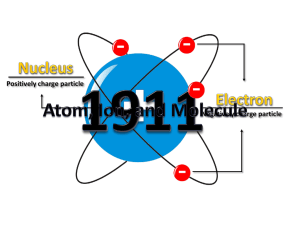
People`s Physics Book 3e Ch 22-1 The Big Idea All matter is
... For any interaction between particles, the five conservation laws (energy, momentum, angular momentum, charge, and CPT) must be followed. For instance, the total electric charge must always be the same before and after an interaction. Electron lepton number is conserved. This means that the total nu ...
... For any interaction between particles, the five conservation laws (energy, momentum, angular momentum, charge, and CPT) must be followed. For instance, the total electric charge must always be the same before and after an interaction. Electron lepton number is conserved. This means that the total nu ...
PPT about Particle Physics
... 1977 Fermilab: discovery of quark « bottom » protons-protons collisions ...
... 1977 Fermilab: discovery of quark « bottom » protons-protons collisions ...
Particle Physics Design Group Studies Worksheet Introduction
... the particles with the detector material. Several different types of interactions are important, the main ones being: ionisation and excitation of atoms by charged particles; electromagnetic interactions in nuclear electric fields; and hadronic interactions of strongly-interacting particles with nuc ...
... the particles with the detector material. Several different types of interactions are important, the main ones being: ionisation and excitation of atoms by charged particles; electromagnetic interactions in nuclear electric fields; and hadronic interactions of strongly-interacting particles with nuc ...
Accelerators and Detectors
... Heavier particles: µ, π, K, p, ... Energy loss Inelastic collisions with the atomic electrons ...
... Heavier particles: µ, π, K, p, ... Energy loss Inelastic collisions with the atomic electrons ...
subatomic structure
... Protons have a mass. We designate this mass as 1 amu (atomic mass unit). Protons determine the atomic number and thus the identity of the substance. Who discovered the proton? What experiment did he use? ...
... Protons have a mass. We designate this mass as 1 amu (atomic mass unit). Protons determine the atomic number and thus the identity of the substance. Who discovered the proton? What experiment did he use? ...
hdwsmp2011 - FSU High Energy Physics
... Nedermeyer, Anderson, Street, Stevenson 1936-1937, using cloud chambers Found mass to be between that of electron and proton --called “mesotron” Later other particles with intermediate mass found – called “mesons” Mesotron renamed “muon” μ -- very different from mesons (no strong interaction ...
... Nedermeyer, Anderson, Street, Stevenson 1936-1937, using cloud chambers Found mass to be between that of electron and proton --called “mesotron” Later other particles with intermediate mass found – called “mesons” Mesotron renamed “muon” μ -- very different from mesons (no strong interaction ...












![PROBLEM 1 [25 PTS] A system consists of N distinquishable](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006063913_1-e1778e5c6114fd66466f556bb5f30c03-300x300.png)