Notes
... How many moles of hydrogen are there in water? How many moles of oxygen are there in water? What is the ration of hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms? ...
... How many moles of hydrogen are there in water? How many moles of oxygen are there in water? What is the ration of hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms? ...
What is a mole? - Chemical Paradigms
... and dissolving it in a known volume of water. More about this later. In a chemical reaction substances need to combine in the correct mole ratio in order for the reaction to occur. Even if the number of moles changes the ratio of moles of reactants and products does not change. In the reaction below ...
... and dissolving it in a known volume of water. More about this later. In a chemical reaction substances need to combine in the correct mole ratio in order for the reaction to occur. Even if the number of moles changes the ratio of moles of reactants and products does not change. In the reaction below ...
density becomes larger between the two nuclei. This re
... cores of the two atoms (for H2 these are the two protons) and the negative electron charge distribution between them. This effect is emphasized in the valence bond model used in chemistry. In the chemically bound molecule both atoms share one or more valence electrons in a common molecular orbital. ...
... cores of the two atoms (for H2 these are the two protons) and the negative electron charge distribution between them. This effect is emphasized in the valence bond model used in chemistry. In the chemically bound molecule both atoms share one or more valence electrons in a common molecular orbital. ...
Chapter 1-Crystal Properties_M A Islam_Lecture 1
... of intentionally introducing impurities into an extremely pure (also referred to as intrinsic) semiconductor in order to change its electrical properties. • The number of dopant atoms needed to create a difference in the ability of a semiconductor to conduct is very small. Where a comparatively smal ...
... of intentionally introducing impurities into an extremely pure (also referred to as intrinsic) semiconductor in order to change its electrical properties. • The number of dopant atoms needed to create a difference in the ability of a semiconductor to conduct is very small. Where a comparatively smal ...
Lecture Slides - School of Chemical Sciences
... The macroscopic description of a system of ~1023 particles may involve only a few variables! “Simple systems”: Macroscopically homogeneous, isotropic, uncharged, large enough that surface effects can be neglected, not acted upon by electric, magnetic, or gravitational fields. Only those few part ...
... The macroscopic description of a system of ~1023 particles may involve only a few variables! “Simple systems”: Macroscopically homogeneous, isotropic, uncharged, large enough that surface effects can be neglected, not acted upon by electric, magnetic, or gravitational fields. Only those few part ...
экзаменационные тесты по органической химии
... a. The amount of products is greater than the amount of reactants. b. The amount of products is equal to the amount of reactants. c. The rate of the forward reaction is greater than the rate of the reverse reaction. d. The rate of the forward reaction is equal to than the rate of the reverse reactio ...
... a. The amount of products is greater than the amount of reactants. b. The amount of products is equal to the amount of reactants. c. The rate of the forward reaction is greater than the rate of the reverse reaction. d. The rate of the forward reaction is equal to than the rate of the reverse reactio ...
Metal
... Secondary-van der waals-bonding Secondary, van der Waals, or physical bonds are weak in comparison to the primary or chemical ones; bonding energies are typically on the order of only 10 kJ/mol (0.1 eV/atom). Secondary bonding exists between virtually all atoms or molecules, but its presence may be ...
... Secondary-van der waals-bonding Secondary, van der Waals, or physical bonds are weak in comparison to the primary or chemical ones; bonding energies are typically on the order of only 10 kJ/mol (0.1 eV/atom). Secondary bonding exists between virtually all atoms or molecules, but its presence may be ...
Answers to For Review Questions from the Textbook
... the carbon-12 isotope weighing exactly 12.0000 amu. One can determine from experiment how much heavier or lighter any specific isotope is than 12C. From this information, we assign an atomic mass value to that isotope. For example, experiment tells one that 16O is about 4/3 heavier than 12C, so a ma ...
... the carbon-12 isotope weighing exactly 12.0000 amu. One can determine from experiment how much heavier or lighter any specific isotope is than 12C. From this information, we assign an atomic mass value to that isotope. For example, experiment tells one that 16O is about 4/3 heavier than 12C, so a ma ...
Chapter 4: Imperfections in Solids Imperfections in Solids
... Impurities in Solids •A pure metal consisting of only one type of atom is not possible; impurity or foreign atoms will always be present. •Even with relatively sophisticated techniques, it is difficult to refine metals to a purity in excess of 99.9999%. At this level, on the order of 1022 to 1023 im ...
... Impurities in Solids •A pure metal consisting of only one type of atom is not possible; impurity or foreign atoms will always be present. •Even with relatively sophisticated techniques, it is difficult to refine metals to a purity in excess of 99.9999%. At this level, on the order of 1022 to 1023 im ...
C2.3 Atomic Structure, Analysis and Quantitative Chemistry
... Know the use of mass number and atomic number Know the mass of each sub atomic particle. Atoms of the same element with a different number of neutrons are known as isotopes Elements and compounds can be detected using instrumental methods ...
... Know the use of mass number and atomic number Know the mass of each sub atomic particle. Atoms of the same element with a different number of neutrons are known as isotopes Elements and compounds can be detected using instrumental methods ...
HCC9 Chapter 9 Objectives and Notes
... 1. law of definite proportions/law of constant composition: Discovered by Joseph Proust in the early 1800’s. In a given chemical compound the elements are always combined in the same proportion by mass. a. H2O is always 2.02 g hydrogen for every 16.0 g oxygen, the ratio of the masses never varies. 2 ...
... 1. law of definite proportions/law of constant composition: Discovered by Joseph Proust in the early 1800’s. In a given chemical compound the elements are always combined in the same proportion by mass. a. H2O is always 2.02 g hydrogen for every 16.0 g oxygen, the ratio of the masses never varies. 2 ...
THE MOLE - bYTEBoss
... made technically and economically recoverable, the United States could more than double its domestic natural gas resource. ...
... made technically and economically recoverable, the United States could more than double its domestic natural gas resource. ...
Monodisperse FePt Nanoparticles and Ferromagnetic FePt
... support recording densities about 10 times larger than the CoCr-based alloy media presently used industry wide (12). A critical factor in achieving such a goal is the thermal stability of the magnetic transitions, which can be assessed with a dynamic coercivity method. This method relies on remanent ...
... support recording densities about 10 times larger than the CoCr-based alloy media presently used industry wide (12). A critical factor in achieving such a goal is the thermal stability of the magnetic transitions, which can be assessed with a dynamic coercivity method. This method relies on remanent ...
Colloidal Crystal: emergence of long range order from colloidal fluid
... colloidal crystal shows that the concentration in this situation is playing the role of temperature in molecular crystals. At very high volume fraction of particles, crystallization was not observed, rather a glassy state formed due to the very slow dynamics of the system and frustrated rearrangemen ...
... colloidal crystal shows that the concentration in this situation is playing the role of temperature in molecular crystals. At very high volume fraction of particles, crystallization was not observed, rather a glassy state formed due to the very slow dynamics of the system and frustrated rearrangemen ...
Intermolecular forces liquids and Solids
... • Melting: change of a solid to a liquid. H2O(s) H2O(l) • Freezing: change a liquid to a solid. H2O(l) H2O(s) • Vaporization: change of a solid or liquid to a gas. Change of solid to vapor often called sublimation. ...
... • Melting: change of a solid to a liquid. H2O(s) H2O(l) • Freezing: change a liquid to a solid. H2O(l) H2O(s) • Vaporization: change of a solid or liquid to a gas. Change of solid to vapor often called sublimation. ...
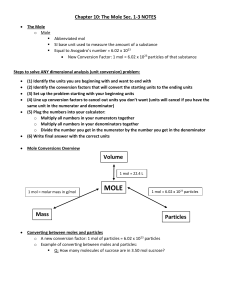
MOLE Mass Volume Particles
... SI base unit used to measure the amount of a substance Equal to Avogadro’s number = 6.02 x 1023 New Conversion Factor: 1 mol = 6.02 x 1023 particles of that substance ...
... SI base unit used to measure the amount of a substance Equal to Avogadro’s number = 6.02 x 1023 New Conversion Factor: 1 mol = 6.02 x 1023 particles of that substance ...
Balancing Chemical Equations
... Atomic and molecular weight The atomic weight is the numerical value tabulated for the mass of each atom in the periodic table in atomic units. The use of the word “weight” is not precise here since weight in physics represents a force (w = mg). However, the name atomic weight is so ingrained that ...
... Atomic and molecular weight The atomic weight is the numerical value tabulated for the mass of each atom in the periodic table in atomic units. The use of the word “weight” is not precise here since weight in physics represents a force (w = mg). However, the name atomic weight is so ingrained that ...
11-16 States of Matter
... Changing from solid to liquid to gas or back the other way occurs by increasing or decreasing energy (heat) in a substance Changing the state does not change the chemical structure. It merely makes the particles in the substance move around faster or slower. Ex: H2O Water …notice that in each stat ...
... Changing from solid to liquid to gas or back the other way occurs by increasing or decreasing energy (heat) in a substance Changing the state does not change the chemical structure. It merely makes the particles in the substance move around faster or slower. Ex: H2O Water …notice that in each stat ...
2.1-Properties of Matter
... Attractions are strong enough to keep particles close but weak enough to let particles move past each other ...
... Attractions are strong enough to keep particles close but weak enough to let particles move past each other ...
chapter 3 notes for power point
... • The idea of an atomic theory is more than 2000 years old. • Until recently, scientists had never seen evidence of atoms. • The law of definite proportions, the law of conservation of mass and the law of multiple proportions support the current atomic theory. • The figure on the right is a more acc ...
... • The idea of an atomic theory is more than 2000 years old. • Until recently, scientists had never seen evidence of atoms. • The law of definite proportions, the law of conservation of mass and the law of multiple proportions support the current atomic theory. • The figure on the right is a more acc ...
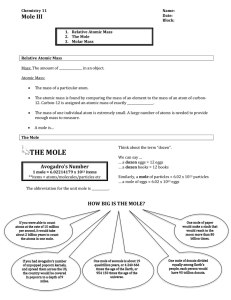
1.21 moles and formulae
... The mole is the key concept for chemical calculations DEFINITION: The mole is the amount of substance in grams that has the same number of particles as there are atoms in 12 grams of carbon-12. DEFINITION: Relative atomic mass is the average mass of one atom compared to one twelfth of the mass of on ...
... The mole is the key concept for chemical calculations DEFINITION: The mole is the amount of substance in grams that has the same number of particles as there are atoms in 12 grams of carbon-12. DEFINITION: Relative atomic mass is the average mass of one atom compared to one twelfth of the mass of on ...
Document
... The Boltzmann equation seeks to find the maximum number of configurations. For a system with large N, there is a configuration with so great a weight that is overwhelms the rest. The system will almost always be found in it, and it will determine the properties of the system. The Boltzmann equation ...
... The Boltzmann equation seeks to find the maximum number of configurations. For a system with large N, there is a configuration with so great a weight that is overwhelms the rest. The system will almost always be found in it, and it will determine the properties of the system. The Boltzmann equation ...
Bose–Einstein condensate

A Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) is a state of matter of a dilute gas of bosons cooled to temperatures very close to absolute zero (that is, very near 5000000000000000000♠0 K or 5000000000000000000♠−273.15 °C). Under such conditions, a large fraction of bosons occupy the lowest quantum state, at which point macroscopic quantum phenomena become apparent.This state was first predicted, generally, in 1924–25 by Satyendra Nath Bose and Albert Einstein.