Solutions to Math 51 First Exam — April 21, 2011
... (4 points) We’ve seen that one basis for C(A) is formed by taking the columns of A that correspond to the pivot-columns of rref(A). Thus, {a1 , a2 , a4 } is a basis for C(A). From this, it immediately follows that dim C(A) = 3 and therefore no set of size 1, 2, or 4 can ever be a basis for C(A); we ...
... (4 points) We’ve seen that one basis for C(A) is formed by taking the columns of A that correspond to the pivot-columns of rref(A). Thus, {a1 , a2 , a4 } is a basis for C(A). From this, it immediately follows that dim C(A) = 3 and therefore no set of size 1, 2, or 4 can ever be a basis for C(A); we ...
Getting Ready SPH4U Significant figures 1. Indicate the number of
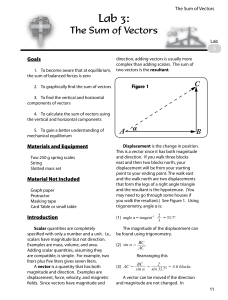
... Scalar and Vector quantities Note: For vector directions we will use the same convention as described in the book thus [30 N of E] means turn East and then turn 30 toward North. The other convention is to write the same vector as follows [N70E] which means turn North and then turn 70 toward East ...
... Scalar and Vector quantities Note: For vector directions we will use the same convention as described in the book thus [30 N of E] means turn East and then turn 30 toward North. The other convention is to write the same vector as follows [N70E] which means turn North and then turn 70 toward East ...
1. What is the cardinality of the following sets
... 3. Does A ∩ C = B ∩ C imply A = B prove your answer. 4. Show (A − B) − C ⊂ A − C. 5. Use symbolic notation to write the definition of A ⊂ B. 6. Is the function f : Z → N defined by f (x) = x2 − x one to one? Justify your answer. 7. Is the function f : students in CS247 → eyecolor defined choosing th ...
... 3. Does A ∩ C = B ∩ C imply A = B prove your answer. 4. Show (A − B) − C ⊂ A − C. 5. Use symbolic notation to write the definition of A ⊂ B. 6. Is the function f : Z → N defined by f (x) = x2 − x one to one? Justify your answer. 7. Is the function f : students in CS247 → eyecolor defined choosing th ...