Goal Recognition with Markov Logic Networks for Player
... likely goal for a given sequence of observed player actions in the game environment. Current work assumes that a given sequence of actions maps to a single goal, and no interleaving occurs between actions associated with different goals. Under these conditions, goal recognition is cast as a classifi ...
... likely goal for a given sequence of observed player actions in the game environment. Current work assumes that a given sequence of actions maps to a single goal, and no interleaving occurs between actions associated with different goals. Under these conditions, goal recognition is cast as a classifi ...
Evolution and Game Theory - DARP
... center stage: Should we expect Nash equilibrium play—that is, should we expect the choice of each player to be a best response to the choices of the other players? If so, which of the multiple Nash equilibria that arise in many games should we expect? In the 1980s, game theorists addressed these que ...
... center stage: Should we expect Nash equilibrium play—that is, should we expect the choice of each player to be a best response to the choices of the other players? If so, which of the multiple Nash equilibria that arise in many games should we expect? In the 1980s, game theorists addressed these que ...
Interpretations on the Racialized Experience of Video Games
... (APA 2004). On the other hand, other studies have become more skeptical as to whether such a causal link exists. One study by Dunkin and Barber concluded that there was “no evidence obtained of negative outcomes among game players” and that gamers received higher scores than non-gamer participants i ...
... (APA 2004). On the other hand, other studies have become more skeptical as to whether such a causal link exists. One study by Dunkin and Barber concluded that there was “no evidence obtained of negative outcomes among game players” and that gamers received higher scores than non-gamer participants i ...
Constitutive Rules in Game Theory: Two Accounts, One Rejection
... him to be doing this presupposes the rule-like practice which constitutes the game” (Rawls 1955, p.25). The practice of playing baseball, which is defined by the fact of following a set of well-defined rules, is thus logically prior to any specific case where the practice is instantiated. The point ...
... him to be doing this presupposes the rule-like practice which constitutes the game” (Rawls 1955, p.25). The practice of playing baseball, which is defined by the fact of following a set of well-defined rules, is thus logically prior to any specific case where the practice is instantiated. The point ...
Playout Policy Adaptation for Games - LAMSADE
... A related domain is the learning of playout policies in single-player problems. Nested Monte Carlo Search (NMCS) [3] is an algorithm that works well for puzzles. It biases its playouts using lower level playouts. At level zero NMCS adopts a uniform random playout policy. Online learning of playout s ...
... A related domain is the learning of playout policies in single-player problems. Nested Monte Carlo Search (NMCS) [3] is an algorithm that works well for puzzles. It biases its playouts using lower level playouts. At level zero NMCS adopts a uniform random playout policy. Online learning of playout s ...
pdf
... In [Halpern and Rêgo 2006], we discussed generalizations of games with awareness to include situations where players may be aware of their own unawareness and, more generally, games where players may not have common knowledge of the underlying game is; for example, players may disagree about what t ...
... In [Halpern and Rêgo 2006], we discussed generalizations of games with awareness to include situations where players may be aware of their own unawareness and, more generally, games where players may not have common knowledge of the underlying game is; for example, players may disagree about what t ...
Games in logic
... By Kamp theorem over sequences FOL=LTL, so we have an equivalent LTL formula α (with predicates from Σ × {l, r} × Tpk ) ...
... By Kamp theorem over sequences FOL=LTL, so we have an equivalent LTL formula α (with predicates from Σ × {l, r} × Tpk ) ...
538, Eden, Use Mathematical Games to Develop Problem
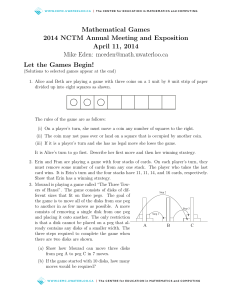
... Explain why Xavier has a winning strategy if he goes first and calls 4. (b) The second time the game is played, the person who calls the number 50 is the winner. If Xavier goes first,how does he guarantee that he will win? (c) In the game described in (b), the target number was 50. For what differen ...
... Explain why Xavier has a winning strategy if he goes first and calls 4. (b) The second time the game is played, the person who calls the number 50 is the winner. If Xavier goes first,how does he guarantee that he will win? (c) In the game described in (b), the target number was 50. For what differen ...
What Is Oligopoly?
... If both players are rational and choose their actions in this way, the outcome is an equilibrium called Nash equilibrium—first proposed by John Nash. Finding the Nash Equilibrium The following slides show how to find the Nash equilibrium. ...
... If both players are rational and choose their actions in this way, the outcome is an equilibrium called Nash equilibrium—first proposed by John Nash. Finding the Nash Equilibrium The following slides show how to find the Nash equilibrium. ...
NauVTslides - Duke University`s Fuqua School of Business
... under conditions where players are risk averse is a risk neutral equilibrium • Definition: a risk neutral equilibrium of the game is a distribution that satisfies G* 0, i.e., that assigns nonnegative expected value to each of the rows of G* • Implementation would require a mediator to use a ran ...
... under conditions where players are risk averse is a risk neutral equilibrium • Definition: a risk neutral equilibrium of the game is a distribution that satisfies G* 0, i.e., that assigns nonnegative expected value to each of the rows of G* • Implementation would require a mediator to use a ran ...
Algorithms for Playing Games with Limited Randomness
... Perhaps the most significant technical contribution in this paper pertains to a generalization of the “unbalanced” games that we saw above, namely, games of small rank. This is a broad class of games (encompassing some natural examples – see Section 6.3) for which sparse equilibria are known to exis ...
... Perhaps the most significant technical contribution in this paper pertains to a generalization of the “unbalanced” games that we saw above, namely, games of small rank. This is a broad class of games (encompassing some natural examples – see Section 6.3) for which sparse equilibria are known to exis ...
Introduction to Game Theory: Static Games
... In his will it states the two sons must each specify an amount si that they are willing to accept. If s1 + s2 ≤ 1000, then each gets the money he asked for and the remainder goes to a church. If s1 + s2 > 1000, then neither son receives any money and $1000 goes to a church. Assume (a) the two men ca ...
... In his will it states the two sons must each specify an amount si that they are willing to accept. If s1 + s2 ≤ 1000, then each gets the money he asked for and the remainder goes to a church. If s1 + s2 > 1000, then neither son receives any money and $1000 goes to a church. Assume (a) the two men ca ...
Noncooperative Convex Games: Computing
... algorithms applicable t o solve variational inequalities (Harker and Pang 1990). Likewise, (b) directs attention to proximal point procedures (Rockafellar 1976), and especially, to splitting methods (Eckstein and Bertsekas 1992). Finally, (c) indicates that subgradient projections might offer a good ...
... algorithms applicable t o solve variational inequalities (Harker and Pang 1990). Likewise, (b) directs attention to proximal point procedures (Rockafellar 1976), and especially, to splitting methods (Eckstein and Bertsekas 1992). Finally, (c) indicates that subgradient projections might offer a good ...
Monte Carlo Tree Search
... – Can MCTS be improved by making this multidimensional – E.g. for a line of play, balance effectiveness with variability / fun ...
... – Can MCTS be improved by making this multidimensional – E.g. for a line of play, balance effectiveness with variability / fun ...
PDF
... stationary distribution of the Markov chain. The structure of this paper is given as follows. The second section provides formal definitions of perfection and properness in finite strategy strategic games. The third section of this paper will provide a characterization of these algorithms in terms o ...
... stationary distribution of the Markov chain. The structure of this paper is given as follows. The second section provides formal definitions of perfection and properness in finite strategy strategic games. The third section of this paper will provide a characterization of these algorithms in terms o ...
Department of Economics Working Paper No. 197
... equilibrium selection criterion is the solution concept of 1/2–dominant equilibrium proposed by Morris, Rob and Shin (1995), which is a generalization of risk dominant equilibrium (Harsanyi and Selten, 1988). It is chosen by various equilibrium selection methods including the “evolutionary learning ...
... equilibrium selection criterion is the solution concept of 1/2–dominant equilibrium proposed by Morris, Rob and Shin (1995), which is a generalization of risk dominant equilibrium (Harsanyi and Selten, 1988). It is chosen by various equilibrium selection methods including the “evolutionary learning ...
Robust equilibria and ε-dominance
... a prisoner’s dilemma repeated 100 times, where every Nash equilibrium leads both players to play tough on every round, Luce and Raiffa [19] state that they would not play to a Nash equilibrium. In fact, if strategies were restricted to those which play nice before some round k, 1 ≤ k ≤ 100, as long ...
... a prisoner’s dilemma repeated 100 times, where every Nash equilibrium leads both players to play tough on every round, Luce and Raiffa [19] state that they would not play to a Nash equilibrium. In fact, if strategies were restricted to those which play nice before some round k, 1 ≤ k ≤ 100, as long ...
Social Norms: Repeated Interactions, Punishment, and Context
... In models of repeated interactions punishment behaviour can be modelled in a way unavailable to one-shot models. In this case some plays of the base game constitute sanctioning behaviour. Take, for instance, the indefinitely repeated PD. Permanent mutual cooperation can be the outcome of equilibrium ...
... In models of repeated interactions punishment behaviour can be modelled in a way unavailable to one-shot models. In this case some plays of the base game constitute sanctioning behaviour. Take, for instance, the indefinitely repeated PD. Permanent mutual cooperation can be the outcome of equilibrium ...
Multiple Criteria Games Theory and Applications
... functions, they must posses certain additional properties that will be analyzed in detail in this paper. In particular, such scalarizing functions must be parameterized in such a way as to enable an easy scanning and selection of game equilibria, independently of convexity properties. A specific pro ...
... functions, they must posses certain additional properties that will be analyzed in detail in this paper. In particular, such scalarizing functions must be parameterized in such a way as to enable an easy scanning and selection of game equilibria, independently of convexity properties. A specific pro ...
Using Counterfactual Regret Minimization to Create Competitive
... The directed edges leaving a choice node represent the legal actions for that player. Each terminal node contains the utilities of all players for one potential game result. Stochastic events (Backgammon dice rolls or Poker cards) are represented as special nodes, for a player called the chance play ...
... The directed edges leaving a choice node represent the legal actions for that player. Each terminal node contains the utilities of all players for one potential game result. Stochastic events (Backgammon dice rolls or Poker cards) are represented as special nodes, for a player called the chance play ...
Extensive Games with Imperfect Information
... It is here that the notion of beliefs is introduced. For games with perfect information, such a concept was implicit in so much as a player’s belief about her opponent’s strategy was simply equal to the strategy itself. When dealing with extensive games with imperfect information a player’s beliefs ...
... It is here that the notion of beliefs is introduced. For games with perfect information, such a concept was implicit in so much as a player’s belief about her opponent’s strategy was simply equal to the strategy itself. When dealing with extensive games with imperfect information a player’s beliefs ...
The Distribution of Optimal Strategies in Symmetric Zero-sum
... depends on the parity of S. For the proof of this result we assume that the distribution of games is symmetric and regular. A distribution is symmetric if it is invariant under negation of all payoffs when the row player chooses an action from a certain set and the column player chooses an action fr ...
... depends on the parity of S. For the proof of this result we assume that the distribution of games is symmetric and regular. A distribution is symmetric if it is invariant under negation of all payoffs when the row player chooses an action from a certain set and the column player chooses an action fr ...
Verifiable Equilibria in Boolean Games
... In this paper, we introduce and formalise verifiable equilibria in Boolean games, an increasingly popular game theoretic model, with a natural computational interpretation [Harrenstein et al., 2001; Bonzon et al., 2006; Dunne et al., 2008; Endriss et al., 2011]. In a Boolean game, each player i has ...
... In this paper, we introduce and formalise verifiable equilibria in Boolean games, an increasingly popular game theoretic model, with a natural computational interpretation [Harrenstein et al., 2001; Bonzon et al., 2006; Dunne et al., 2008; Endriss et al., 2011]. In a Boolean game, each player i has ...
DownloadDownload publication - HHL Leipzig Graduate School of
... game, and that she need not worry about the “extra” moves included in '1. Again, it does not seem absurd to say that Ivy knows of two distinct games that they will be played. ...
... game, and that she need not worry about the “extra” moves included in '1. Again, it does not seem absurd to say that Ivy knows of two distinct games that they will be played. ...