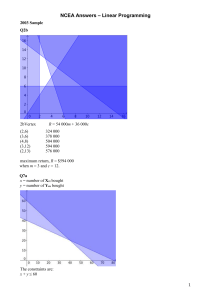
10.3 Slope-Intercept Form of Linear Equations
... chicken costs $3 per pound, the graph at the right shows all the possible combinations of beef and chicken he can buy. If he buys no beef, he can buy 5 pounds of chicken. If he buys no chicken, he can buy 3 pounds of beef. The number 5 on the x-axis and the number 3 on the y-axis are called ...
... chicken costs $3 per pound, the graph at the right shows all the possible combinations of beef and chicken he can buy. If he buys no beef, he can buy 5 pounds of chicken. If he buys no chicken, he can buy 3 pounds of beef. The number 5 on the x-axis and the number 3 on the y-axis are called ...
U.S. NAVAL ACADEMY COMPUTER SCIENCE DEPARTMENT TECHNICAL REPORT Algorithmic Reformulation of Polynomial Problems
... rewritings of a formula. The following definition and theorem make that precise. Definition 2 Given rewrite graph G = (VQ , VOR , E, S), define the function H mapping vertices into Tarski formulas as follows: 1. If v is a Q-node with children w1 , . . . , wa , H(v) = S(v) ∪ H(w1 ) ∪ H(w2 ) ∪ · · · ∪ ...
... rewritings of a formula. The following definition and theorem make that precise. Definition 2 Given rewrite graph G = (VQ , VOR , E, S), define the function H mapping vertices into Tarski formulas as follows: 1. If v is a Q-node with children w1 , . . . , wa , H(v) = S(v) ∪ H(w1 ) ∪ H(w2 ) ∪ · · · ∪ ...
9781285852751_PPT_ch20 - Business and Computer Science
... there is an edge between them C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Seventh Edition ...
... there is an edge between them C++ Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures, Seventh Edition ...
graph homomorphism profiles
... of A. Given the power sums λi for 1 ≤ k ≤ n, Newton’s relations yield the elementary symmetric polynomials in the λi and hence the λi are uniquely determined (as the roots of the characteristic polynomial of A). Restricting attention to simple unweighted undirected graphs, graphs determined by their ...
... of A. Given the power sums λi for 1 ≤ k ≤ n, Newton’s relations yield the elementary symmetric polynomials in the λi and hence the λi are uniquely determined (as the roots of the characteristic polynomial of A). Restricting attention to simple unweighted undirected graphs, graphs determined by their ...
as a PDF
... in the final solution plan. The decision about validity/invalidity of the node is done by the solver. We also augment the precedence network by a description of splitting and joining operations that implicitly define dependencies between nodes in the network. The dependency relations specify which n ...
... in the final solution plan. The decision about validity/invalidity of the node is done by the solver. We also augment the precedence network by a description of splitting and joining operations that implicitly define dependencies between nodes in the network. The dependency relations specify which n ...
Presentation - MIT Lincoln Laboratory
... This work was sponsored by DARPA under Air Force Contract FA8721-05-C-0002. Opinions, interpretations, conclusions and recommendations are those of the authors and are not necessarily endorsed by the United States Government. ...
... This work was sponsored by DARPA under Air Force Contract FA8721-05-C-0002. Opinions, interpretations, conclusions and recommendations are those of the authors and are not necessarily endorsed by the United States Government. ...
Centrality

In graph theory and network analysis, indicators of centrality identify the most important vertices within a graph. Applications include identifying the most influential person(s) in a social network, key infrastructure nodes in the Internet or urban networks, and super-spreaders of disease. Centrality concepts were first developed in social network analysis, and many of the terms used to measure centrality reflect their sociological origin.They should not be confused with node influence metrics, which seek to quantify the influence of every node in the network.