Biology Keystone Practice PowerPoint
... energy, which is the key distinction, as opposed to facilitated diffusion which is also specific to a molecule (or ion) but does not require energy. An example would be glucose is too big to pass through the cell membrane on its own, but can do so the with help of a specific protein. ...
... energy, which is the key distinction, as opposed to facilitated diffusion which is also specific to a molecule (or ion) but does not require energy. An example would be glucose is too big to pass through the cell membrane on its own, but can do so the with help of a specific protein. ...
Chemical Equations
... • MS-PS1-5. I can explain the conservation of mass through a model of chemical reactions. • MS-PS1-3 I can gather information to describe the origins and impacts of synthetic material ...
... • MS-PS1-5. I can explain the conservation of mass through a model of chemical reactions. • MS-PS1-3 I can gather information to describe the origins and impacts of synthetic material ...
Animal cell culture and applications
... Protein and Gene Manipulation Protein Structure and Engineering : Introduction to the world of proteins, 3-D shape of proteins, Structure function relationship in proteins, Purification of proteins, Characterization of proteins, protein based products, designing proteins and proteomics. Recombinant ...
... Protein and Gene Manipulation Protein Structure and Engineering : Introduction to the world of proteins, 3-D shape of proteins, Structure function relationship in proteins, Purification of proteins, Characterization of proteins, protein based products, designing proteins and proteomics. Recombinant ...
Diagnosis Test: EDEXCEL ADDITIONAL SCIENCE Biology
... QWC Suggested marking guidance (Total 6 marks) Marks awarded for this answer will be determined by the Quality of Written Communication (QWC) as well as the standard of the scientific response. Teachers should apply a ‘best-fit’ approach to the marking. ...
... QWC Suggested marking guidance (Total 6 marks) Marks awarded for this answer will be determined by the Quality of Written Communication (QWC) as well as the standard of the scientific response. Teachers should apply a ‘best-fit’ approach to the marking. ...
Chapter 14: Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein
... polynucleotide only in the 5' Æ direction. Which enzyme, DNA polymerase III or RNA polymerase, does not require a primer to begin synthesis? ...
... polynucleotide only in the 5' Æ direction. Which enzyme, DNA polymerase III or RNA polymerase, does not require a primer to begin synthesis? ...
Nutrition Notes
... considered a major nutrient. Vitamins and minerals are needed in lower amounts. 2. Nutrients are needed by the body to build proteins, and other macromolecules. Simple sugars are needed by the cells to produce ATP during cell respiration. 3. What are essential nutrients? These are nutrients that the ...
... considered a major nutrient. Vitamins and minerals are needed in lower amounts. 2. Nutrients are needed by the body to build proteins, and other macromolecules. Simple sugars are needed by the cells to produce ATP during cell respiration. 3. What are essential nutrients? These are nutrients that the ...
Amino acids and prot..
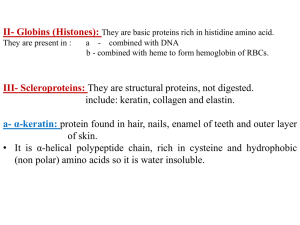
... III- Scleroproteins: They are structural proteins, not digested. include: keratin, collagen and elastin. a- α-keratin: protein found in hair, nails, enamel of teeth and outer layer of skin. • It is α-helical polypeptide chain, rich in cysteine and hydrophobic (non polar) amino acids so it is water i ...
... III- Scleroproteins: They are structural proteins, not digested. include: keratin, collagen and elastin. a- α-keratin: protein found in hair, nails, enamel of teeth and outer layer of skin. • It is α-helical polypeptide chain, rich in cysteine and hydrophobic (non polar) amino acids so it is water i ...
File - Ms. Daley Science
... 30. Using the same axes, draw two graphs. One graph should show a reaction without an enzyme and the second should show the reaction with an enzyme. You should show that the enzymes lower the activation energy. (Energy on Y and time on X) Label where the reactants and products would be on the graph. ...
... 30. Using the same axes, draw two graphs. One graph should show a reaction without an enzyme and the second should show the reaction with an enzyme. You should show that the enzymes lower the activation energy. (Energy on Y and time on X) Label where the reactants and products would be on the graph. ...
How Genes Work
... Its complex unwinds DNA It copies bases using complimentary base pairing (U v.s. T) Moves down one strand Stops at terminator ...
... Its complex unwinds DNA It copies bases using complimentary base pairing (U v.s. T) Moves down one strand Stops at terminator ...
The Necessities of Life
... Most living things use oxygen in the chemical process that releases energy from food. Oxygen may come from the air or may be dissolved in water. Green plants, algae, and some bacteria need carbon dioxide gas in addition to oxygen. These organisms produce food and oxygen by using photosynthesis -when ...
... Most living things use oxygen in the chemical process that releases energy from food. Oxygen may come from the air or may be dissolved in water. Green plants, algae, and some bacteria need carbon dioxide gas in addition to oxygen. These organisms produce food and oxygen by using photosynthesis -when ...
chapter 1 - Juan Diego Academy
... Only time will reveal the consequences of these and other changes. Scientists predict that even if we stopped burning fossil fuels today, it would take several centuries to return to pre-industrial CO2 levels. ...
... Only time will reveal the consequences of these and other changes. Scientists predict that even if we stopped burning fossil fuels today, it would take several centuries to return to pre-industrial CO2 levels. ...
Chemistry of Life - Dr. Wilson`s Site
... Water’s polar covalent bonds and its V-shaped molecule gives water a set of properties that account for its ability to support life. 60%–80% of the volume of living cells Most important inorganic compound in living organisms because of its properties: ...
... Water’s polar covalent bonds and its V-shaped molecule gives water a set of properties that account for its ability to support life. 60%–80% of the volume of living cells Most important inorganic compound in living organisms because of its properties: ...
Introduction: Themes in the Study of Life
... An animal’s muscle cells use sugar as fuel to power movements, converting chemical energy to kinetic energy, the energy of motion. ○ The cells in a leaf use sugar to drive the process of cell division during leaf growth, transforming stored chemical energy into cellular work. ...
... An animal’s muscle cells use sugar as fuel to power movements, converting chemical energy to kinetic energy, the energy of motion. ○ The cells in a leaf use sugar to drive the process of cell division during leaf growth, transforming stored chemical energy into cellular work. ...
Compounds of Living Things
... Lipids have many roles in living things. One role is to store energy. When carbohydrates or glycogen are not available, cells use energy stored in your body fat. Fat layers under your skin and around your organs also protect and insulate your body. The vitamins A, D, E, and K are necessary for good ...
... Lipids have many roles in living things. One role is to store energy. When carbohydrates or glycogen are not available, cells use energy stored in your body fat. Fat layers under your skin and around your organs also protect and insulate your body. The vitamins A, D, E, and K are necessary for good ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... • Describe the common structure of amino acids. • What type of bond is a peptide bond? Where can one be found? • What are two types of secondary structure in proteins? What causes the formation of each? • What types of bonds and what level of structure is destroyed when a protein is denatured? ...
... • Describe the common structure of amino acids. • What type of bond is a peptide bond? Where can one be found? • What are two types of secondary structure in proteins? What causes the formation of each? • What types of bonds and what level of structure is destroyed when a protein is denatured? ...
Biocatalytic Synthesis of Polymers of Precisely Defined Structures
... availability of suitably designed templates, which ideally must be uniform polymers themselves, and by formulation of appropriate mechanisms for the transfer of sequence information from the template to the reactive monomers. The best realized example of this process is protein biosynthesis, in whic ...
... availability of suitably designed templates, which ideally must be uniform polymers themselves, and by formulation of appropriate mechanisms for the transfer of sequence information from the template to the reactive monomers. The best realized example of this process is protein biosynthesis, in whic ...
Chapter 2: Chemistry Level
... Compact, spherical proteins with tertiary and quaternary structures ...
... Compact, spherical proteins with tertiary and quaternary structures ...
Cells - Dr Magrann
... Two fatty acid groups (“tails”) and a phosphorus group (“head”) Main use- major component of cell membranes Lipids made from one fatty acid Cholesterol- all animal cells have this in the membrane Steroids –modified cholesterol- estrogen, progesterone, testosterone (hormones) 3. PROTEINS are ...
... Two fatty acid groups (“tails”) and a phosphorus group (“head”) Main use- major component of cell membranes Lipids made from one fatty acid Cholesterol- all animal cells have this in the membrane Steroids –modified cholesterol- estrogen, progesterone, testosterone (hormones) 3. PROTEINS are ...
CHAPTER 2: THE CHEMICAL BASIS OF LIFE
... List the major electrolytes released by inorganic salts when placed in water and explain how these electrolytes are needed for metabolic reactions. ...
... List the major electrolytes released by inorganic salts when placed in water and explain how these electrolytes are needed for metabolic reactions. ...
What are atoms and molecules?
... LIPIDS – What do they do They are a great source of STORED ENERGY so we have it in the future. They INSULATE the body to maintain normal body temperature and they CUSHION the internal organs for ...
... LIPIDS – What do they do They are a great source of STORED ENERGY so we have it in the future. They INSULATE the body to maintain normal body temperature and they CUSHION the internal organs for ...
AP Biology - John D. O`Bryant School of Math & Science
... 5. Dehydration reactions are used in forming which of ...
... 5. Dehydration reactions are used in forming which of ...
BIOL 105 S 2012 QZ2 Q 120204.2
... 19. Cell membranes allow certain molecules to pass, while blocking others. This property is called A) impermeable. B) freely permeable. C) selectively permeable. D) actively permeable. E) none of the above 20. The movement of water across a membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an a ...
... 19. Cell membranes allow certain molecules to pass, while blocking others. This property is called A) impermeable. B) freely permeable. C) selectively permeable. D) actively permeable. E) none of the above 20. The movement of water across a membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an a ...
The Chemistry of Digestion - American Chemical Society
... polar. In a water molecule, hydrogen and oxygen form covalent bonds by sharing electrons. A water molecule is polar because oxygen tends to attract electrons more than hydrogen. The shared electrons are attracted to the oxygen atom more than to either of the hydrogen atoms, leaving the positively ch ...
... polar. In a water molecule, hydrogen and oxygen form covalent bonds by sharing electrons. A water molecule is polar because oxygen tends to attract electrons more than hydrogen. The shared electrons are attracted to the oxygen atom more than to either of the hydrogen atoms, leaving the positively ch ...
Programming Languages for Biology
... Systems Biology • Emerging area of biology – study of the relationships and interactions between biological components – many thousand of molecules interact in complex series of reactions to perform some function (called a pathway) • e.g., lactose interacting with a receptor triggers a series of ac ...
... Systems Biology • Emerging area of biology – study of the relationships and interactions between biological components – many thousand of molecules interact in complex series of reactions to perform some function (called a pathway) • e.g., lactose interacting with a receptor triggers a series of ac ...