Snímek 1
... *Animation of gene expression: http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072835125/student_view0/animations.html# ...
... *Animation of gene expression: http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072835125/student_view0/animations.html# ...
CrossingOver - sciencewithskinner
... in the pictures to the right. These alleles code for 3 different traits. What is the genotype of this person for each trait? ______________________ 3. Use the figure to the right as a guide in joining and labeling these model chromatids. Although there are four chromatids, assume that they started o ...
... in the pictures to the right. These alleles code for 3 different traits. What is the genotype of this person for each trait? ______________________ 3. Use the figure to the right as a guide in joining and labeling these model chromatids. Although there are four chromatids, assume that they started o ...
Zoo/Bot 3333
... Produces a very peaceful laid-back personality in people and mice homozygous for Pax6 null mutations. IV. Will program other tissues to become eye tissue if expressed in those tissues during fruit fly development. 2. Gregor Mendel: I. Was an abbot in a monastery located in the present Czech Republic ...
... Produces a very peaceful laid-back personality in people and mice homozygous for Pax6 null mutations. IV. Will program other tissues to become eye tissue if expressed in those tissues during fruit fly development. 2. Gregor Mendel: I. Was an abbot in a monastery located in the present Czech Republic ...
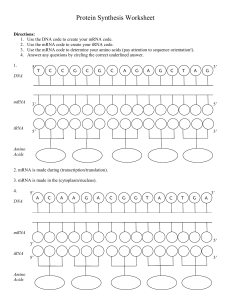
Protein Synthesis Worksheet
... 14. Proteins are made at the (nucleus/ribosome). 15. (tRNA/mRNA) attaches the amino acids into a chain. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 17. (Translation/Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in the (cytoplasm/nucleus). 19. (DNA/RNA) can leave the nucl ...
... 14. Proteins are made at the (nucleus/ribosome). 15. (tRNA/mRNA) attaches the amino acids into a chain. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 17. (Translation/Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in the (cytoplasm/nucleus). 19. (DNA/RNA) can leave the nucl ...
Chapter 8 – Fundamentals of Genetics
... explanation for how we inherit traits. He said that we had pangenes in our blood, and they contained a memory of each structure in our body. From his idea comes the term “bloodline” we use today. In the 1600’s, scientists realized that both parents must contribute to the offspring. But no one unders ...
... explanation for how we inherit traits. He said that we had pangenes in our blood, and they contained a memory of each structure in our body. From his idea comes the term “bloodline” we use today. In the 1600’s, scientists realized that both parents must contribute to the offspring. But no one unders ...
Lenny Moss (2001) "DECONSTRUCTING THE GENE"
... second point here: As I understood it, gene-D and gene-P can never be the same because they are logically, explanatorily and conceptually different epistemic concepts with completely different conditions of satisfactions, just because they are defined differently and play pivotal roles in different ...
... second point here: As I understood it, gene-D and gene-P can never be the same because they are logically, explanatorily and conceptually different epistemic concepts with completely different conditions of satisfactions, just because they are defined differently and play pivotal roles in different ...
ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
... - to consider gain-of function mutations, - identifying genes acting within a common pathway as well as genes encoding for interacting proteins and - it is not restricted to any tissue type. Because of its wide area of applications, this method is often the preferred strategy in functional studies. ...
... - to consider gain-of function mutations, - identifying genes acting within a common pathway as well as genes encoding for interacting proteins and - it is not restricted to any tissue type. Because of its wide area of applications, this method is often the preferred strategy in functional studies. ...
for Genetic Testing
... mutant gene and is destined to be a carrier of the disease, but will not have symptoms. ...
... mutant gene and is destined to be a carrier of the disease, but will not have symptoms. ...
Review of BASIC transmission genetics
... purple. Not only is it hard to calculate map distance from these results, there are hidden recombinants! Again, there are more genotypes than phenotypes. Note that the genotypes and phenotypes are the same, it’s their ratio that has changed. Try to confirm these numbers for yourself. This situation ...
... purple. Not only is it hard to calculate map distance from these results, there are hidden recombinants! Again, there are more genotypes than phenotypes. Note that the genotypes and phenotypes are the same, it’s their ratio that has changed. Try to confirm these numbers for yourself. This situation ...
11.1 The Work of Gregor Mendel
... 3. In complete dominance, the heterozygous phenotype lies somewhere between the two homozygous phenotypes. 4. A heterozygous individual that exhibits the traits of both parents is an example of codominance. 5. Many genes exist in several forms and are said to have codominant alleles. 6. While multip ...
... 3. In complete dominance, the heterozygous phenotype lies somewhere between the two homozygous phenotypes. 4. A heterozygous individual that exhibits the traits of both parents is an example of codominance. 5. Many genes exist in several forms and are said to have codominant alleles. 6. While multip ...
Autosomal Recessive Disorders
... condition requires both carrier mom and father with the condition ...
... condition requires both carrier mom and father with the condition ...
Genetics - Osteogenesis Imperfecta Foundation
... Results of these studies show that the great majority of people with OI, even those who are the only affected person in a family, have dominantly inherited forms of the disorder. Recessive inheritance probably causes osteogenesis imperfect only about 10% of the time. How Genes Work Genes are units o ...
... Results of these studies show that the great majority of people with OI, even those who are the only affected person in a family, have dominantly inherited forms of the disorder. Recessive inheritance probably causes osteogenesis imperfect only about 10% of the time. How Genes Work Genes are units o ...
Basic Genetics Concepts
... examines flies containing several different mutant genes. However, it is rare for any human to have 2 mutant genes that give clear visible phenotypes. • Rather than map genes relative to each other, genes are usually mapped relative to various genetic markers. Genetic markers are loci (sites at spec ...
... examines flies containing several different mutant genes. However, it is rare for any human to have 2 mutant genes that give clear visible phenotypes. • Rather than map genes relative to each other, genes are usually mapped relative to various genetic markers. Genetic markers are loci (sites at spec ...
Word document - Personal Genetics Education Project
... evidence in a text support the author’s claim or a recommendation for solving a scientific or technical problem. CCSS.ELA-Literacy.RST.9-10.9 Compare and contrast findings presented in a text to those from other sources (including their own experiments), noting when the findings support or contradic ...
... evidence in a text support the author’s claim or a recommendation for solving a scientific or technical problem. CCSS.ELA-Literacy.RST.9-10.9 Compare and contrast findings presented in a text to those from other sources (including their own experiments), noting when the findings support or contradic ...
Ch. 5: Presentation Slides
... Mystery of Russian tsar-family: bones in grave could be identified based on comparison of mitochondrial DNA with that of living descendants (through the maternal line). Many copies (many circles per organel, many ...
... Mystery of Russian tsar-family: bones in grave could be identified based on comparison of mitochondrial DNA with that of living descendants (through the maternal line). Many copies (many circles per organel, many ...
Concepts of Inheritance: Classical Genetics Concept 1: Why did
... Mendel concluded that the yellow trait was dominant to the green trait. What did he mean by this? When he took some of the yellow peas from the resulting first generation and bred them together, the green trait reappeared in their offspring! Draw the results. ...
... Mendel concluded that the yellow trait was dominant to the green trait. What did he mean by this? When he took some of the yellow peas from the resulting first generation and bred them together, the green trait reappeared in their offspring! Draw the results. ...
Immunoglobulin Genes: Organization and Expression
... • For immunoglobulin genes, the joining of a number of the exons occurs via a rearrangement of the gene segments at the level of the DNA, rather than at the level of the mRNA. • There are multiple copies of each of the various segments of the heavy and light chains of the immunoglobulin genes, with ...
... • For immunoglobulin genes, the joining of a number of the exons occurs via a rearrangement of the gene segments at the level of the DNA, rather than at the level of the mRNA. • There are multiple copies of each of the various segments of the heavy and light chains of the immunoglobulin genes, with ...
Lecture Series 9 Presentation Slides
... frequencies are likely to be numerous in most populations • Thousands of generations may be necessary to eliminate a moderately disadvantageous allele • Environmental change likely to occur before allele eliminated • Recessive alleles will accumulate at low frequencies in population ...
... frequencies are likely to be numerous in most populations • Thousands of generations may be necessary to eliminate a moderately disadvantageous allele • Environmental change likely to occur before allele eliminated • Recessive alleles will accumulate at low frequencies in population ...
Genetic Analysis of Peas and Humans
... cross have pink flowers. These plants have only one functional allele, R, of a gene encoding an enzyme required for making the red flower pigment. Two copies of R are necessary to make enough pigment for red flowers. In peas, half the normal dosage of an analogous gene (P) is enough to make adequa ...
... cross have pink flowers. These plants have only one functional allele, R, of a gene encoding an enzyme required for making the red flower pigment. Two copies of R are necessary to make enough pigment for red flowers. In peas, half the normal dosage of an analogous gene (P) is enough to make adequa ...
manual of aliquotG
... Figure 1. An Example of the algorithm. Black edge: edge in Gobs or G. Gray dashed edge: edge in Gdup or H. Top. Inferring strong adjacencies: each normal nature integers(gene family ID) represents a gene family, while the subscript(copy ID) represents different gene in the same gene family. Gray sh ...
... Figure 1. An Example of the algorithm. Black edge: edge in Gobs or G. Gray dashed edge: edge in Gdup or H. Top. Inferring strong adjacencies: each normal nature integers(gene family ID) represents a gene family, while the subscript(copy ID) represents different gene in the same gene family. Gray sh ...
Name Class Date Skills Worksheet Look
... In the spaces provided, write the letters of the two terms or phrases that are linked together by the term or phrase in the middle. The choices can be placed in any order. 15. ______ transformation ______ 16. ______ transformation not stopped by proteindestroying enzymes _______ 17. ______ five-carb ...
... In the spaces provided, write the letters of the two terms or phrases that are linked together by the term or phrase in the middle. The choices can be placed in any order. 15. ______ transformation ______ 16. ______ transformation not stopped by proteindestroying enzymes _______ 17. ______ five-carb ...
Pedigree Analysis in Human Genetics
... • Defective color vision caused by reduction or absence of visual pigments • Three forms: red, green, and blue blindness • About 8% of the male population in the US affected ...
... • Defective color vision caused by reduction or absence of visual pigments • Three forms: red, green, and blue blindness • About 8% of the male population in the US affected ...
DNA sequencing: methods
... The techniques used at each of the three participating centres for sequencing, closure and annotation are described in the accompanying Letters7–9. To ensure that each centres’ annotation procedures produced roughly equivalent results, the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute (‘Sanger’) and the Institute ...
... The techniques used at each of the three participating centres for sequencing, closure and annotation are described in the accompanying Letters7–9. To ensure that each centres’ annotation procedures produced roughly equivalent results, the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute (‘Sanger’) and the Institute ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.