Recombinant DNA - Minneapolis Medical Research Foundation
... or b) defective animal or plant viruses in the presence of helper virus? ...
... or b) defective animal or plant viruses in the presence of helper virus? ...
Inferring Cellular Networks Using Probabilistic Graphical Models
... • We associated each gene with the processes in which it participates. Resulted in 923 GO categories, 208 MIPS categories, and 87 KEGG pathways. For each module and for each annotation, we calculated the fration of genes in the module associated with that annotaiton and used the hypergeometric distr ...
... • We associated each gene with the processes in which it participates. Resulted in 923 GO categories, 208 MIPS categories, and 87 KEGG pathways. For each module and for each annotation, we calculated the fration of genes in the module associated with that annotaiton and used the hypergeometric distr ...
PowerPoint - New Mexico FFA
... genes that consist of DNA. DNA is a protein-like nucleic acid on genes that controls inheritance. Each DNA molecule consists of two stands shaped as a double helix There are 4 nitrogen bases found in DNA. They are: cytosine, guanine, adenine, and thymine. The genetic code is the sequence of ni ...
... genes that consist of DNA. DNA is a protein-like nucleic acid on genes that controls inheritance. Each DNA molecule consists of two stands shaped as a double helix There are 4 nitrogen bases found in DNA. They are: cytosine, guanine, adenine, and thymine. The genetic code is the sequence of ni ...
blueprint_of_life_-_core_module_2_-_notes_ - HSC Guru
... 2: The effect of mutation on phenotype: mutations that do not change the phenotype of an individual may be harmful, beneficial or neutral in their effect on the individual and its survival. The phenotypic difference that a mutation produces may be present in the individual only (somatic), or may be ...
... 2: The effect of mutation on phenotype: mutations that do not change the phenotype of an individual may be harmful, beneficial or neutral in their effect on the individual and its survival. The phenotypic difference that a mutation produces may be present in the individual only (somatic), or may be ...
(GWAS) and Personalized Medicine
... • A brute force approach of examining the entire genome to identify SNPs that might be disease causing mutations • Far exceeds the scope of family linkage and candidate gene approaches • Must obtain a comprehensive picture of all possible genes involved in a disease and how they interact • Objective ...
... • A brute force approach of examining the entire genome to identify SNPs that might be disease causing mutations • Far exceeds the scope of family linkage and candidate gene approaches • Must obtain a comprehensive picture of all possible genes involved in a disease and how they interact • Objective ...
Protein Synthesis
... What are the 3 types of RNA? A sequence of 3 nucleotides on the mRNA strand that codes for a specific amino acid is called a what? What is the name of the bond that is formed between two amino acids? How do amino acids get into the body in the ...
... What are the 3 types of RNA? A sequence of 3 nucleotides on the mRNA strand that codes for a specific amino acid is called a what? What is the name of the bond that is formed between two amino acids? How do amino acids get into the body in the ...
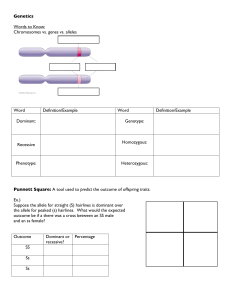
Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance
... The results of the experiment: some seeds were round and yellow some seeds were wrinkled and green some seeds were round and green some seeds were wrinkled and yellow Mendel had discovered the principle of ...
... The results of the experiment: some seeds were round and yellow some seeds were wrinkled and green some seeds were round and green some seeds were wrinkled and yellow Mendel had discovered the principle of ...
Chapter 11 from book
... RNA polymerase and direct it to specific promoters Global gene regulation: Genes that encode proteins with related functions may have a different location but have the same promoter sequence—they are turned on at the same time. Sporulation occurs when nutrients are depleted—genes are expressed seque ...
... RNA polymerase and direct it to specific promoters Global gene regulation: Genes that encode proteins with related functions may have a different location but have the same promoter sequence—they are turned on at the same time. Sporulation occurs when nutrients are depleted—genes are expressed seque ...
Case 18: Student Organizer-‐ Elaborate Case 18: Which gene is
... Case 18: Which gene is causing Arrow’s illness? Congratulations! You’ve learned how bog breath is inherited, now you will use the Gene-‐to-‐Protein Genie to determine which gene on that chromosome is causing bog breath. ...
... Case 18: Which gene is causing Arrow’s illness? Congratulations! You’ve learned how bog breath is inherited, now you will use the Gene-‐to-‐Protein Genie to determine which gene on that chromosome is causing bog breath. ...
Sociology article - UNC
... genetic data is becoming available in sociological studies. The National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health (known as Add Health), not coincidentally run at UNC, will soon make available additional genetic information to complement other surveys on another 15,000 individuals. ...
... genetic data is becoming available in sociological studies. The National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health (known as Add Health), not coincidentally run at UNC, will soon make available additional genetic information to complement other surveys on another 15,000 individuals. ...
UNRAVELING THE DNA MYTH The spurious foundation of genetic
... single gene by alternative splicing is held by the fruit fly, in which one gene generates up to 38,016 variant protein molecules. Alternative splicing thus has a devastating impact on Crick’s theory: it breaks open the hypothesized isolation of the molecular system that transfers genetic information ...
... single gene by alternative splicing is held by the fruit fly, in which one gene generates up to 38,016 variant protein molecules. Alternative splicing thus has a devastating impact on Crick’s theory: it breaks open the hypothesized isolation of the molecular system that transfers genetic information ...
Using public resources to understanding associations
... You can download the human genome sequence from here: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/projects/genome/assembly/grc/human/ It looks like this: ...
... You can download the human genome sequence from here: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/projects/genome/assembly/grc/human/ It looks like this: ...
changes in the frequency of alleles (called ______)
... The theory that a series of random __________ mutations coupled with the process of natural ___________ resulted in selection all of the life forms on the planet is known as ___________. The first scientist to evolution popularize this idea was named _______________. Charles Darwin ...
... The theory that a series of random __________ mutations coupled with the process of natural ___________ resulted in selection all of the life forms on the planet is known as ___________. The first scientist to evolution popularize this idea was named _______________. Charles Darwin ...
CHAPTER 12 - powerpoint
... • When a stop codon—UAA, UAG, or UGA— enters the A site, a release factor and a water molecule enter the A site, instead of an amino acid. • The newly completed protein then separates from the ribosome. ...
... • When a stop codon—UAA, UAG, or UGA— enters the A site, a release factor and a water molecule enter the A site, instead of an amino acid. • The newly completed protein then separates from the ribosome. ...
No Slide Title
... 1) Cloning by Complementation: rescue of mutant phenotype by a member of a librar 2) Differential or "Subtraction" Hybridizati 3) Cloning from the protein: either from pr sequence, or using antibodies, or some biochemical property of the protein (e.g., or DNA binding) ...
... 1) Cloning by Complementation: rescue of mutant phenotype by a member of a librar 2) Differential or "Subtraction" Hybridizati 3) Cloning from the protein: either from pr sequence, or using antibodies, or some biochemical property of the protein (e.g., or DNA binding) ...
No Slide Title
... - Plasmid is transformed into a host cell (E. coli) - Cell culture is prepared - Each cell contains several copies of the plasmid with gene - Gene expression leads to the production of protein - Protein level may reach 30% of total cellular protein -Isolation of protein ...
... - Plasmid is transformed into a host cell (E. coli) - Cell culture is prepared - Each cell contains several copies of the plasmid with gene - Gene expression leads to the production of protein - Protein level may reach 30% of total cellular protein -Isolation of protein ...
Sten_Ilmjärv_Different Aspects of Gene Regulation
... as they sequentially relinquish their tRNA carriers. As amino acids are joined together, the ribosome travels down the message, thereby exposing new codons for tRNA binding. The termination of protein synthesis takes place when one of the mRNA codons UAG, UAA, or UGA is exposed on the ribosome. Thes ...
... as they sequentially relinquish their tRNA carriers. As amino acids are joined together, the ribosome travels down the message, thereby exposing new codons for tRNA binding. The termination of protein synthesis takes place when one of the mRNA codons UAG, UAA, or UGA is exposed on the ribosome. Thes ...
INHERITANCE
... which you acquired your characteristics from your parents and transmit some of your traits to your children. The branch of biology that deals with inheritance is called genetics. Genotype and Phenotype The nuclei of all human cells except the gametes contain 23 pairs of chromosomes, the diploid numb ...
... which you acquired your characteristics from your parents and transmit some of your traits to your children. The branch of biology that deals with inheritance is called genetics. Genotype and Phenotype The nuclei of all human cells except the gametes contain 23 pairs of chromosomes, the diploid numb ...
The Future of Genetic Testing is Now
... tions of nucleotides between genomes at precise locations in the genome. These are called single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs. These studies are one of the triumphs of the Human Genome Project. They identify the gene where the SNP is located and the impact the variation has on coding for that g ...
... tions of nucleotides between genomes at precise locations in the genome. These are called single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs. These studies are one of the triumphs of the Human Genome Project. They identify the gene where the SNP is located and the impact the variation has on coding for that g ...
GEM_McMullen_05
... • Transcription factors and signal transduction components. • Unique genes with no significant BLAST homologies. ...
... • Transcription factors and signal transduction components. • Unique genes with no significant BLAST homologies. ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.