Chemistry-Chapter 2 Lecture Notes Page
... CHEMICAL BONDS continued HYDROGEN BONDS - Form weak attraction within or between polar molecules - Involves association between slightly positive H and two other atoms (slightly negative O or N) - Easily broken by Temp or pH - Found in: H2O, Proteins, Nucleic Acids ...
... CHEMICAL BONDS continued HYDROGEN BONDS - Form weak attraction within or between polar molecules - Involves association between slightly positive H and two other atoms (slightly negative O or N) - Easily broken by Temp or pH - Found in: H2O, Proteins, Nucleic Acids ...
E L E M E N T S
... Atomic weight – refers to the mass of the atom. Number of protons and neutrons ...
... Atomic weight – refers to the mass of the atom. Number of protons and neutrons ...
Quiz 3 Practice - philipdarrenjones.com
... will appear on the actual weekly quizzes and final exam. There will be no key provided—all answers can be deduced by referencing your lecture notes and Goodenough textbook. Trust me: looking up the answers to these questions to see how you’ve done is a valuable form of studying…as is making up your ...
... will appear on the actual weekly quizzes and final exam. There will be no key provided—all answers can be deduced by referencing your lecture notes and Goodenough textbook. Trust me: looking up the answers to these questions to see how you’ve done is a valuable form of studying…as is making up your ...
Proteins
... Proteins are a basic part of living cells • Cells put together molecules (mainly proteins) to carry out __________________ _________________________. • Proteins are made of long chains that are smaller than molecules called amino acids. • There are _________ different amino acids that can be arrang ...
... Proteins are a basic part of living cells • Cells put together molecules (mainly proteins) to carry out __________________ _________________________. • Proteins are made of long chains that are smaller than molecules called amino acids. • There are _________ different amino acids that can be arrang ...
Chapter 12 - Pathways to Biomolecules
... • The selectivity of enzymes is one of their most important features. • This selectivity arises because the shape and functional groups in the active site of the enzyme allow it to bind only with certain substrates. (Thus the lock and key process). ...
... • The selectivity of enzymes is one of their most important features. • This selectivity arises because the shape and functional groups in the active site of the enzyme allow it to bind only with certain substrates. (Thus the lock and key process). ...
04 Biochemistry
... – Twenty different amino acids are used to build proteins in organisms. – Amino acids differ in side groups, or R groups. ...
... – Twenty different amino acids are used to build proteins in organisms. – Amino acids differ in side groups, or R groups. ...
Biology Standards Checklist
... interaction types 1. Mechanisms: g. History of life on Earth: fossil record, common ancestors, cladograms ...
... interaction types 1. Mechanisms: g. History of life on Earth: fossil record, common ancestors, cladograms ...
BIOL 103 Chapter 1-11 Review
... 2. Cell culture: effects of nutrients on cells 3. Epidemiological: study of disease/death rates in population to identify factors that may be related to cause of disease • Correlation is not always causation ...
... 2. Cell culture: effects of nutrients on cells 3. Epidemiological: study of disease/death rates in population to identify factors that may be related to cause of disease • Correlation is not always causation ...
第一章 绪论
... physiochemical properties of a given candidate compound library. Chemical modifications can improve the pharmacophores of the candidate compounds, their pharmacokinetics, or indeed their reactivity and stability during their metabolic degradation. A number of methods have contributed to quantitative ...
... physiochemical properties of a given candidate compound library. Chemical modifications can improve the pharmacophores of the candidate compounds, their pharmacokinetics, or indeed their reactivity and stability during their metabolic degradation. A number of methods have contributed to quantitative ...
Click here for powerpoint
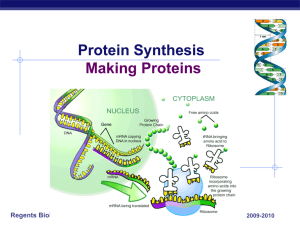
... Once a copy is made in the nucleus mRNA goes to the ribosome TRANSLATION: ribosome decodes the instructions on mRNA and makes a protein ...
... Once a copy is made in the nucleus mRNA goes to the ribosome TRANSLATION: ribosome decodes the instructions on mRNA and makes a protein ...
Unit 2: Biochem Notes
... - A solution with a pH __________ 7, has more OH- ions than H+ ions, and is basic. - A solution with a pH _________ 7, has more H+ ions than OH- ions, and is acidic. b. buffer – Weak acids or bases that can react with strong acids or bases to prevent sharp, sudden changes in pH. Buffers make acidic ...
... - A solution with a pH __________ 7, has more OH- ions than H+ ions, and is basic. - A solution with a pH _________ 7, has more H+ ions than OH- ions, and is acidic. b. buffer – Weak acids or bases that can react with strong acids or bases to prevent sharp, sudden changes in pH. Buffers make acidic ...
PPT - gserianne.com
... Important Definitions of Organizational Terms • Cell – The basic unit of biological structure and function (what is a ‘basic unit’ of something?) • Tissues – A group of cells working together to perform one or more specific functions • Organs – Two or more tissues working in combination to perform ...
... Important Definitions of Organizational Terms • Cell – The basic unit of biological structure and function (what is a ‘basic unit’ of something?) • Tissues – A group of cells working together to perform one or more specific functions • Organs – Two or more tissues working in combination to perform ...
Cell Physiology
... Synthesis of RNA • During synthesis of RNA, two strands of DNA molecules separate temporarily; one of these strands is used as a template for synthesis of the RNA molecules. • The code triplets in the DNA cause the formation of complementary code triplets (called codons) in the RNA; these codons in ...
... Synthesis of RNA • During synthesis of RNA, two strands of DNA molecules separate temporarily; one of these strands is used as a template for synthesis of the RNA molecules. • The code triplets in the DNA cause the formation of complementary code triplets (called codons) in the RNA; these codons in ...
Chapter 2 – Chemical Composition of the Body
... • Bonds formed between the hydrogen end (+ charged) of a polar molecule and the – end of any other polar molecule or highly electronegative atom (e.g. P, N, O) are called hydrogen bonds. • These hydrogen bonds are very important because they alter the physical and chemical properties of many molec ...
... • Bonds formed between the hydrogen end (+ charged) of a polar molecule and the – end of any other polar molecule or highly electronegative atom (e.g. P, N, O) are called hydrogen bonds. • These hydrogen bonds are very important because they alter the physical and chemical properties of many molec ...
THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE
... 1. Building block for nucleic acids; contains a five-carbon sugar, a nitrogen base, and a phosphate group. 2. Contains deoxyribose; nucleotides form a double helix. 3. DNA molecules associated with protein. 4. Formed when chromatin condenses during cell division. 5. Single strand of nucleotides that ...
... 1. Building block for nucleic acids; contains a five-carbon sugar, a nitrogen base, and a phosphate group. 2. Contains deoxyribose; nucleotides form a double helix. 3. DNA molecules associated with protein. 4. Formed when chromatin condenses during cell division. 5. Single strand of nucleotides that ...
Connective Tissue - White Plains Public Schools
... Proteoglycans are heavily glycosylated proteins. They have a core protein with one or more attached glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chain(s). The chains are long, linear carbohydrate polymers that are negatively charged under physiological conditions, due to the occurrence of sulfate and uronic acid groups. ...
... Proteoglycans are heavily glycosylated proteins. They have a core protein with one or more attached glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chain(s). The chains are long, linear carbohydrate polymers that are negatively charged under physiological conditions, due to the occurrence of sulfate and uronic acid groups. ...
Electrons - davis.k12.ut.us
... more hydroxyl ions (OH-) and one or more positively charged ions (cations) Bases are proton acceptors ...
... more hydroxyl ions (OH-) and one or more positively charged ions (cations) Bases are proton acceptors ...
Chemistry Enzymes, Vitamins, and Hormones
... nutrition, but they are not carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, or fats. The British sailors lacked ascorbic acid, or vitamin C, in their onboard diets. A daily ration of lemon or lime juice provided the necessary nutrient to help control the symptoms of scurvy and earned the sailors the nickname “lime ...
... nutrition, but they are not carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, or fats. The British sailors lacked ascorbic acid, or vitamin C, in their onboard diets. A daily ration of lemon or lime juice provided the necessary nutrient to help control the symptoms of scurvy and earned the sailors the nickname “lime ...
57 chapter summary
... 2. All of the following are examples of the four major elements contributing to body mass except (a) hydrogen, (b) carbon, (c) nitrogen, (d) sodium, (e) oxygen. 3. The mass number of an atom is (a) equal to the number of protons it contains, (b) the sum of its protons and neutrons, (c) the sum of al ...
... 2. All of the following are examples of the four major elements contributing to body mass except (a) hydrogen, (b) carbon, (c) nitrogen, (d) sodium, (e) oxygen. 3. The mass number of an atom is (a) equal to the number of protons it contains, (b) the sum of its protons and neutrons, (c) the sum of al ...
Chemical reactions take place inside cells.
... and hydrogen. Inside cells, sugar molecules are broken down. This process provides usable energy for the cell. Simple sugar molecules can also be linked into long chains to form more complex carbohydrates, such as starch, cellulose, and glycogen. Starch and cellulose are complex carbohydrates made b ...
... and hydrogen. Inside cells, sugar molecules are broken down. This process provides usable energy for the cell. Simple sugar molecules can also be linked into long chains to form more complex carbohydrates, such as starch, cellulose, and glycogen. Starch and cellulose are complex carbohydrates made b ...
Clicker REVIEW ?s
... D Both bacteria are true bacteria. 4) What type of bacteria produce CH4 gas as a product of respiration? A Thermophiles B Hydrophiles C Halophiles D Methanogens 5) Eu- means ________. A green B true C membrane-bound D harmful 6) Archaea bacteria is ________ bacteria. A membrane-bound B green C true ...
... D Both bacteria are true bacteria. 4) What type of bacteria produce CH4 gas as a product of respiration? A Thermophiles B Hydrophiles C Halophiles D Methanogens 5) Eu- means ________. A green B true C membrane-bound D harmful 6) Archaea bacteria is ________ bacteria. A membrane-bound B green C true ...
Introduction: Key Ideas, Central Dogma and Educational Philosophy
... We will begin with an exploration of the macroscopic factors that influence molecular biology, including a closer look at the mechanisms of evolution: inheritance, variation and selection. For more than half the history of life, reproduction involved single celled organisms making copies of themselv ...
... We will begin with an exploration of the macroscopic factors that influence molecular biology, including a closer look at the mechanisms of evolution: inheritance, variation and selection. For more than half the history of life, reproduction involved single celled organisms making copies of themselv ...