Progress on Component-Based Subsurface Simulation I: Smooth
... data belong together in a component • Granularity: At what level is componentization compatible with performance? • Abstraction of Interfaces: Can interfaces be defined that support multiple implementations representing different models and/or algorithms? • Resource Allocation: Which components allo ...
... data belong together in a component • Granularity: At what level is componentization compatible with performance? • Abstraction of Interfaces: Can interfaces be defined that support multiple implementations representing different models and/or algorithms? • Resource Allocation: Which components allo ...
lesson_matrices
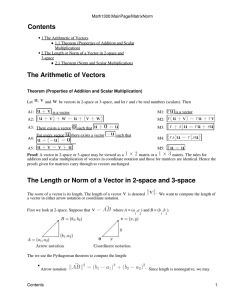
... Types of Matrices A matrix is described by the numbers of rows and columns it has, specifically called the dimensions of the matrix. The number of rows is stated first. ...
... Types of Matrices A matrix is described by the numbers of rows and columns it has, specifically called the dimensions of the matrix. The number of rows is stated first. ...
counting degrees of freedom of the electromagnetic field
... is “pure gauge”. This part of the vector potential obviously cannot be determined from J~ and any initial data by the field equation, since it is entirely at our whim. (Even if the Lorenz gauge condition is imposed, we can still perform a gauge transformation with χ a solution of the scalar wave eq ...
... is “pure gauge”. This part of the vector potential obviously cannot be determined from J~ and any initial data by the field equation, since it is entirely at our whim. (Even if the Lorenz gauge condition is imposed, we can still perform a gauge transformation with χ a solution of the scalar wave eq ...
A.1 Summary of Matrices
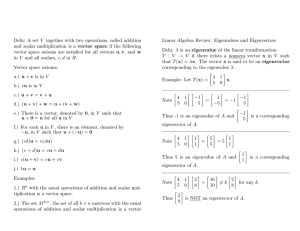
... where the jth col consists of components of eigenvector e j. For the transformation to be unitary, the eigenvectors must be orthonormal (orthogonal and normalized). A.3 ...
... where the jth col consists of components of eigenvector e j. For the transformation to be unitary, the eigenvectors must be orthonormal (orthogonal and normalized). A.3 ...