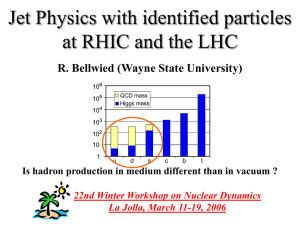
The Future of High Energy Nuclear Physics in Europe
... would dominate the initial conditions at LHC and allow the study of QCD in the classical limit of quantum field theory. So also the discovery phase is likely to continue, at both RHIC and LHC, and further surprises should lay ahead. Finally, not even the search may be completely over yet. In case su ...
... would dominate the initial conditions at LHC and allow the study of QCD in the classical limit of quantum field theory. So also the discovery phase is likely to continue, at both RHIC and LHC, and further surprises should lay ahead. Finally, not even the search may be completely over yet. In case su ...
Control of size of nano / micro particles synthesized by atmospheric
... development of micro and nano-electronics and other important technologies. Nanoparticles formed from different materials are already used in modern techniques to tailor properties on composite materials, ceramics, catalyzing agents etc. Low temperature plasma created in reactive gas ambient by high ...
... development of micro and nano-electronics and other important technologies. Nanoparticles formed from different materials are already used in modern techniques to tailor properties on composite materials, ceramics, catalyzing agents etc. Low temperature plasma created in reactive gas ambient by high ...
Synchrotron - schoolphysics
... protons to 400 GeV. Each pulse contains 1013 protons and lasts for between 2 and 24 microseconds. The machine has a diameter of 2.2 km with six long straight sections and over seven hundred bending magnets, each one just over 6 m long. In the acceleration to 400 GeV, which lasts some 2.7s, the proto ...
... protons to 400 GeV. Each pulse contains 1013 protons and lasts for between 2 and 24 microseconds. The machine has a diameter of 2.2 km with six long straight sections and over seven hundred bending magnets, each one just over 6 m long. In the acceleration to 400 GeV, which lasts some 2.7s, the proto ...
College Physics - Gianpietro Cagnoli's Homepage
... traveling with velocity 13.0 m/s toward the east, and the other is traveling north with speed v2i. Neither driver sees the other. The vehicles collide in the intersection and stick together, leaving parallel skid marks at an angle of 55.0° north of east. The speed limit for both roads is 35 mi/h, an ...
... traveling with velocity 13.0 m/s toward the east, and the other is traveling north with speed v2i. Neither driver sees the other. The vehicles collide in the intersection and stick together, leaving parallel skid marks at an angle of 55.0° north of east. The speed limit for both roads is 35 mi/h, an ...
Theory and HPC - Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies
... The goal: to study of the phase transition from hadronic to partonic matter and properties of the Quark-Gluon-Plasma from microscopic origin need a consistent non-equilibrium transport model with explicit parton-parton interactions (i.e. between quarks and gluons) explicit phase transition fro ...
... The goal: to study of the phase transition from hadronic to partonic matter and properties of the Quark-Gluon-Plasma from microscopic origin need a consistent non-equilibrium transport model with explicit parton-parton interactions (i.e. between quarks and gluons) explicit phase transition fro ...
E - indico in2p3
... CME, particle acceleration (shock) ICME, particle acceleration ICME at Earth, shielding of galactic cosmic rays ...
... CME, particle acceleration (shock) ICME, particle acceleration ICME at Earth, shielding of galactic cosmic rays ...
Study Notes Lesson 23 Atomic and Nuclear Physics
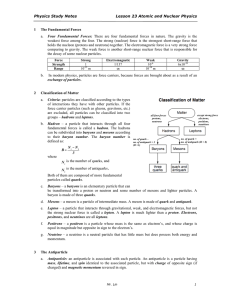
... Criteria: particles are classified according to the types of interactions they have with other particles. If the force carrier particles (such as gluons, gravitons, etc.) are excluded, all particles can be classified into two groups – hadrons and leptons. Hadron – a particle that interacts through a ...
... Criteria: particles are classified according to the types of interactions they have with other particles. If the force carrier particles (such as gluons, gravitons, etc.) are excluded, all particles can be classified into two groups – hadrons and leptons. Hadron – a particle that interacts through a ...
Particle physics
... • Real world is not done by single quarks • Quarks exist only in groups, to form the so-called hadrons (protons and neutrons are hadrons) • Example: a proton is made of two quarks of up type and one quark of type down. • The matter around, and even each of us, is made of quarks up and down and of el ...
... • Real world is not done by single quarks • Quarks exist only in groups, to form the so-called hadrons (protons and neutrons are hadrons) • Example: a proton is made of two quarks of up type and one quark of type down. • The matter around, and even each of us, is made of quarks up and down and of el ...